Batteries Study Guide
INTRODUCTION
What would our life be like if we didn’t have batteries? Take a lookout. Almost every other appliance we see is powered by batteries. Maybe it’s your television remote or your alarm clock. The invention of batteries has greatly simplified our lives. The batteries in the cell phones we carry with us or the computers we use for work are the reason we can take these gadgets with us everywhere we go without having to worry about plugging them in every time we want to use them. Even our automobiles and motorcycles run on batteries. Now let’s know about, what is in a battery and the battery’s working.
WHAT IS A BATTERY?
- A battery comprises electrochemical cells that store chemical energy before converting it to electricity.
- The dry cell and the lead storage battery are two variants of the fundamental voltaic cell.
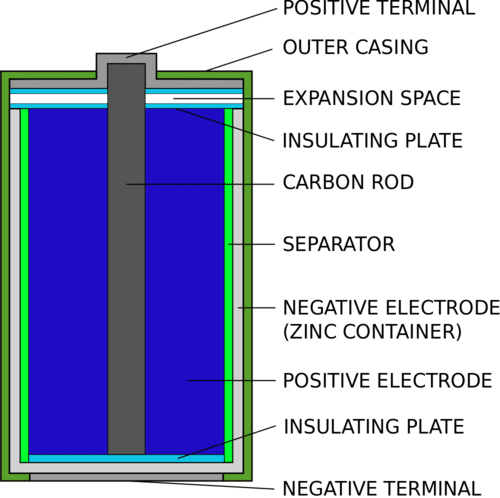
DRY CELL:
-
The electrolyte is immobilized as a paste in a dry cell, with barely enough moisture to permit current to pass.
-
Because it contains no loose liquid, unlike a wet cell, a dry cell may work in any direction without spilling.
-
Because of its adaptability, it’s ideal for portable equipment.
-
The early wet-cell batteries, on the other hand, were often fragile glass canisters with lead rods suspended from an open top. As a result, they are required to be handled with care to avoid leakage.
-
The invention of the dry-cell battery resulted in significant improvements in battery safety and mobility.
-
The zinc-carbon cell, which employs a cell known as the Leclanché cell, is a typical dry-cell battery.
-
The module is composed of an anode, which is a zinc container on the outside.
-
A core carbon rod is flanked by a combination of carbon and manganese (IV) dioxide as the cathode (MnO₂).
-
The electrolyte is an ammonium chloride paste (NH₄Cl). The two electrodes are separated by fibrous material, and a brass peg in the cell’s core carries electricity to the outside circuitry.
-
To enable energy storage, there occur chemical reactions in a battery; the processes may be represented using balanced chemical equations that outline the electron flow.
-
The following half-reaction occurs when ammonium chloride paste is applied:
2NH₄(aq) + 2e −→ 2NH₃(g) + H₂(g) -
According to the following process, the manganese (IV) oxide in the cell eliminates the hydrogen generated by the ammonium chloride:
2MnO₂(s) + H₂(g) → Mn₂O₃(s) + H₂O(l) -
At the cathode, the combined outcome of these two processes occurs. When we combine these two responses, we get:
2NH₄(aq) + 2MnO₂(s) + 2e → Mn₂O₃(s) + 2NH₃(g) + H₂O(l) -
Finally, the half-reaction of the anode is as follows:
Zn(s) → Zn₂ + 2e− -
As a result, the cell’s total equation is:
Zn(s) + 2MnO₂(s) + 2NH₄(aq) → Mn₂O3(s) + H₂O(l) + Zn₂ + 2NH₃(g)
The above reaction has a potential of 1.50 V.
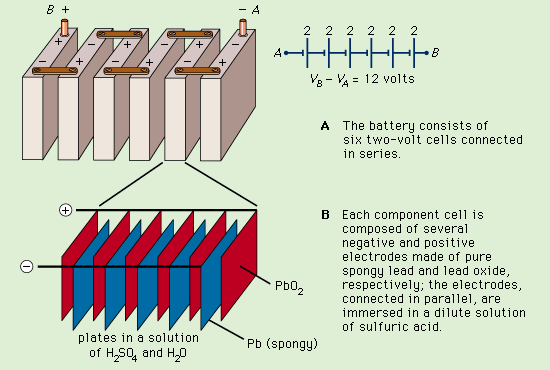
LEAD STORAGE BATTERY:
- Lead-acid batteries, often known as lead storage batteries, can hold a lot of charges and provide a considerable current for a small period.
- Lead-acid batteries can be recharged, which is crucial for their usage in automobiles.
- Both the positive and negative plates must become lead (II) sulphate, and the electrolyte must lose substantially of its dissolved sulfuric acid in order to discharge the stored energy.
CONCLUSION:
- A battery is made up of electrochemical cells that store chemical energy before converting it to electricity.
- The dry cell and the lead storage battery are two variants of the fundamental voltaic cell.
- Lead storage batteries can hold a lot of charges and provide a considerable of current for a small period.
FAQs:
1. What is a battery and what are its types?
There are a few additional types of secondary batteries, but the 3 most common are:
- Lead-acid Batteries
- Nickel-cadmium Batteries
- Lithium-ion Batteries
2. What is the use of batteries?
A battery is used to provide backup power during a power failure. The batteries are usually connected to electrical gadgets at home. These gadgets continue to function even if the power is out. Many clients, for example, have energy tariffs that vary depending on the time of day.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Batteries! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
SOURCES
- Batteries: https://www.ck12.org/c/chemistry/batteries/lesson/Batteries-CHEM/. Accessed 16 March 2022.
- Electric Battery: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_battery. Accessed 16 March 2022.
- Batteries: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-chemistry/chapter/batteries/. Accessed 16 March 2022.