Endocrine Glands Study Guide
Introduction
- Glands are organs of the body that make hormones, tears, saliva, milk, sweat, or digestive juices.
- There are mainly two types of glands, endocrine glands, which release the produced substances directly into the bloodstream, and exocrine glands, which secrete the produced substances into either internal or external ducts of the body.
What is the Endocrine System?
It is a network of various organs called glands that secrete vital substances into the blood and is situated throughout the body. It is a messenger type of system of which the hypothalamus is the controlling neural center.
Functions
- It controls important processes such as metabolism, growth, mental state, and reproduction in the body.
- Secretes hormones into the circulatory system, and makes sure they influence the desired effect.
- Controls when the hormones have to be produced and released.
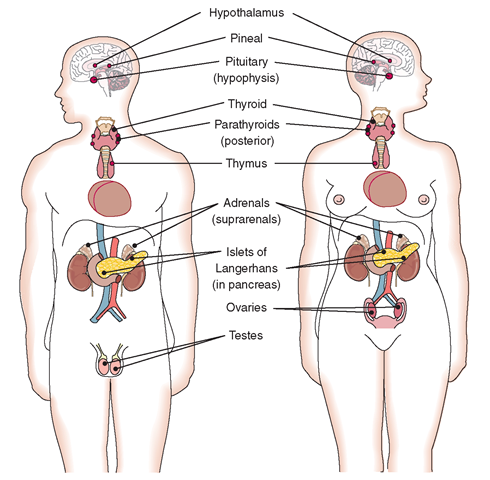
Parts of the Endocrine System
Endocrine glands are situated in multiple parts of the body like the thyroid and parathyroid in the neck, the thymus between the lungs, the hypothalamus, the pituitary, and pineal glands in the brain. They are also located in the adrenals above the kidneys and the pancreas behind the stomach.
- The pituitary gland
It is the master endocrine gland of the body and directs the functioning of the other glands according to the brain signal it receives. It produces hormones such as:
- The Anti-Diuretic Hormone (ADH) or Vasopressin, which controls the blood pressure and water content of the body
- Oxytocin which is a milk-producing hormone
- Corticosteroid or Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) influences the adrenal glands
- Thyroid Stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones
- Luteinizing hormone controls the testosterone and estrogen levels of males and females, respectively.
- Thyroid glands
This gland secretes the thyroid hormone which directly affects growth and metabolism, and calcitonin, which controls the calcium levels of bones.
- The thymus gland
This gland controls the production of T-lymphocytes, which are responsible for immunity.
- The pancreas
This gland produces the hormones insulin and glucagon, which controls blood sugar levels. It also produce digestive enzymes needed to break down food.
- Testes
This gland present in males produce testosterone which is responsible for the production of facial and pubic hair. It influences the enlargement of the penis and the production of sperms within.
- Ovaries
This gland present in females produce progesterone and estrogen, which affect the development of breasts, regulate the menstrual cycle, and support a pregnancy.
- The adrenal glands
This gland produces adrenaline and corticosteroids, which influence heart rate, oxygen intake, blood flow, and levels of sexual activity.
- Parathyroid glands
They control the level of calcium and phosphorus in bones.
- The pineal gland
This gland controls the sleep patterns of the body by producing a sleep hormone called melatonin.
- Hypothalamus
This gland is responsible for connecting the nervous system to the endocrine system.
Endocrine System Disorders
Certain ailments are caused due to the direct malfunctioning of the endocrine system. Let’s look at a few of these disorders:
-
Cushing’s disease is when the body produces too much cortisol leading to excessive weight gain, getting stretch marks, etc.
-
Hyperthyroidism is when too much thyroid hormone is produced, which causes insomnia, weight loss, and a quicker heartbeat.
-
Hypothyroidism is when too little thyroid hormone is produced, which causes a slow heartbeat, pain in the joints and muscles, and weight gain.
-
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is when the ovary does not produce and release an egg. This is caused due to an imbalance in the reproductive hormones and leads to irregular menstruation, growth of hair on the face and neck, and acne.
-
Hypopituitarism is caused when the adrenal glands and thyroid gland slack in their functioning.
-
Adrenal insufficiency is when there is a shortage in cortisol production, which leads to stress in a person.
-
Acromegaly is a condition in which a person’s bones get bigger, especially the feet, hands, and face, due to the excessive production of the growth hormone. This normally happens in middle-aged people.
-
Multiple endocrine neoplasias are the growth of tumors on at least two endocrine glands or even in the body’s other organs.
Conclusion
The functioning of the endocrine system in the body is affected by factors such as stress, lack of exercise, lack of sleep, overeating, and many more unhealthy habits. Therefore, it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
FAQs:
1) What are the five endocrine glands?
They are the Hypothalamus, pituitary, adrenal, pancreas, thyroid, and more.
2) What is the meaning of endocrine glands?
It is an organ that produces and secretes hormones directly into the circulatory system.
3) What are exocrine and endocrine glands?
Exocrine glands secrete hormones into ducts which may be within the body or on the exterior. Endocrine glands secrete hormones within the body directly into the bloodstream.
4) What are the three main functions of the endocrine system?
Initiating the production of hormones and their secretion, thus affecting various processes within the body such as reproduction, growth, production of milk, etc.
5) How do hormones work?
Hormones bind to specific hormone receptors on the target cells and bring about cellular changes such as fertilization of the egg, metabolizing sugar, maintaining the right blood pressure, and so on.
6) What hormones do the endocrine glands produce?
They produce hormones like insulin, cortisol, melatonin, estrogen, progesterone, etc.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about the Endocrine Glands! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun😎
Sources:
- The Endocrine System and Glands of the Human Body. https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/endocrine-system-facts. Accessed on 27 Nov, 2021.
- What is the Endocrine System?. https://www.epa.gov/endocrine-disruption/what-endocrine-system. Accessed on 27 Nov, 2021.
- Endocrine Glands. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/13.20/primary/lesson/glands-bio/. Accessed on 27 Nov, 2021.
- Anatomy of the Endocrine System. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/anatomy-of-the-endocrine-system. Accessed on 28 Nov, 2021.