Male Reproductive Organs Study Guide
Introduction
The male reproductive system is designed to produce sperm and deposit it into the female during copulation. It consists of the testicles which produce the sperm, a duct system that transfers the sperm, and a penis that delivers the sperm. Unlike in females, males can also pass urine through some of their reproductive structures.
Anatomy of the Human Male Reproductive System
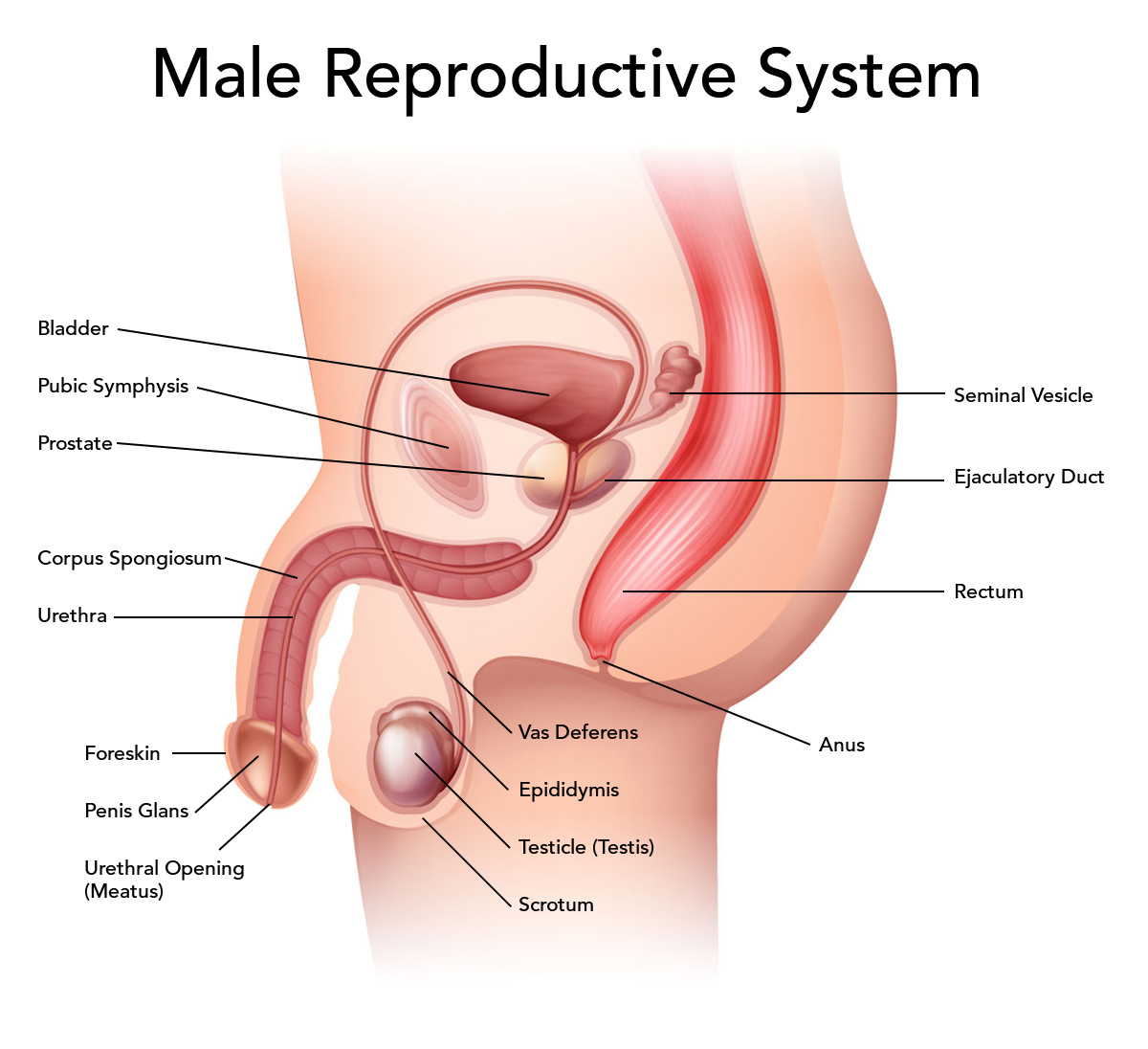
The reproductive organs in males consist of the penis, testicles, and epididymis. The diagram of male reproductive system shows the position of each part in detail:
Penis:
The penis is an externally visible organ of the male reproductive system. It is a long cylindrical shaft with an enlarged tip called the glans. This organ contains the urethra and performs both the function of excreting urine out of the body and ejaculating the semen. The penis contains erectile tissue, filling with blood to become stiff during erecting.
Testes:
The testes (plural) are two egg-shaped organs housed inside a hanging sac of skin called the scrotum below the penis. The testis function is the production of sperm and testosterone. The testes and stability of the reproductive cells require the organ to be at a temperature that is a few degrees below the body temperature. Hence the scrotum and the testes hang outside the body, which is relatively cooler.
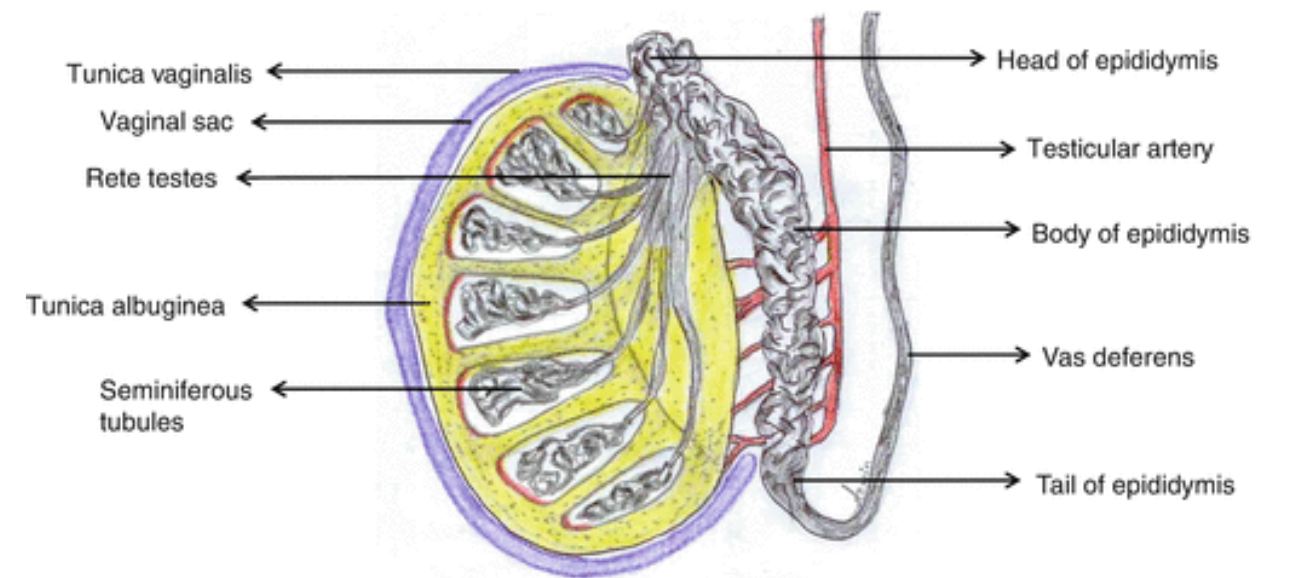
Epididymis:
The epididymis is a tube-like organ that rests on top of the testes. It is about 6m long and coils inside the scrotum. This structure is where the sperm cells grow and mature and are stored until they are ejaculated outside.
Vas deferens:
The vas deferens is a tube that transports the sperm cells from the epididymis into the urethra.
Prostate Gland:
This gland located beneath the bladder secretes a fluid with the sperm to form semen. Semen is a milky-white fluid that is a mixture of sperm cells with enzymes, sugars, and other substances that help the sperm cells to survive inside the female reproductive organs for a few days. It is also a source of energy for the sperm cells, which will have to swim their way up to meet the egg in females.
What is the Function of the Male Reproductive System?
The two main functions of the male reproductive system are to produce sperm and secretion of the male sex hormone testosterone.
Sperm
The sperm are male reproductive cells or gametes. For a baby to be born, the male and the female gametes need to join inside the female reproductive system. For the production of sperm, the human male must have reached sexual maturity. After puberty, males can produce millions of sperm cells every day.
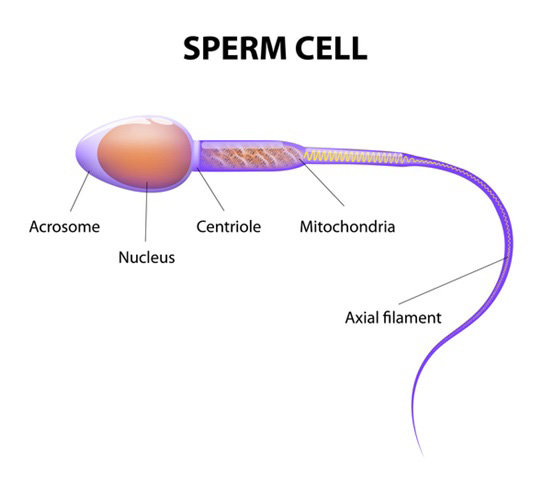
Each sperm cell is about 0.05 mm long. They have small head and a tail that makes them look like tadpoles. The male’s genetic material, half a set of 23 chromosomes, is stored in the head.
- The head of the sperm contains an acrosome which has enzymes that help the sperm penetrate the egg.
- The tail helps with the movement of the sperm through the reproductive organs.
- It acts as a propeller and can push the sperm forward at a speed of 30 inches per hour.
- The sperm develop inside the small seminiferous tubules.
- Before hormones related to the male reproductive system begin, the sperm are tiny undeveloped cells inside the tubules.
- The cells complete their development in the epididymis. Then they move to the vas defers being mixed with the seminal fluid produced by the prostate gland to form semen.
Testosterone
Testosterone is one of the most important hormones related to the male reproductive system. The hormone has two major functions:
- Testosterone leads to the maturity of the male reproductive parts during puberty. It also causes the appearance of secondary sexual characters in males, such as facial hair and muscle growth and definition.
- In adult males, testosterone is responsible for the production of sperm.
Conception
During sexual intercourse, the semen is ejaculated from the penis into the female vagina. The millions of sperm cells in the semen then “swim” up through the cervix and uterus over a period of time and wait for the release of the egg in the fallopian tube.
Only one in the millions of sperm cells can penetrate and fertilize the egg when the egg is released. The fertilized egg now has 46 chromosomes- half of which came from the sperm and half from the egg.
Conclusion:
- The male reproductive system consists of the penis, scrotum, testes, and prostate glands.
- The two main functions of the male reproductive system are to secrete testosterone and produce sperm cells.
- Each sperm has a head and a tail mixed with the seminal fluid before ejaculation.
FAQs:
1. What are the main reproductive organs?
The main reproductive organs in males are:
- Penis
- Scrotum
- Testicles
- Prostate
2. What are the male and female reproductive organs?
The male reproductive organs consist of the penis, scrotum, testicles, and prostate gland. The female reproductive organs consist of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, the uterus, the cervix, and the vagina.
3. How many holes are there in a girl’s private part?
There are two openings in the vulva- the urethral opening through which urine is excreted and the vaginal opening, which leads to the cervix and uterus.
4. What is the main organ of the male reproductive system?
The main male reproductive organ is the testes. The testicles produce testosterone and sperm cells.
5. What are the 5 main parts of the female reproductive system?
The 5 main organs of the female reproductive system are:
- Vagina
- Cervix
- Uterus
- Fallopian tubes
- Ovary
6. What is the normal size of the male reproductive organ?
The mean total length of the penis is around 12.18 +/- 1.7 cm. The mean shaft length is about 7.76 +/- 1.3 cm.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Male Reproductive Organs! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
Sources:
- Male Reproductive Organs. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/13.58/primary/lesson/male-reproductive-structures-bio/
- Male Reproductive System.https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/9117-male-reproductive-system Accessed on 1 Dec 2021
- Male Reproductive Systemhttps://kidshealth.org/en/parents/male-reproductive.html Accessed on 1 Dec 2021