CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Revision Notes
Chapter 15: Some Natural Phenomena Revision Notes
LIGHTNING AND CHARGES
- Lightning is an electric spark on a big scale.
- Rubbing some objects together can charge them: called charged objects.
- The two types of charges are positive and negative charges.
- Similar charges repel each other, while dissimilar charges attract each other.
- Electrical charges formed by rubbing are called static charges.
TRANSFER OF CHARGE
- An electric current is formed when charges move.
- An electroscope can be employed to determine if a body is charged or not (aluminium foil strips).
- Earthing is transferring charge from a charged object to the ground.
LIGHTNING
- An electric discharge causes lightning between clouds and the earth or between clouds.
- Clouds are formed by the impact of water droplets in the atmosphere.
- The particles in the atmosphere are charged due to friction between the water droplets and air currents.
- Negative charges build towards the bottom of the cloud, while positive charges accumulate at the top.
- As the charge accumulation increases, the air allows the flow of these negative charges toward the earth (positive charge).
- This movement is seen as a narrow streak of electrical discharge known as lightning.
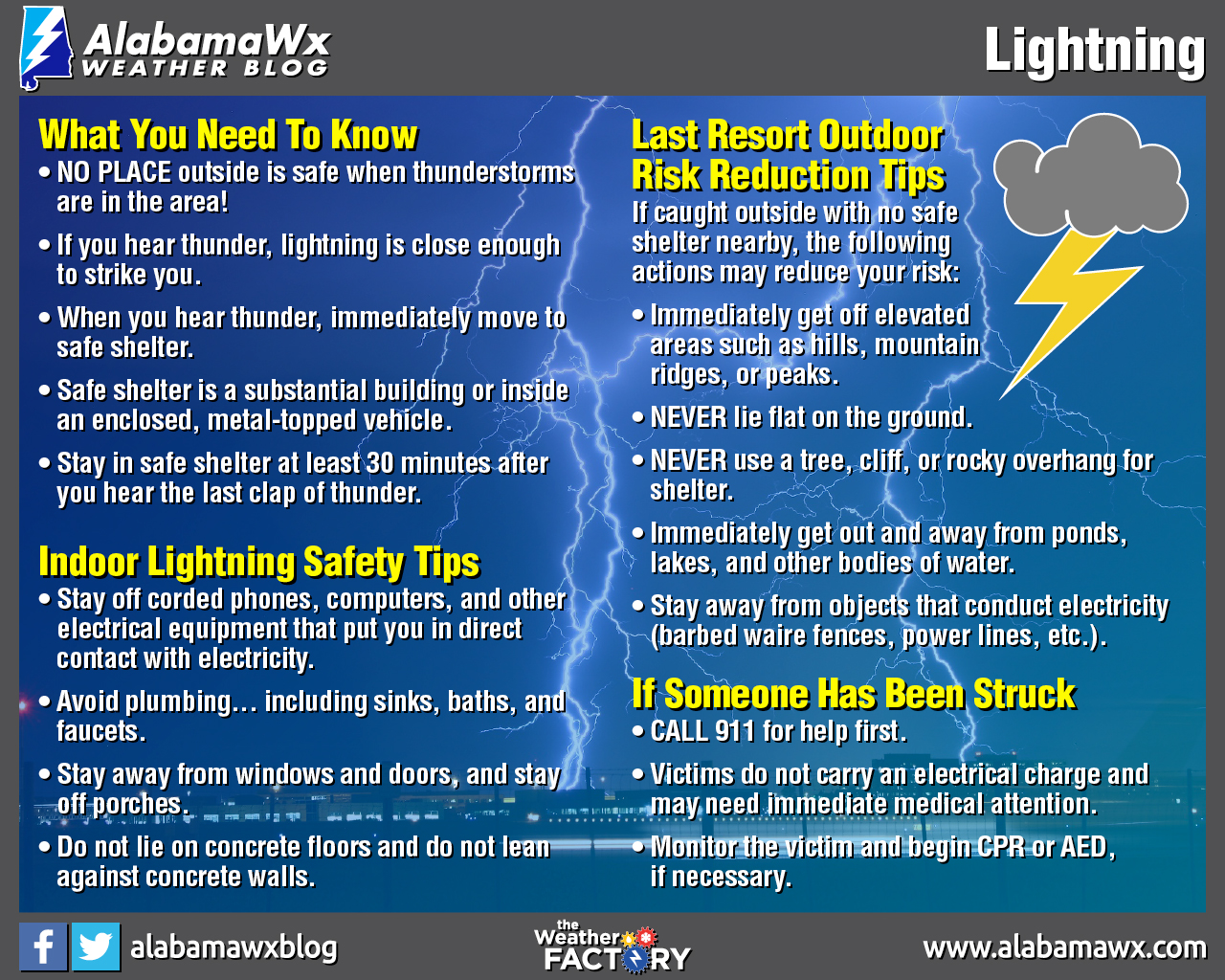
LIGHTNING SAFETY
During a lightning strike, it’s critical to take precautions as it can hurt both people and property. The most popular measure is sheltering in interiors.
Buildings are safeguarded against the impacts of lightning by using lightning conductors. A metallic rod taller than the structure is inserted into the walls. With one end in the air and the other driven deep in the ground, the electric charge is transferred to the earth.
EARTHQUAKES
An earthquake is a sudden shaking or trembling of the earth that cannot be predicted.
Earthquakes can cause floods, landslides, and tsunamis.
CAUSE
- Oceans and continents make up the crust of the earth.
- The crust is separated into tectonic plates, made up of different sections.
- These sections slide against each another and lead to earthquakes.
- Such areas are known as seismic or fault zones.
- A seismograph is a device that measures the magnitude of an earthquake.
- The energy generated at the epicentre of an earthquake travels outward in the form of seismic waves.
- The Richter scale is used to measure an earthquake’s destructive energy. An earthquake of 7 or higher magnitude on the Richter scale can damage people and property.
PROTECTION AGAINST EARTHQUAKES
- Seismic zones are likely to suffer the most damage and must be made ‘Quake Safe.’
- Employ mud and timber in homes.
- Furniture and home appliances fixed to the walls if possible.
- Installing firefighting equipment.
Source: Chapter_15.pmd (ncert.nic.in)
]]>