Characteristics of Life Study Guide
Check out awesome, educational VR rooms on Inspirit’s mobile app (available for iOS and Android devices)🤩
Introduction:
Biology is that branch of science that studies life. However, have you ever sat back and wondered – what defines the term ‘life’? It might sound like a silly question at first, but in reality it is not easy to define the meaning of life.
You’ll be relieved to learn that you are not the only one still figuring out the exact meaning of life. Many scientists are yet to agree upon the meaning of life and what it is made of. Multiple characteristics of life separate a living being from a non living being.

Look at it this way. Both a car and a cat can move, and both a crystal and a cell have structure. But even with such similarities, one is a living being, and the other is nonliving. Biologists have discriminated between living and nonliving through seven characteristics of life. The presence of all seven of these characteristics makes a living being, while the absence of even one turns them into non-living things.
What are the 7 characteristics of life?
Whether it is the largest whale or the smallest bacteria, all living organisms share some common characteristics of life.
The 7 characteristics of living things are as follows:
Environmental response
One of the primary characteristics of all living things is their ability to respond to their surroundings. For instance, you step on rocks, and they will not feel hurt and move. But, if you step on your pet’s tail while going to your room, they will react to it.
Living beings respond and adapt to the changes happening around them. These adaptations include behavioral, physiological, and structural traits that improve the organism’s reproduction and survival capabilities.
Cells – Fundamental units
Now think about what all living things have in common. The answer is simple, cells! All organisms are made of cells. When you observe a leaf and a beetle under the microscope, they both will look similar at a cellular level.
All living organisms consist of one or multiple cells, and they are the basic unit of function and structure of life.
Change and Growth
Another characteristic of life is the capability of organisms to change and grow. A block of wood would not grow into a piece of furniture under any circumstances. But if you put a seed under the right circumstances, it will grow into a plant.
All living organisms change and grow. That is, even the smallest bacterium will grow under the right conditions.
Reproduction
One of the significant characteristics of living organisms that distinguishes them from others is that they can reproduce. Life creates more life on Earth, whether it is a bacterium, tree, rabbit, or human being.
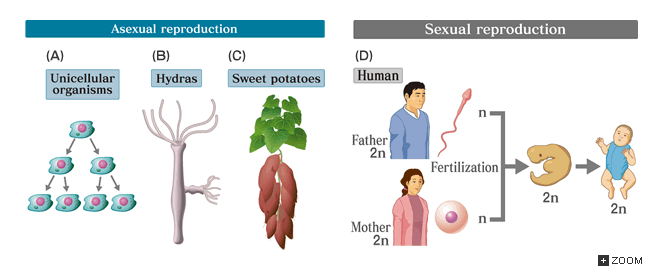
Reproduction can take place through an asexual or sexual process. While sexual reproduction requires the fusion of gametes from two parents, asexual reproduction involves a single parent. That is, the organism will produce identical offspring without the fusion of gametes.
Complex Chemistry
What makes something living is its complex chemistry. Take the example of a rose. It has a beautiful yet complicated structure. If you look carefully, you will observe the rose transporting water and nutrients through its stem. The flower also produces pigment molecules and breaks down sugar to get the energy (metabolism) to stay alive.
Maintaining Homeostasis
The ideal body temperature of humans is 37 degrees Celsius. Hence, if the temperature is cold outside, you will automatically try to keep yourself warm. And if the temperature is warm outside, you will drink cold beverages to keep yourself cool.
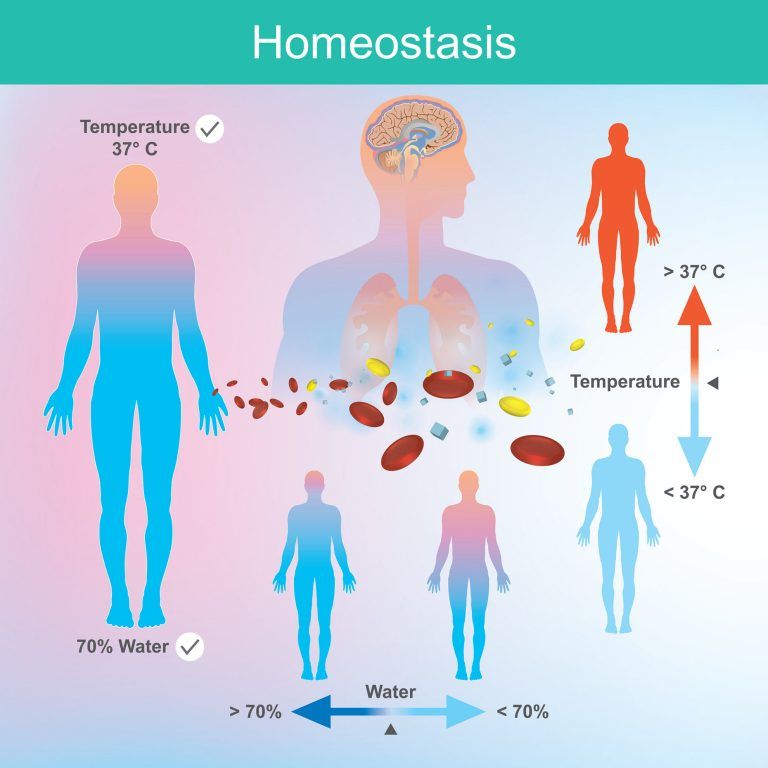
Living organisms try to keep their internal temperature stable despite changes in the external environment. Such a process is called homeostasis, and it is the sixth most important characteristic of life biology.
Energy processing
Living organisms use energy for performing metabolic activities. Some organisms, such as plants, capture the sun’s energy and then convert it into chemical energy for food. This process is called photosynthesis. Others use chemical energy present in their food molecules. This is called cellular respiration.
Levels of Organization of Living Things
Living matters are surprisingly prepared and structured, following a particular hierarchy.
- The atom is the smallest and most essential unit of matter. It includes a nucleus neighbored by electrons.
- Atoms make molecules.
- A molecule is a structure which includes at least 2 atoms held collectively by a chemical bond.
- Many molecules which are biologically essential are macromolecules, huge molecules which are generally formed by combining smaller segments are referred to as monomers.
- Some cells comprise aggregates of macromolecules neighbored by membranes; those are referred to as organelles.
- Organelles are small systems that exist inside cells and carry out specialised functions.
- All living matters are manufactured from cells.
- The cell itself is the smallest essential unit of structure and forms in the living organisms.
- This is why viruses aren’t considered living. They’re not made from cells.
- To make brand new viruses, they must invade and hijack a residing cell; only then can they gain the materials they require to reproduce.
- Some organisms include a single cell while others are multicellular. Cells are categorised as prokaryotic or eukaryotic.
- Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms that deficit organelles neighbored by a membrane. Moreover, they do not have nuclei neighbored by nuclear membranes.
- On the other hand, the eukaryotes have membrane-bound organelles and nuclei.
- In maximum multicellular organisms, cells integrate to make tissues, that are groups of homogeneous cells carrying out the same feature.
- Organs are groups of tissues assembled collectively based on a common feature.
- Organs are present in animals as well as in flora.
- An organ system is a higher stage of organisation that includes functionally associated organs.
- For instance vertebrates have various organ systems, including the circulatory system for transportation of blood throughout the body. Further, it consists of organs such as the heart and blood vessels.
- Organisms are living entities. For instance, every tree in a woodland is an organism. Single-celled prokaryotes and eukaryotes also are considered organisms and are generally stated as microorganisms.
- All the individuals of a species residing inside a particular location are collectively referred to as a population.
- For instance, a woodland may encompass many white pine bushes. All of those pine bushes represent the population of white pine bushes in this woodland.
- Different populations may also live withinside the same particular location. For instance, the woodland with the pine bushes consists of populations of flowering plant life and additionally insects and microbes.
- A community is the collection of populations inhabiting a specific location. For instance, all the bushes, flowers, bugs, and different populations in a woodland shape the woodland’s community.
- The woodland is an ecosystem. An ecosystem includes all the living matter in a specific location collectively with the abiotic, or non-residing, parts of that surroundings such as nitrogen in the soil or rainwater.
- At the highest stage of organisation, the biosphere is the gathering of all ecosystems.
- It represents the zones of existence on Earth. It consists of water, land, and segments of the atmosphere.
Conclusion:
- The seven characteristics what makes an organism living are: Environmental responses, cells, change and growth, reproduction, having complex chemistry, and homeostasis and energy processing
- Sometimes non-living things can portray some of the above characteristics, but a living being consists of all.
FAQs:
1. What are the 7 characteristics of life?
The seven characteristics are:
- Environmental responses
- Cells, change and growth
- Reproduction
- Having complex chemistry
- Homeostasis
- Energy processing
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about the Characteristics of Life! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
]]>