Common Ancestry Study Guide
Introduction:
The concept of common ancestry stems from evolutionary biology. It can be defined as one specifies being the ancestor of two or more species in the later period. Homology is a connection that shows descent from a common ancestor by defining a relationship between structures or DNA generated from a common ancestor. Let’s learn more about this concept below.
Indications of common ancestry
Anatomy that is homologous (shared by ancestors) or analogous (different species) can be present in distinct species (shared due to similar selective pressures). Molecular similarities support the shared ancestry of life. Comparing DNA sequences can reveal how closely two species are related.
Structural evidence indicates the common ancestry of all eukaryotes.
- Membrane-bound organelles
- Linear chromosomes
- Genes that contain introns
Homologous features
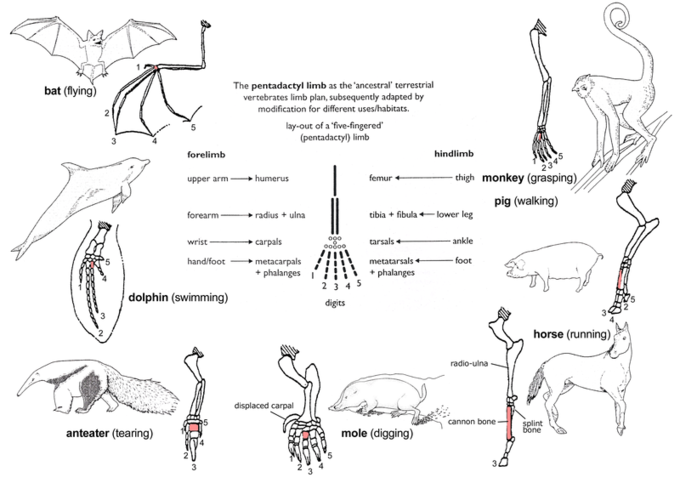
The link between structures or DNA generated from the most recent common ancestor is known as homology. The wings of bats and the arms of primates are both examples of homologous structures in evolutionary biology.
Even though these two structures do not appear to be related or serve the same purpose, they are genetically related and descend from the same last common ancestor structure. As a result, species’ homologous features can be explained by descent from a common ancestor.
- It’s worth noting that designating two structures as homologous is contingent on which ancestor is referred to as the common ancestor.
- Homology is determined in genetics by comparing protein or DNA sequences. Homologous gene sequences have a high similarity, implying that they came from the same ancestor.
- Homology can also be partial: New structures might emerge due to the process. Embryos are the only place where homologous structures may be detected. All vertebrate embryos (including humans) have gill slits and a tail during early development. Later in life, the developmental processes of these animals diverge even further (which is why your embryonic tail is now your tailbone, and your gill slits have turned into your jaw and inner ear).
- Vertebrates’ developmental plans vary on a similar scheme in their last common ancestor, as evidenced by homologous embryonic features.
Vestigial organs:
- Structures homologous to significant structures in other creatures but have lost their primary ancestral role can sometimes be found in organisms.
- Vestigial structures have lost their function and are typically decreased in size.
- The tailbone of humans (a vestigial tail), the hind leg bones of whales, and the undeveloped legs observed in some snakes are all examples of vestigial features.
Molecular biology:
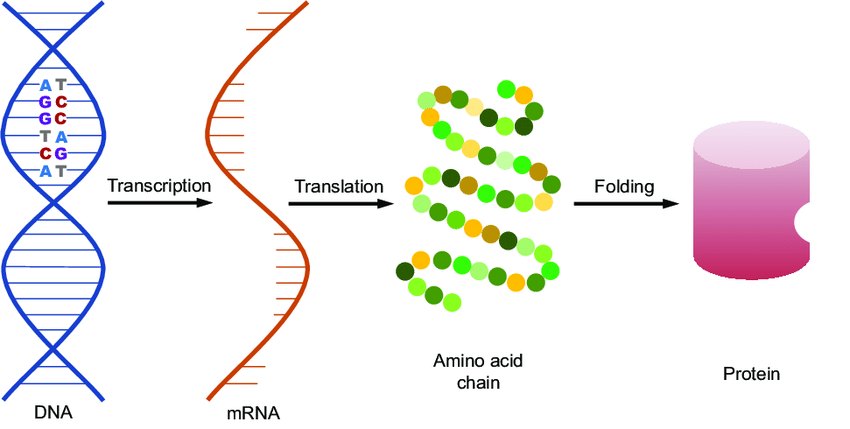
Similarities between biological molecules, like structural homologies, might indicate common evolutionary origin. All living creatures have the following characteristics at their most fundamental level:
- Identical genetic material (DNA)
- Genetic codes that are the same or nearly identical
- The basic method of gene expression is the same (transcription and translation)
- Amino acids, for example, are the same molecular building components.
These similarities show that all living creatures had a common ancestor who possessed DNA as its genetic material, utilized the genetic code, and expressed its genes through transcription and translation. All living species share these characteristics since they were “inherited” from the ancestor (and because any big changes in this basic machinery would have broken the basic functionality of cells).
Although they’re important for determining the common beginnings of life, traits like having DNA or being able to do transcription and translation aren’t as effective for determining how closely different creatures are related. Different sorts of molecular characteristics, such as gene nucleotide sequences, can be used to identify which creatures in a group are most closely related.
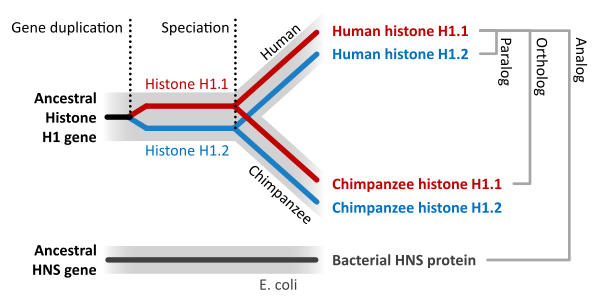
Homologous genes:
- Biologists frequently compare the sequences of comparable genes present in various species (commonly referred to as homologous or orthologous genes) to determine how those species are connected evolutionarily.
- The underlying premise behind this method is that two species have the “same” gene since they share an ancestor. Because this gene was already present in their last common ancestor, humans, cows, chickens, and chimps all share genes that encode the hormone insulin.
- The more DNA changes in homologous genes (or amino acid variances in the proteins they encode) between two species, the more apart they are. Human and chimp insulin proteins, for example, are almost identical (about 98%) compared to human and chicken insulin proteins (about 64%), indicating that humans and chimps are more closely related than humans and chickens.
Conclusion:
- Homology is a connection that shows descent from a common ancestor by defining a relationship between structures or DNA generated from a common ancestor.
- Anatomy that is homologous (shared by ancestors) or analogous (different species) can be present in distinct species (shared due to similar selective pressures). Molecular similarities support the shared ancestry of life. Comparing DNA sequences can reveal how closely two species are related.
- Similarities between biological molecules, like structural homologies, might indicate common evolutionary origin.
FAQs:
1. What indicates common ancestry?
Anatomy that is homologous (shared by ancestors) or analogous (different species) can be present in distinct species (shared due to similar selective pressures). Molecular similarities support the shared ancestry of life. Comparing DNA sequences can reveal how closely two species are related.
2. What are human’s most common ancestors?
Modern humans developed from their most common ancestor, Homo erectus, which means “upright man” in Latin, and arose in Africa during the last 200,000 years. Homo erectus was a human species that existed between 1.9 million and 135,000 years ago and is now extinct.
3. Are common ancestors extinct?
A common ancestor, by definition, cannot survive after a speciation event and is replaced by a new species. The notion is that if speciation or extinction happened along that lineage’s “branch” after the period when that fossil was alive, it would no longer be an existing species.
4. Do we all have a common ancestor?
A new statistical study indicates that all life on Earth had a single common ancestor. Because various types of microbes frequently trade genes, some scientists believe that numerous primordial life-forms flung their genetic material into the mix, resulting in a web rather than a tree of life.
5. What do you call the descendants of a common ancestor?
A clade is a branch in a cladogram that comprises a single common ancestor and all of its offspring. A cladogram is an evolutionary tree that depicts species’ ancestral connections. Today, cladograms may be drawn using similarities in DNA sequences between species.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Common Ancestry! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun VR classrooms – we promise it makes studying much more fun! 😎
Sources:
- Common Descent. https://biologydictionary.net/common-descent/. Accessed 20 Dec, 2021.
- Common Ancestry. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/earth-and-planetary-sciences/common-ancestry. Accessed 20 Dec, 2021.
- Common Ancestry and Natural Selection in Darwin’s Origin. https://nationalhumanitiescenter.org/on-the-human/2010/06/common-ancestry-and-natural-selection-in-darwin%E2%80%99s-origin/. Accessed 20 Dec, 2021.