Double-Displacement Reaction Study Guide
In chemistry, there are multiple terms used to describe a reaction based on the nature of its reactants. When one of the reactants is a salt (for example the reaction between sodium hydroxide and ammonium chloride), the reaction is termed a salt metathesis reaction. When one of the reactants doesn’t dissolve in the solvent, the reaction is termed a double decomposition reaction.
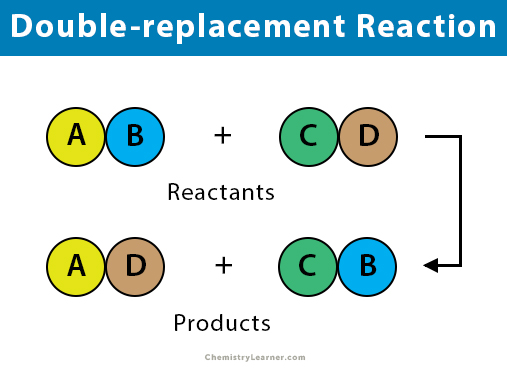
A double-displacement reaction occurs when the positive and negative ions of two ionic compounds switch places to form two entirely new compounds in an aqueous solution. These compounds can come in the form of precipitates, gasses, or molecular compounds.
The general form of a double-displacement reaction is described by the following equation:
AB + CD = AD + BCTYPES OF DOUBLE-DISPLACEMENT REACTIONS
There are two types of double displacement reactions: precipitation and neutralization.
- Precipitation reaction: In a precipitation reaction, the ions of the reactants compound interchange to form new compounds. However, one of the compounds in these reactions is insoluble in the solvent.
- Neutralization reaction: Neutralization reactions occur between acids and bases and form a salt and a gas. For a neutralization reaction to move in a forward direction, the acids and bases involved must be strong.
TIPS FOR RECOGNIZING A DOUBLE- DISPLACEMENT REACTION
Let’s take a look at some pointers that will help you identify a double-displacement reaction:
- The first thing you should see in a reaction is whether the anions and cations of reactants are being exchanged. You can do this by taking note of the products that are formed.
- You can also identify a double-displacement reaction through the state of matter of its reactants. If the reactants are in an aqueous solution, and a precipitate is formed as one of the products, the reaction is a double-displacement reaction.
DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT REACTION EXAMPLES
Let’s look at some common double-displacement reactions:
-
Sodium hydroxide (a base) reacts with ammonium chloride (salt) to form sodium chloride, hydrochloric acid, and water.
NaOH + NH₄Cl = NaCl + NH₄OH -
Silver nitrate reacts with sodium chloride to form silver chloride and sodium nitrate.
AgNO₃ + NaCl = AgCl + NaNO₃
CONCLUSION
-
A double-displacement reaction occurs when the positive and negative ions of two ionic compounds switch places to form two entirely new compounds.
-
A double-displacement reaction must occur in an aqueous solution.
-
The compounds formed in a double-displacement reaction can come in the form of precipitates, gasses, or molecular compounds.
-
A general formula for a double-displacement reaction is written as: AB + CD = AD + BC.
-
Examples of double-displacement reactions include:
-
Sodium hydroxide (a base) reacts with ammonium chloride (salt) to form sodium chloride, hydrochloric acid, and water.
NaOH + NH₄Cl = NaCl + NH₄OH -
Silver nitrate reacts with sodium chloride to form silver chloride and sodium nitrate.
AgNO₃ + NaCl = AgCl + NaNO₃ -
A precipitation reaction is a form of double-displacement reaction where one of the products is insoluble in the solvent.
-
A neutralization reaction is a form of double-displacement reaction that takes place between acids and bases.
FAQs
1. What happens when ammonium chloride reacts with sodium hydroxide?
NaOH + NH₄Cl = NaCl + NH₄OH
2. What type of reaction are NH₄Cl and NaOH?
Double-displacement reaction.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Double Displacement Reactions! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
]]>