Transcription and RNA Processing Study Guide
Introduction
Transcription is one of the fundamental processes that happen to our genome. It’s the process of turning DNA into RNA. The central dogma is the transformation of DNA, then RNA to protein. Well, transcription refers to that first part of going from DNA to RNA. And we transcribe DNA to RNA in specific places. Let’s know more about this process in detail.
Flow of genetic information
Genetic information flows from a sequence of nucleotides in DNA to a sequence of bases in a messenger RNA molecule to a sequence of amino acids in a protein. The process by which DNA is copied to RNA is called transcription, and that by which RNA is used to produce proteins is called translation.
Transcription overview
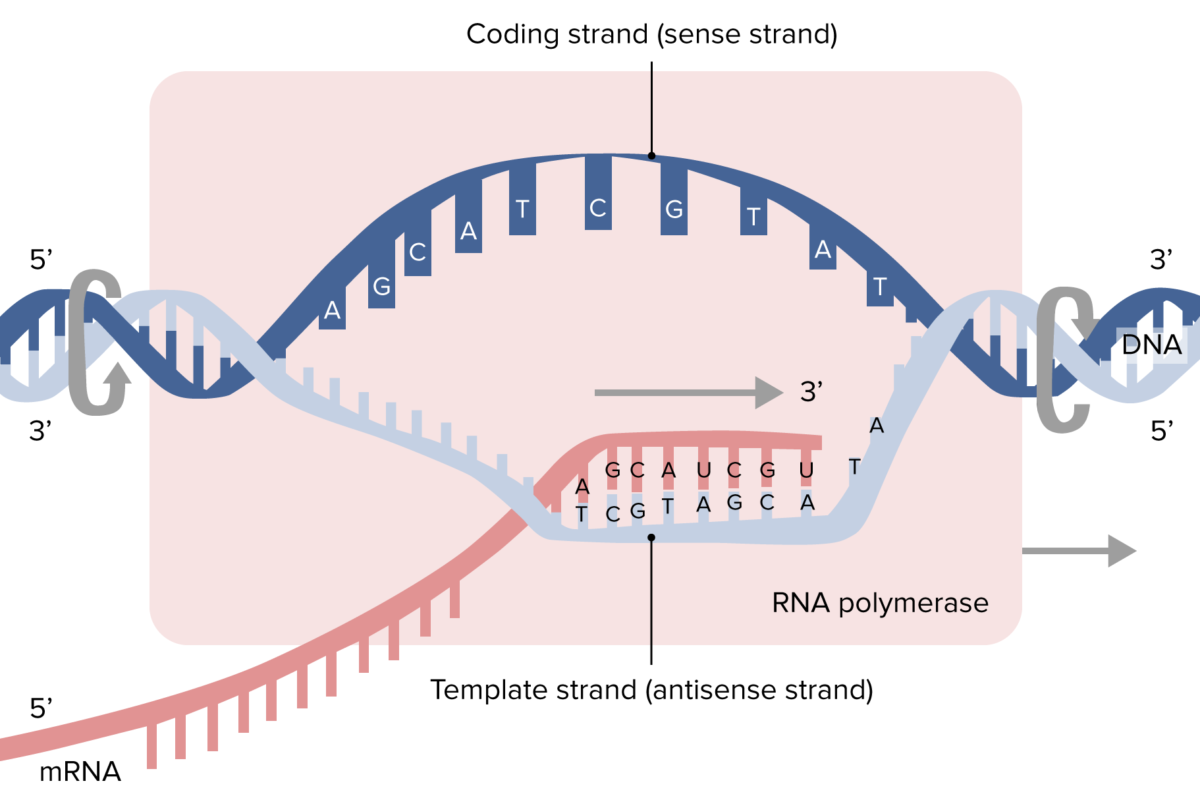
Transcription is the first step in gene expression. It involves copying a gene’s DNA sequence to make an RNA molecule. In this process, RNA polymerase enzymes and other transcriptional proteins. The main enzyme involved in transcription is RNA polymerase. RNA polymerase uses a single-stranded DNA template to synthesize a complementary RNA strand.
The segments of DNA are transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins, produces messenger (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are copied into RNA molecules and are known as non-coding RNAs.
Transcription takes place in two broad steps
- Formation of Pre-messenger RNA- First, pre-messenger RNA is formed with the involvement of RNA polymerase enzymes. The resultant single RNA strand is the reverse complement of the original DNA sequence.
- RNA Splicing- Second, the pre-messenger RNA is then “edited” to produce the desired mRNA molecule.This process is called RNA splicing and it removes the non-coding sequences of genes (introns) from pre-mRNA and joins the protein-coding sequences (exons) together in order to enable translation of mRNA into a protein.
Purpose of transcription
- In transcription, information from a gene is used to construct a functional product like protein. It is the first step in gene expression.
- The main goal of transcription is to make an RNA copy known as a transcript to carry the information to build a polypeptide. A polypeptide is a protein or its subunit.
Stages of transcription
There are four stages of transcription:
-
Promoter recognition and identification- In this stage, the promoter is recognized by RNA polymerase and an associated sigma factor. These are often brought to the promoter DNA by an activator protein binding to its DNA binding site nearby.
-
Initiation of transcript synthesis- Here, the RNA polymerase binds to the promoter (a sequence of DNA found near the beginning of a gene). Each gene has its promoter. Once bound, RNA polymerase separates the DNA strands and provides the single-stranded template needed for transcription.
-
Transcript elongation- In this stage, a template strand (one strand of DNA) acts as a template for RNA polymerase. The polymerase builds an RNA molecule out of the complementary nucleotides, making a chain that grows. The RNA transcript carries the same information as the non-template (coding) strand of DNA, but it contains the base uracil (U) instead of thymine (T).
-
Transcription termination- After the transcription, the transcript is released from RNA polymerase. Sequences called terminators signal that the RNA transcript is complete.
Types of transcription
There are three main types of RNA transcripts directly involved in protein synthesis. They are:
- mRNA- The Messenger RNA
- rRNA- The Ribosomal RNA
- tRNA- The Transfer RNA
While mRNA determines amino acid sequence, tRNA and rRNA are crucial for the mechanism of translating the mRNA code. The mRNA carries the message from the DNA. If a cell requires a certain protein to be synthesized, the gene for this product is turned on, and the mRNA is synthesized through transcription. Then this mRNA interacts with ribosomes and other cellular machinery to direct the synthesis of the protein it encodes during the translation.
RNA Processing
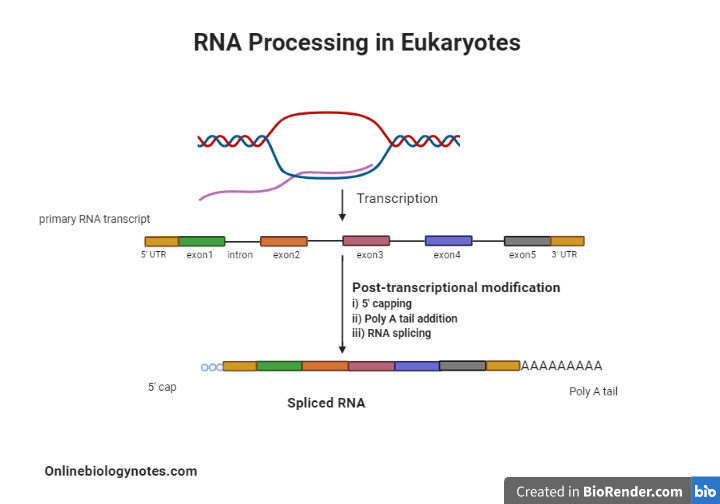
RNA processing is the term collectively used to describe the sequence of events through which the primary transcript from a gene acquires its mature form. RNA processing occurs in a special structure within the nucleus called the nucleolus. The mRNA that was transcribed until this point is referred to as pre-mRNA. To convert this into mature mRNA, the following processes take place:
1. 5′ Capping
- A methylated guanine cap is added to the 5′ end of mRNA.
- This helps protect the immature molecule from degradation by RNAases.
2. Polyadenylation
- A poly(A) tail that consists of many molecules of adenosine monophosphate is then added to the 3′ end of mRNA to stabilize the RNA.
3. Splicing
- The genetic sequence of a single pre-MRNA can code for several distinct proteins by splicing. This allows the conservation of genetic material. This process occurs within the transcript and involves these two steps:(i). Spliceosome excision which involves the removal of introns (non-coding sequences)(ii). Ligation that involves joining together of exons (coding sequence)
Conclusion
- In transcription, the DNA sequence of a gene is “rewritten” in the form of RNA.
- The three main types of RNA directly involved in protein synthesis are messenger RNA (mRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and transfer RNA (tRNA).
- Not all genes are transcribed all the time. Instead, transcription is controlled individually for each gene.
FAQs:
1. What is transcription and RNA Processing?
Transcription- Transcription is the process in which a gene’s DNA sequence is copied, i.e., transcribed to make an RNA molecule. RNA Processing- RNA processing is the term used to express the collective sequence of events through which the primary transcript from a gene acquires its mature form.
2. Is RNA processing the same as transcription?
RNA processing can be described as a collective term to express the sequence of events through which the primary transcript from a gene acquires its mature form. In contrast, transcription is when a gene’s DNA sequence is copied (transcribed) to make an RNA molecule.
3. Where does the transcription and RNA processing occur?
Transcription and RNA processing occurs in a special structure within the nucleus called the nucleolus. RNA then leaves the nucleus and goes to a ribosome in the cytoplasm, where translation occurs. The translation reads the genetic code in mRNA and makes a protein.
4. What are the four steps of transcription?
The four steps of transcription are:
- Promoter recognition and identification
- Initiation of transcription synthesize
- Transcript Elongation
- Transcription termination5. What is the purpose of transcription?
The purpose of transcription is to make an RNA copy of a gene’s DNA sequence. The transcript (RNA copies of individual genes) carries the information needed to build a protein for a protein-coding gene.
6. What is RNA translation?
Translation is the process in which the genetic code in mRNA is read to make a protein. In this process
- Ribosomes floating in the cytoplasm or ER synthesize proteins after the process of transcription of DNA to RNA.
- Along with the mRNA template, several other molecules such as ribosomes, tRNAs, and various enzymatic factors contribute to the process of translation
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Transcription and RNA Processing! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
Sources:
- RNA processing. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/biochemistry-genetics-and-molecular-biology/rna-processing. Accessed 20 Dec, 2021.
- Molecular Biology of Transcription and RNA Processing. https://www.pearson.com/content/dam/one-dot-com/one-dot-com/us/en/higher-ed/en/products-services/sanders-2e-info/pdf/ch8.pdf. Accessed 20 Dec, 2021.
- Transcription. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/4.5/primary/lesson/transcription-of-dna-to-rna-bio/. Accessed 20 Dec, 2021.