Human Body Overview Study Guide
Introduction
The human body is one single structure that is made of smaller networks. They are grouped hierarchically as systems, organs, tissues, and cells. The organ system performs a complex function, and consists of different organs arranged systematically.
Organs are part of different body systems consisting of various tissues grouping themselves into complex structures that perform one or more simple functions that help complete the organ system’s complex process. Tissues are groups of similar cells that perform a single function that forms an organ together with other tissues.
What are the Systems of the Body?
There are ten different body systems. The central body systems are skeletal, nervous, muscular, endocrine, circulation, digestive, respiratory, reproductive, and urinary.
All the body systems perform one single complex function:
- The reproductive system propagates
- The respiratory system breathes or gas exchange
- The urinary system removes waste products and purifies blood
- The circulatory system maintains the blood flow
- The endocrine system controls the hormonal balance
- The digestive system extracts nutrients from the food consumed
- The muscular system helps in body movement
- The nervous system responds to the environment
- The skeletal system provides support and framework to the human body.
Anatomy of the Human body:
Anatomy refers to the science that elaborates on the inner structure of the human body. The human body is divided into various regions such as the head, neck, chest or thorax, arms or hands, abdomen, legs or limbs, back, and pelvis. These regions constitute the vital organs that perform various functions.
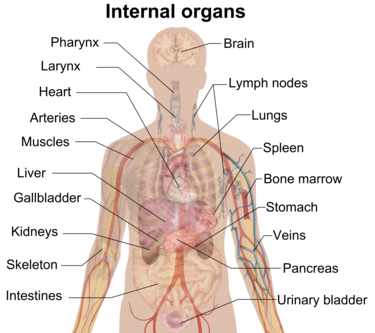
The vital organs located in these regions of the body: the brain in the head, spine in the neck and back, lungs and heart in the thorax, stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen and intestines in the abdomen, urinary bladder, kidneys, and uterus or testes in the pelvis.
The body’s anatomy divides the positioning of the organs and their systems in the body based on the direction. Several directions are defined for the human body, as shown in the picture above.
Conclusion:
- The human body is the most complex form of life.
- It can be easily understood by knowing the effective systems that perform the primary functions and locating the vital organs that perform life-sustaining functions.
FAQs:
1. What are the basics of the human body?
The basics of the human body are the microscopic structure, or the fundamental unit of life is the cell that groups into tissues, organs, and organ systems.
2. What are the 7 levels of organization in the human body?
The 7 levels of organization in the human body start from the basic structure of life are: the atom, molecule, organelles, cell, tissues, organ, organ system, and the human organism.
3. What are the 11 major body parts of the human body?
The 11 major body parts of the human body are the brain, heart, lungs, stomach, intestines, kidney, liver, uterus or testes, spine, pancreas, and extremities (arms and legs).
4. What are the 12 systems of the body?
The body’s systems are circulatory, nervous, digestive, respiratory, muscular, reproductive, urinary, skeletal, endocrine, immune, cardiovascular, and integumentary.
5. What are the 78 organs in the human body?
The 78 organs in the human body are:
- Anus
- Arteries
- Appendix
- Adrenal glands
- Brain
- Bones
- Bronchi
- Bladder
- Bone marrow
- Bulbourethral glands
- Colon
- Cervix
- Clitoris
- Capillaries
- Cerebellum
- Diaphragm
- Ears
- Eyes
- Fallopian tubes
- Genitals
- Gallbladder
- Heart
- Hair follicle
- Hypothalamus
- Interstitium
- Kidneys
- Joints
- Liver
- Lungs
- Larynx
- Ligaments
- Lymph nodes
- Large intestine
- Lymphatic vessel
- Mouth
- Mesentery
- Mammary glands
- Nose
- Nails
- Nerves
- Nasal cavity
- Ovaries
- Esophagus
- Penis
- Pancreas
- Pharynx
- Placenta
- Prostate
- Pineal gland
- Pituitary gland
- Parathyroid gland
- Rectum
- Skin
- Spleen
- Scrotum
- Stomach
- Spinal cord
- Small intestine
- Salivary glands
- Skeletal muscles
- Seminal vesicles
- Subcutaneous tissues
- Teeth
- Tonsils
- Testes
- Tendons
- Tongue
- Thyroid
- Trachea
- Thymus gland
- Ureters
- Urethra
- Uterus
- Vulva
- Veins
- Vagina
- Vas deferens
- Vestigial organs
6. What is the largest organ in the body?
Skin is the largest organ in the body. It is evident because it has to cover the entire outer surface of the body.
7. What is the smallest organ?
The pineal gland is the smallest organ in the body that helps in regulating the female reproductive fertility cycles.
8. Which organ of the body works 24 hours?
The brain, the lungs, and the heart are the vital organs of the body that work 24 hours to sustain life.
9. What is skin made of?
The skin is made of cells composed of water, protein, fats, and minerals. The three layers of skin are the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Human Body Overview! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! We promise, it makes studying much more fun!😎
Sources:
- Review: Introduction to the Human Body. https://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/body/review.html#:~:text=The%20human%20body%20is%20a,can%20perform%20a%20special%20function. Accessed 23 Nov, 2021.
- Anatomy. https://medlineplus.gov/anatomy.html. Accessed 23 Nov, 2021.
- Human Body. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/13.1/primary/lesson/organization-of-the-human-body-bio/. Accessed 23 Nov, 2021.
- Human Body. https://www.britannica.com/science/human-body. Accessed 23 Nov, 2021.
