CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 Revision Notes
Chapter 14: Respiration in Plants Revision Notes
- Respiration is a biochemical process in which organisms obtain energy by breaking down the C-C bonds of complex compounds through oxidizing them within the cells.
- Carbohydrates, proteins, fats and even organic acids are oxidised to synthesise and release energy (ATP) and are called respiratory substrates.
- Cellular respiration is the mechanism of breakdown of food materials within the cell to release energy, and the trapping of this energy for synthesis of ATP.
- Respiration occurs in the leaves, stems and roots of the plant.
- The reactants used for the process of respiration are glucose and oxygen. The products obtained due to this process are carbon dioxide, water, and energy.
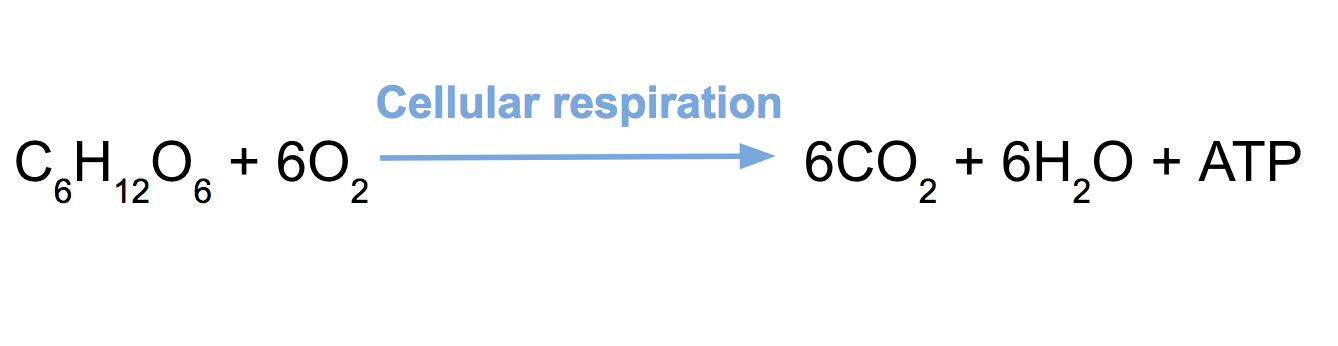
Source: Equation of cell respiration
Respiration in Plants
- Plants are autotrophs, i.e., they make their food.
- Plants do not have specialized organs for the exchange of gases as each plant part takes care of its own gas-exchange needs such that the distance that gases need to diffuse is not large.
- They contain structures known as stomata (in the leaves) and lenticels (in the stem), which help them in respiring.
Types of Respiration
There are mainly two types of respiration occurring in plants:
- Anaerobic Respiration
- Respiration occurring in the absence of oxygen is termed anaerobic respiration.
- It occurs in the prokaryotic cells of plants.
- The liberation of less energy leads to incomplete oxidation of food molecules due to the absence of oxygen.
- The main by-products of anaerobic respiration are ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide.
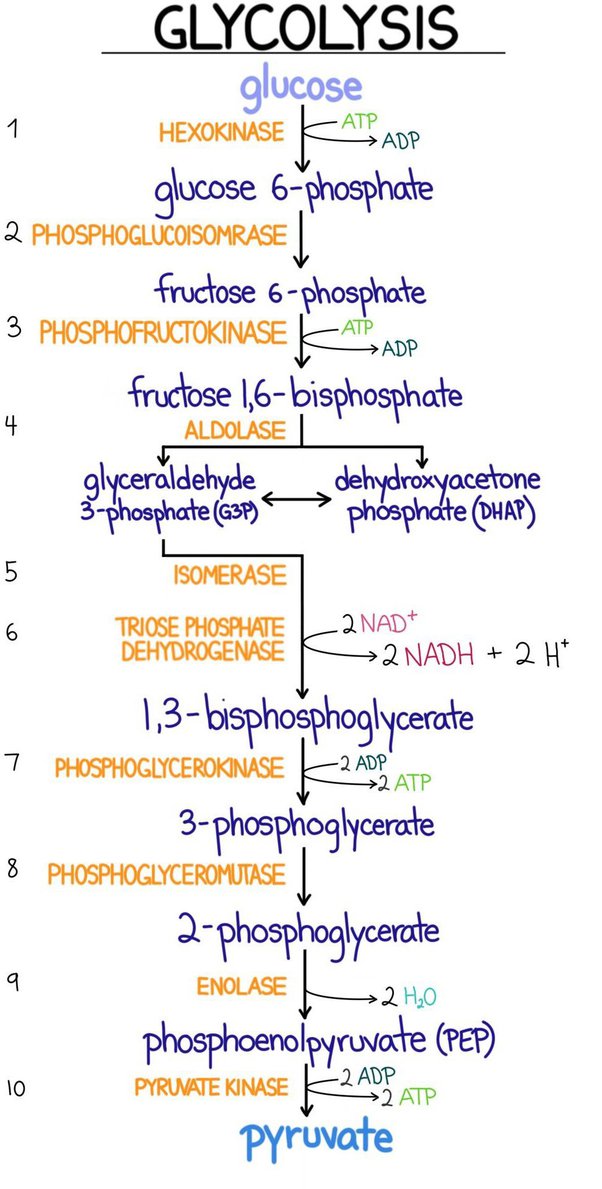
- Glycolysis
- This breakdown of glucose to pyruvic acid is called glycolysis or EMP pathway.
- In anaerobic organisms, it is the only process in respiration.
- Occurs in the cell cytoplasm and forms two molecules of pyruvic acid.
- Sucrose (from photosynthesis) -> glucose and fructose by the enzyme** invertase** and these then enter glycolysis.
- The entire process happens through a series of catalyzed enzyme reactions.
- The pyruvate, obtained from glycolysis is utilized in lactic acid fermentation, alcoholic fermentation and aerobic respiration (Krebs’ cycle).
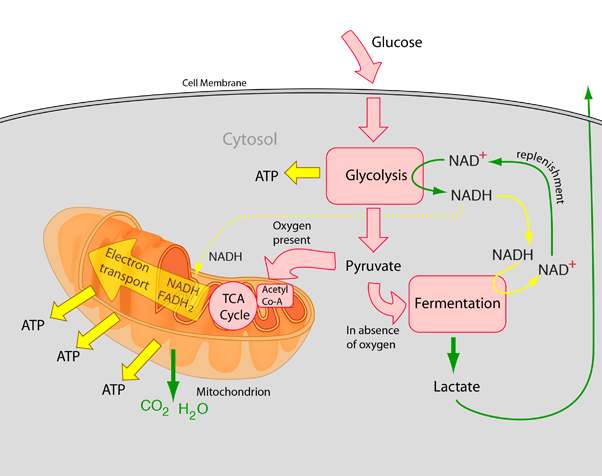
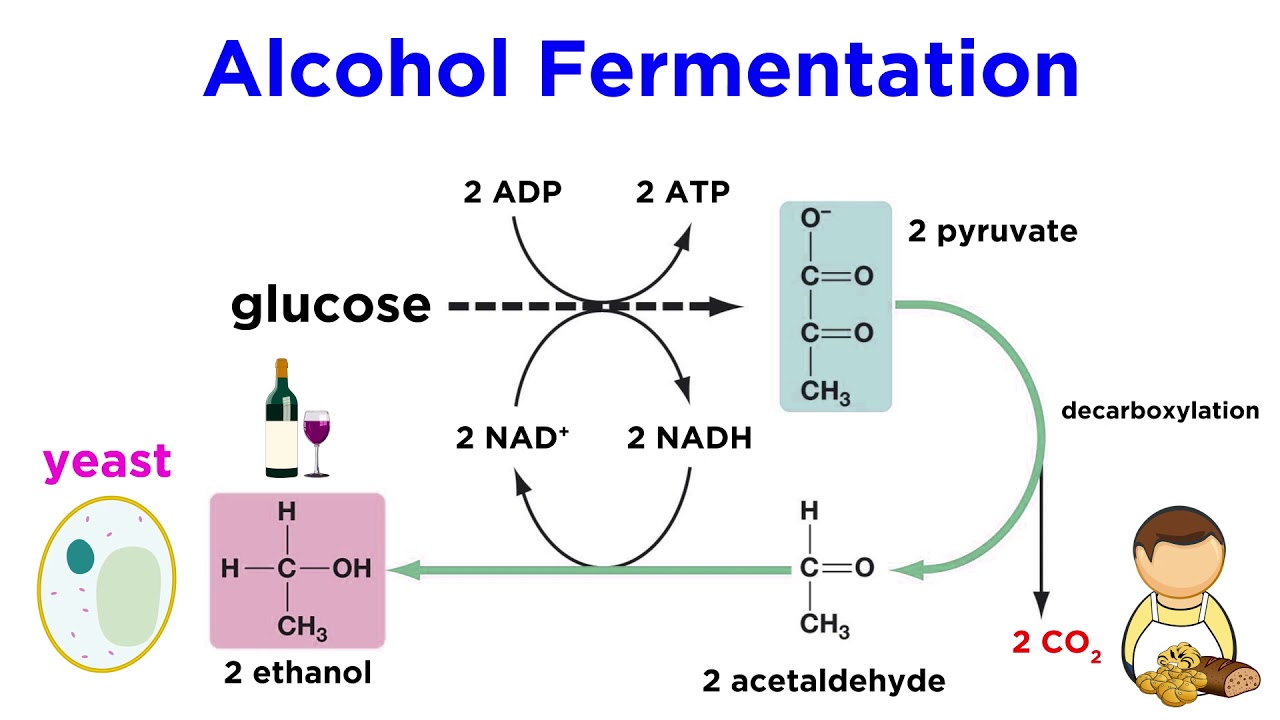
- Fermentation
- In prokaryotes and unicellular eukaryotes, fermentation happens under anaerobic conditions, whereas, in eukaryotes, it happens in the presence of oxygen.
- In fermentation (incomplete oxidation) pyruvic acid is converted to CO2 and ethanol.
- Important enzymes are pyruvic acid decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase catalyse.
- In muscle cells during exercise pyruvic acid is reduced to lactic acid by lactate dehydrogenase.
- Not much energy is generated and the process can be poisonous too.
2. Aerobic Respiration
- Respiration occurring in the presence of oxygen is termed aerobic respiration.
- It occurs in the mitochondria of all eukaryotic plant cells.
- In the presence of oxygen, food molecules are converted into carbon dioxide, water, and energy.
- This type of respiration (complete oxidation of organic substances) is observed only in higher organisms.
- For aerobic respiration, pyruvate is transported from the cytoplasm into the mitochondria.
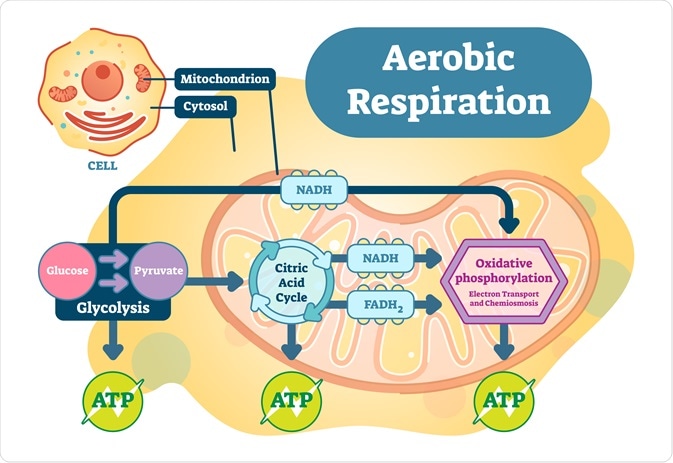
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle or The Kreb’s Cycle
- The pyruvic acid is carried into the mitochondria, and with the release of carbon dioxide, it is converted into acetyl CoA.
- Acetyl CoA enters the Krebs cycle, commonly known as the tricarboxylic acid pathway.
- The entire cycle is operated in the matrix of the mitochondria. Products such as NADH + hydrogen ion and FADH2 are produced in the Krebs cycle.
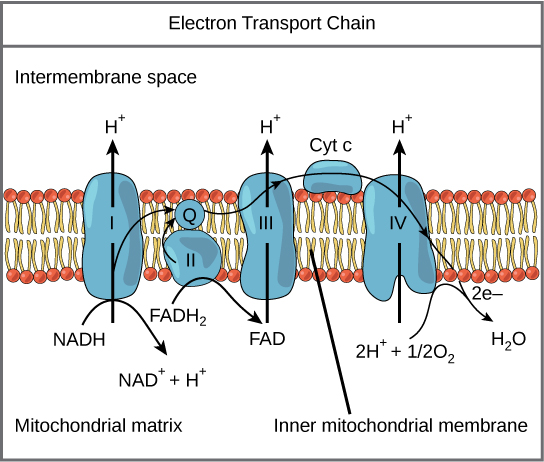
- ATP is synthesized by the release of energy from these molecules and the energy released from the process of glycolysis. A system of electron carriers establishes this and is called the electron transport system (ETS).
- The metabolic pathway in the inner mitochondrial membrane through
- This process is termed Oxidative Phosphorylation as it is the energy of oxidation-reduction that is utilised for the production of proton gradient required for phosphorylation.
The Respiratory Balance Sheet
The calculations of the net gain of ATP for every glucose molecule oxidised is only a theoretical exercise as:
- Glycolysis, TCA cycle and ETS pathways work simultaneously
- Substrates are added and removed from the pathways as required
- The intermediates in the pathway can be utilised to synthesise any other compound
- ATP is utilised as and when needed
- Besides glucose, other alternative substrates also enter in the pathway
- Enzymatic rates are controlled by multiple means
Amphibolic Pathway
- Anabolism creates molecules and catabolism, on the other hand, breaks down molecules.
- Respiration we know involves the breakdown of substrates.
- Fatty acids would be broken down to acetyl CoA as a substrate (catabolism).
- At the same time acetyl CoA as a substrate is withdrawn when the organism needs to synthesise fatty acids (anabolism).
- Because the respiratory pathway is involved in both anabolism and catabolism, the respiratory pathway is considered as an amphibolic pathway.
Respiratory Quotient
- The ratio of the volume of carbon dioxide evolved to the volume of oxygen consumed in the respiration process is called the respiratory quotient.
- It depends mainly on the type of respiratory substrate used during respiration.
- The respiratory quotientof carbohydrates is 1 because equal amounts of CO2 and O2 are evolved and consumed and fats is less than 1.