CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Revision Notes
Chapter 6: Life Processes Revision Notes
NUTRITION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS
- Nutrition is defined as the process of getting and using food.
Mode of nutrition:
- Nutrition that is autotrophic (All green plants)
- Autotrophic nutrition is a type of nutrition in which an organism creates its own nourishment.
- The autotrophic mode of nourishment is followed by green plants and blue-green algae.
Heterotrophic Nutrition (Animals, Man, Non-green plants)
Heterotrophic nutrition
- It is a type of nutrition in which one organism consumes nourishment from another organism.
- Other than green plants and blue-green algae, all organisms feed in a heterotrophic manner.
- Saprophytic nutrition, holozoic nutrition, and parasite nutrition are the three forms of heterotrophic nutrition.
Saprophytic Nutrition
- The organism secretes digestive fluids on the food in saprophytic nutrition. While the meal is still being consumed, it is being digested.
- The creature then consumes the digested meal.
- Saprophytic nutrition is followed by all decomposers.
- This technique of nourishment is also used by some insects, such as houseflies.
Holozoic Nutrition
- In holozoic nutrition, digestion occurs within the organism’s body, after the meal has been consumed. The majority of animals eat in this manner.
- Parasitic Nutrients: Parasites are organisms that live within or outside of another creature (host) and obtain nutrition from it. This sort of nutrition is known as parasitic nutrition. Cuscuta, ticks, and so forth.
Autotrophs
- Autotrophs are creatures that can produce their own nourishment from basic raw materials. For instance, all green vegetation.
Heterotrophs
- This is a type of nutrition in which organisms are unable to create their own food and must rely on others.
Photosynthesis
The process through which green plants create their own nourishment is known as photosynthesis.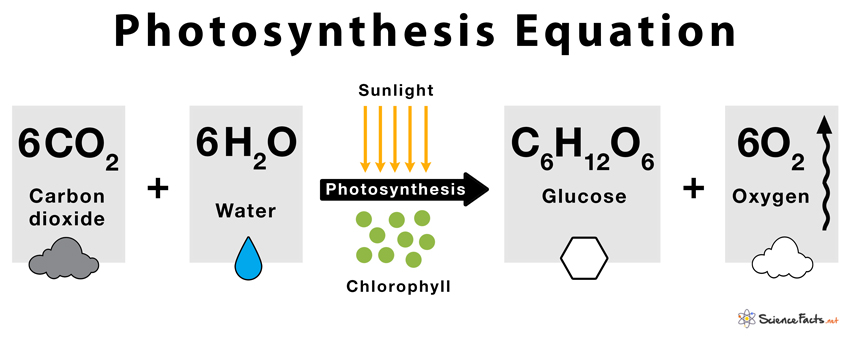 Source:
Source:
Raw materials for photosynthesis:
- Minerals and Water: These are absorbed from the soil by the roots.
- Carbon dioxide is absorbed by the leaves through microscopic holes known as stomata.
- Solar energy is the energy emitted by the sun.
- Chlorophyll is a pigment that aids in the collection of solar energy by plants.
- Carbohydrate-glucose is transformed to starch as a result of photosynthesis.
Symbiotic relationship
- A symbiotic relationship occurs when two species dwell in close proximity and create a mutually beneficial interaction.
- Example, A fungus and an alga form a biological relationship known as lichen. Fungus collects water and offers shelter, while algae use photosynthesis to produce food.
Holozoic Nutrition
- Feeding on solid food is referred to as holozoic nutrition. The organism consumes complicated organic food. For instance, a man, an amoeba, a dog, and so on.
- Herbivores are animals that solely eat plants. For instance, a deer or a cow.
- Carnivores are animals that devour meat or flesh. Take, for example, the tiger.
- Omnivores are animals that eat both plants and meat. Take, for example, a guy and a dog.
Holozoic nutrition consists of the following steps:
- Ingestion is the act of putting food into one’s mouth.
- Enzymes break down big insoluble food molecules into little water-soluble ones during digestion.
- Digested food is absorbed into the bloodstream through the gut wall.
- Assimilation: Absorbing food allows body cells to release energy, develop, and repair themselves.
- Egestion is the process of removing undigested food from the body.
- Human digestive organs include the mouth, oesophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, as well as glands such as the salivary gland, liver, and pancreas.
- Teeth are an organ that breaks down complicated foods and aids in chewing.
- Milk teeth are the baby’s first set of 20 tiny teeth, which appear at the age of 6-7 months.
- Permanent teeth: When a kid is 6-7 years old, the second set of 32 bigger teeth replaces the milk teeth.
- Enamel is a protective coating on teeth that is white, robust, and gleaming.
- Tongue: A muscular organ linked to the buccal cavity’s floor that aids digestion by tasting and combining food with saliva.
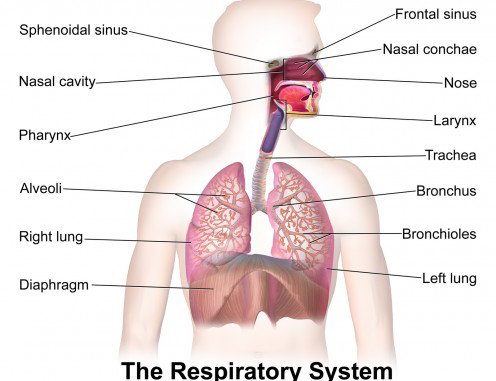
HUMAN RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
- A pair of lungs make up the human respiratory system. These are connected to a series of tubes that exit via the nostrils on the outside.
The major components of the human respiratory system are as follows:
- Nostrils: A nasal channel is formed by the fusion of two nostrils. Hair lines the inside of the nostrils, which stays wet owing to mucus secretion. Mucus and hair aid in the removal of dust particles from breathed air. Furthermore, as air enters the nasal canal, it warms up.
- The pharynx is a tube-like structure that extends beyond the nasal canal.
- Following the pharynx is the larynx. This is also known as the voice box.
- The trachea is made up of cartilage rings. In the absence of air, cartilaginous rings keep the trachea from collapsing.
- Bronchi: A pair of bronchi emerge from the trachea, one bronchus for each lung.
- Bronchioles: Inside the lung, a bronchus separates into branches and sub-branches.
- Air sacs at the end of bronchioles are known as alveoli. The alveolus is a very thin membrane that serves as the opening point for blood vessels. This is the alveolus, where oxygen is mixed with blood and carbon dioxide is expelled. The pressure differential causes the exchange of gases in the alveoli.
TRANSPORTATION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS
Plants
- Vascular tissue is a kind of plant tissue that aids in transport.
- Xylem tissue assists plants in transferring water and minerals.
- Phloem aids in the transportation of food in plants.
- Food is transported from leaves to other regions of the plant through the process of translocation.
- Transpiration is the loss of water from a leaf’s stomata.
Animals
- Blood is a red-colored fluid that flows throughout an animal’s body.
- Plasma is a liquid component of the blood that contains nutrients, hormones, and waste products.
- Blood vessel: A tube-like structure in the body that transports blood throughout the body.
- Artery: It transports oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
- Vein: It transports deoxygenated blood from the body’s various organs to the heart.
- Capillary: A tiny tube with a thin wall that joins an artery with a vein.
- The heart is a muscular organ located in the thoracic cavity that aids in the pumping of blood throughout the body.
- A circulatory system in which blood circulates twice through the heart in a single full cycle.
- One entire contraction and relaxation of the heart is referred to as a heartbeat (72 times in a minute).
- A stethoscope is a device that monitors the rate of a person’s heartbeat.
- Systolic pressure is the highest pressure at which blood flows during a cardiac contraction. (120 millimetres of mercury)
- Diastolic pressure is the lowest pressure at which blood flows when the heart is relaxing. (80 millimetres of mercury)
- Blood pressure is measured with a sphygmomanometer.
- Immunity is provided by lymph, a light yellow liquid that flows from bodily tissue to the blood circulation system.
EXCRETION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS
- The process of eliminating waste items from the body is known as excretion.
- CO2, O2, water vapour, peel of bark, fruits, leaves, gum, raisin, and other excretory products of plants
- Carbon dioxide, urea, and other excretory products of humans
- Kidney: Organ that filters blood and eliminates the harmful chemical urea.
- Urine is a yellowish liquid that is made up of both water and urea.
- Dialysis is a process for cleansing a person’s blood when they have renal failure.
- Nephron: A functional unit of the excretory system that filters blood and is found in the kidney.
- Renal arteries are blood channels that carry blood from the heart to the kidneys.
- Renal Vein: A blood channel that connects the kidneys to the heart.