Solvation, Dissociation, and Electrolytes Study Guide
INTRODUCTION
A solution is defined as a homogeneous mixture of two or more different substances. The major portion of a solution is the solvent, and the minor portion is the solute.
When a solute is dissolved in a solvent, the solvent particles surround and separate the solute particles in a process called dissolution. The interaction between these particles is known as solvation. Solvents and solutes with similar intermolecular forces have a stronger attraction than those with dissimilar forces. The stronger the attraction, the stronger the solubility of the solute in the solvent.
Unlike covalent molecules, ionic compounds break into positively and negatively charged ions when dissolved in a solvent. This process is called dissociation, and such solutes are known as electrolytes.
Now that you have some background, let’s dive deeper into the details of dissociation, solvation, and electrolytes below.
DISSOCIATION
Sodium chloride or table salt is an ionic compound formed by one sodium (Na) and one chlorine (Cl) atom. Due to its ionic nature, NaCl breaks into a positively charged cation (Na+) and a negatively charged anion (Cl-) when dissolved in a solvent. When atoms or molecules gain a positive or negative charge, it is called ionization.
Dissociation is the process by which a larger molecule like NaCl breaks into smaller particles, and compounds that dissociate in a solution are called electrolytes. Some examples of electrolytes include sodium chloride (NaCl), hydrochloric acid (HCl), and sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
SOLVATION
As we mentioned before, dissolution is the process in which solute particles are surrounded by solvent particles to form a solution. Dissolution signifies the kinetic process in which molecules move away from each other, which can be quantified in terms of rate. Solvation, on the other hand, is used to quantify the equilibrium state in which the rate of dissolution becomes equal to the rate of precipitation. Alterations to a solvent’s quantity can affect the rate of solvation within a solution.
ELECTROLYTES
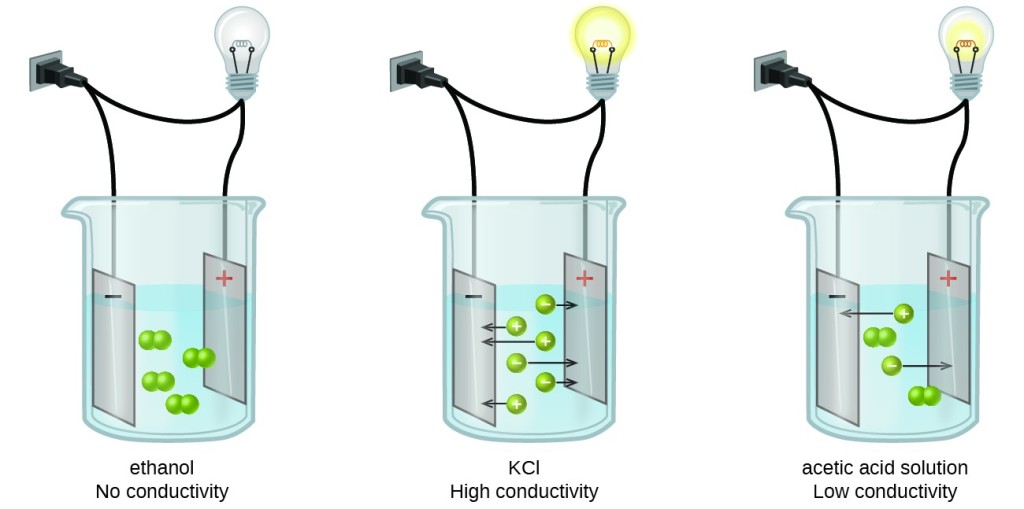
Electrolytes are substances that undergo dissociation when dissolved in water and have a general electrolyte chemical formula of A+ B-.. The process of dissociation leads to the formation of charged particles known as ions. The positively charged ions are known as cations, and the negatively charged ions are known as anions.
A unique property of an electrolyte is that it can conduct electricity when melted or dissolved in water. NaCl is a prime example of an electrolyte’s chemical formula because it breaks into Na+ and Cl- when dissolved in water.
CONCLUSION
- Dissolution occurs when solute particles are surrounded by solvent particles to form a solution.
- Ionic solute compounds break into cations and anions when they come into contact with a solvent in a process known as dissociation.
- Solvation is a process by which solute particles interact and associate themselves with solvent particles. It is used to quantify the equilibrium state in which the rate of dissolution becomes equal to the rate of precipitation.
- Electrolytes are substances that undergo dissociation when dissolved in water to form ions. Dissolved electrolytes have the unique property of being able to conduct electricity.
FAQs
1. What are some examples of electrolytes?
NaCl is a strong ionic compound, which is an example of an electrolyte. Other examples of electrolytes include KCl, NaCl, and HCl.
2. How can you identify an electrolyte?
When in a dilemma regarding the question of which compounds are electrolytes, check if they break into strong ions when dissolved.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Solvation, Dissociation, and Electrolytes! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
SOURCES
- Electrolytes:https://byjus.com/chemistry/electrolytes/.Accessed 8th March 2022.
- Solvation, Dissociation, and Electrolytes: https://www.ck12.org/c/chemistry/electrolytes-and-nonelectrolytes/enrichment/Solvation-Dissociation-and-Electrolytes-Example-1/.Accessed 8th March 2022.