Mixture Study Guide
INTRODUCTION
Whether we believe it or not, our lives are surrounded by mixtures. For example, let’s look at the noodles we eat. We boil the noodles, mix all the veggies, and then add a tastemaker to it. This is a mixture as there is no chemical reaction taking place here. Whether it be the milk or butter we consume, or the food we eat, everything is some kind of mixture. Even the water that we drink is a mixture!
We might think that drinking water is free from any other component other than H₂O, but that’s not true. Various minerals and electrolytes are present in our drinking water. Let’s talk about mixtures in a bit more detail now:
WHAT IS A MIXTURE?
A mixture is formed when two or more chemicals are blended in such a way that each keeps its chemical nature. Chemical bonds are not disrupted or established between the components. New physical characteristics, such as boiling and melting points, may appear in the combination.
TYPES OF MIXTURE:
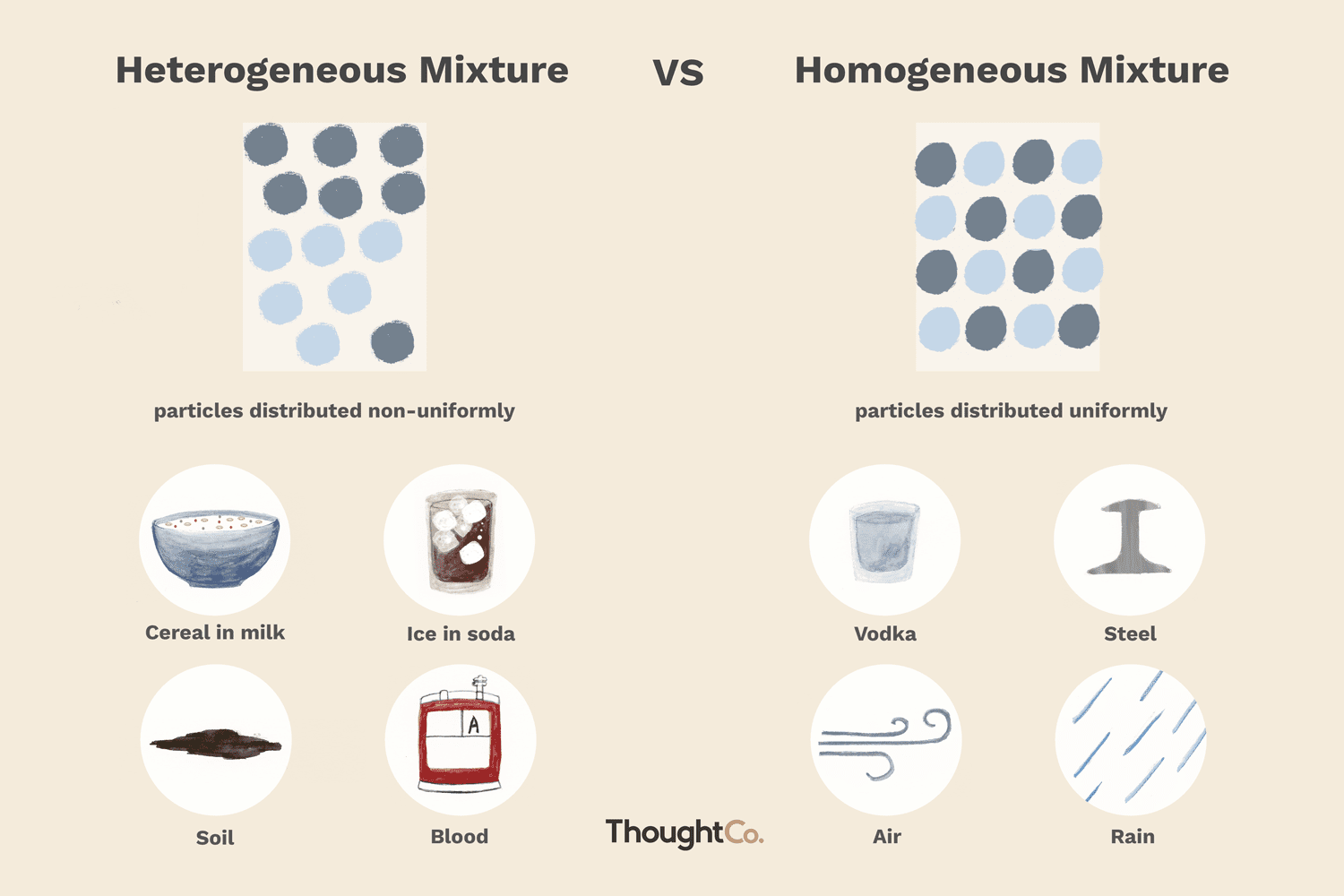
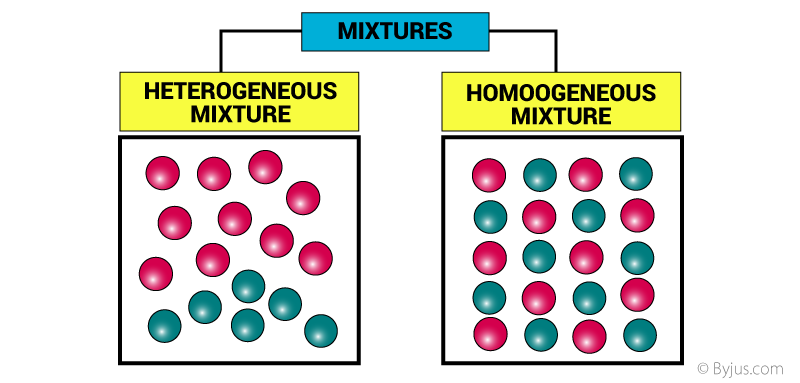
The uniformity of mixtures and the particle sizes of components in relation to each other are used to classify them. Homogeneous mixtures have a consistent composition and phase all through their volume, but heterogeneous mixtures don’t seem to be uniform and might have a variety of phases (e.g., liquid and gas).
A mixture can be classified as heterogeneous or homogeneous based on the particle size of its constituents as well:
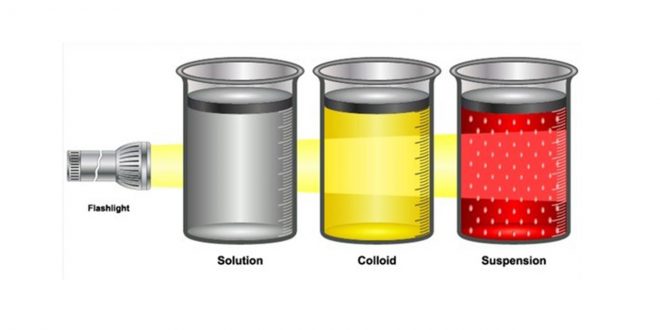
SOLUTION
The particles in a chemical solution are exceedingly tiny. A solution is extremely stable, and sieving or centrifuging the specimen will not separate the components.
COLLOID
Although a colloidal solution seems homogenous to the human eye, particles may be seen under a microscope. Colloids are chemically and physically stable, and the Tyndall effect may be seen in them. The Tyndall effect is the scattering of a beam of light by a medium containing small suspended particles.
Decantation cannot be used to separate colloid components, although centrifugation may. Decantation occurs under the effect of Earth’s gravity and is the process of separation of liquid from solid. Centrifugation is a method of separating molecules having different densities by spinning them in solution around at high speed.
SUSPENSION
In many cases, the molecules in a suspension are big enough to make the combination look heterogeneous. The Tyndall effect may be seen in suspensions. Decantation or centrifugation can be used to separate suspensions.
CONCLUSION:
- A mixture is formed when two or more chemicals are blended in such a way that each keeps its chemical nature.
- Homogeneous mixtures have a consistent composition and phase all through their volume, but heterogeneous mixtures don’t seem to be uniform and might have a variety of phases.
FAQs:
1. What are the four types of mixtures?
Solutions, suspensions, colloids, and emulsions are the four main types of mixtures depending on the particle size.
2. What are the types of mixtures?
Heterogeneous and homogeneous mixtures are the two main types of mixtures. Homogeneous mixtures seem uniform throughout, whereas heterogeneous mixtures have clearly identifiable components. A solution, which could be a solid, liquid, or gas, is the most frequent form of homogeneous combination.
3. What is a mixture simple definition?
Mixtures are substances that are made up of two or more different types of materials. Physical means can be used to separate them. A salt and water solution is one example. The separate components of any combination do not unite through any chemical reaction.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Mixture! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our app to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
SOURCES
- What is a mixture?: https://byjus.com/chemistry/mixtures/ Accessed 5 Feb 2022.
- Mixture Definition and Examples: https://www.thoughtco.com/mixture-definition-chemistry-glossary-606374 Accessed 5 Feb 2022.
- Substances and Mixtures: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/introchem/chapter/substances-and-mixtures/ Accessed 5 Feb 2022.