Plant Adaptation and Responses Study guide
Introduction
Plants live in nearly every part of the earth. To live and survive in different environments, they have developed adaptive capabilities that allow them to survive and reproduce under difficult conditions. Unlike animals, plants can’t run, fly, or swim towards food or against danger, making these adaptations critical for survival. Let’s talk about some of the ways plants have adapted to their environments!
What is Plant Adaptation?
The modification or development of certain body parts in plants that help them to survive and flourish in their environment is termed as plant adaptation. Adaptations helps plants to survive in changing environment. The natural environment in which an organism lives, feeds and reproduces is called its niche or habitat. Various parts of plants modify in various ways to adapt to their habitat.
Types of Adaptations in Plants
- Behavioral Adaptation
- Physiological Adaptation
- Structural Adaptation
Regardless of the kind, all adaptations improve an organism’s compatibility with its ecology and increase the likelihood of its ultimate goals, which are survival and reproduction. The evolution process depends on the adaptations that result from competition. Survival of the fittest refers to those who have the best adaptations.
Behavioral Adaptations
Plants with behavioral adaptations have behaviors that provide them an advantage. To maximize photosynthesis, all plant stems expand swiftly in the direction of the light. Plants are able to adapt to changes in their environment thanks to growth toward the light and other tropisms. Such adaptations are done by the plants to increase their mortality rate and adapt to the changing environment.
Physiological Adaptations
Plants are able to compete with the continuously changing environment thanks to physiological adaptations. The creation of poisons as a kind of defense is an illustration of this. These are internal events that alter the chemical reactions taking place inside an organism’s cells. Production of poisons and toxins in plants helps them against the predators.
Structural Adaptations
The physical characteristics of plants that enable them to compete are their structural adaptations. It can be any physical feature that an organism has evolved in order to survive. An illustration of this is the development of spines, which are present on a variety of plants, including cactus and roses, and which can prevent grazing animals from eating a plant.
Additional examples of structural adaptations include plants with broad, shallow roots that can quickly absorb huge amounts of water after rain, enormous leaves that can maximize photosynthesis, and blooms that draw pollinators.
Photosynthesis and Plant Respiration
Plants depend on the cycle of photosynthesis and respiration for their survival.
-
Photosynthesis is the process used by plants, algae and a few bacteria to turn sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into food and oxygen.
-
Humans and animals inhale the oxygen produced by plants.
-
Respiration is the process of releasing energy from food.
-
Animals take in the oxygen produced by plants, transport it to the cells, and use it to release food. Carbon dioxide is released from the body in the process.
-
Plants absorb this carbon dioxide to provide the energy they need for growth and development. This is the never-ending cycle that helps to sustain life on earth.
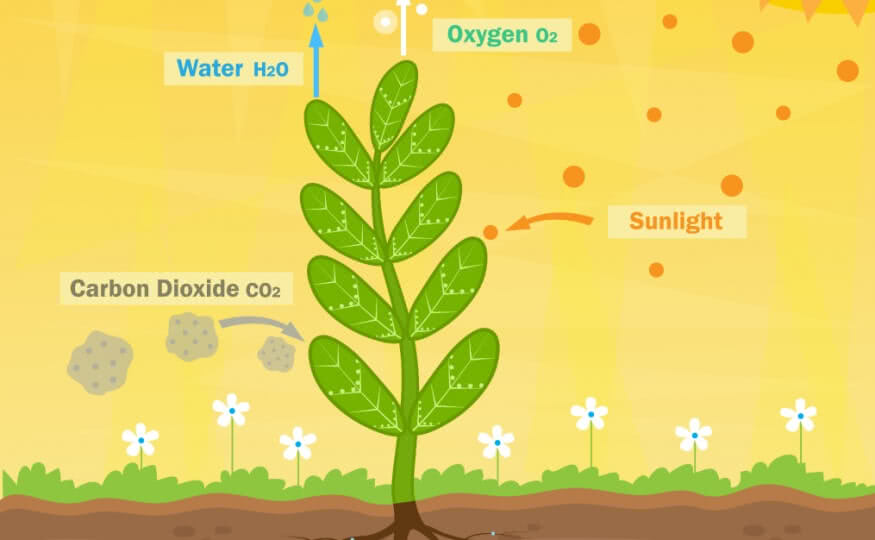
Photosynthesis Adaptation in Leaves
Leaves adapt to environmental conditions to increase the rate of photosynthesis in different ways:
-
Leaves are adapted to photosynthesis by having a large surface area that contains openings called Stomata.
-
Stomata allows carbon dioxide to enter a leaf and allow oxygen to diffuse out.
-
The leaf is coated with a waxy cuticle to stop the water vapor from escaping from the epidermis to reduce water loss. Leaves usually have structures called stomata on their top surface to reduce this water loss.
-
When water evaporates from leaves, it draws more water from the roots in a process called transpiration.
Plant Respiration
Plant Respiration is the process through which cells get their chemical energy by consuming carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen into the atmosphere. In plants, each part, such as root and leaves, executes respiration.
The photosynthesis and respiration process in plants:
-
All living things respire in order to stay alive and energetic.
-
Respiration in plants is the process used by the plants to convert the glucose made during Photosynthesis into energy which fuels the plants’ cellular activities.
-
Apart from this, photosynthesis is the process where light energy is converted into chemical energy and glucose is stored for later use.
-
Photosynthesis occurs on the green parts of the plant that contain chlorophyll.
-
At the time of respiration, plants consume food to keep plant cells alive, while plants create their own food during the process of photosynthesis.
Respiration Through Leaves
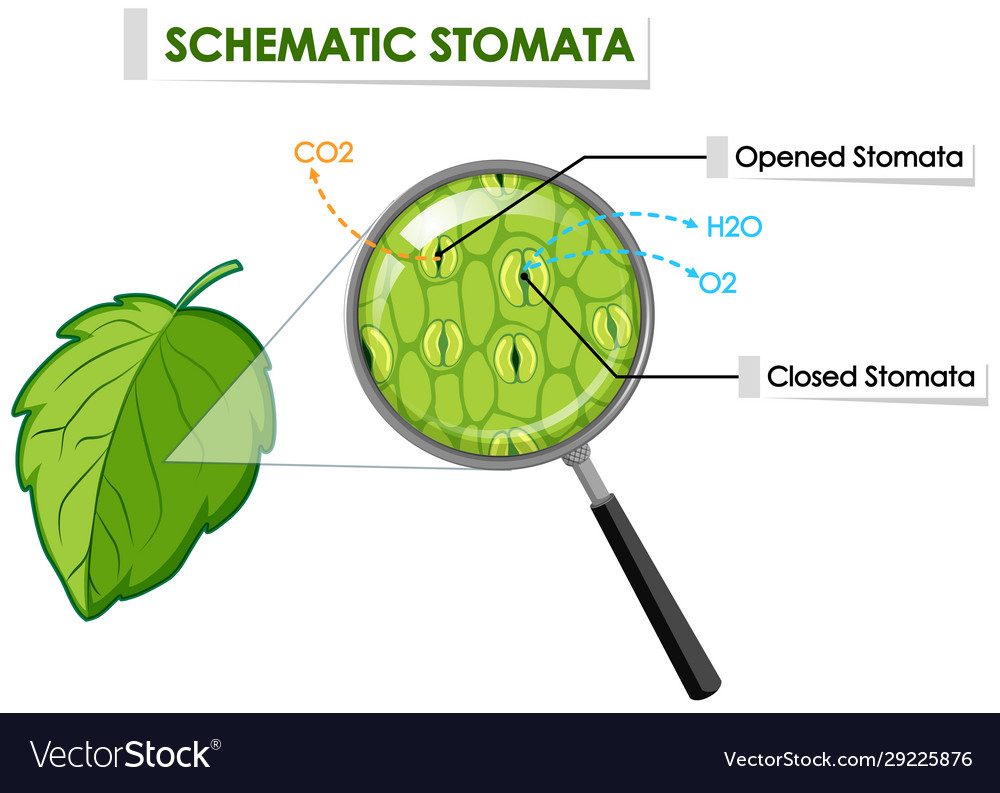 Plant leaves have many minute holes on their surface, known as stomata. The interchange of gas inside the leaves during respiration takes place through stomata.
Plant leaves have many minute holes on their surface, known as stomata. The interchange of gas inside the leaves during respiration takes place through stomata.
From the atmosphere, oxygen enters inside the leaf from stomata and reaches all the parts and cells by the process of diffusion. The oxygen is used as respiration for the leaves, and carbon dioxide produced during this process is diffused out from the leaf into the air through the same stomata.
Respiration Through Roots
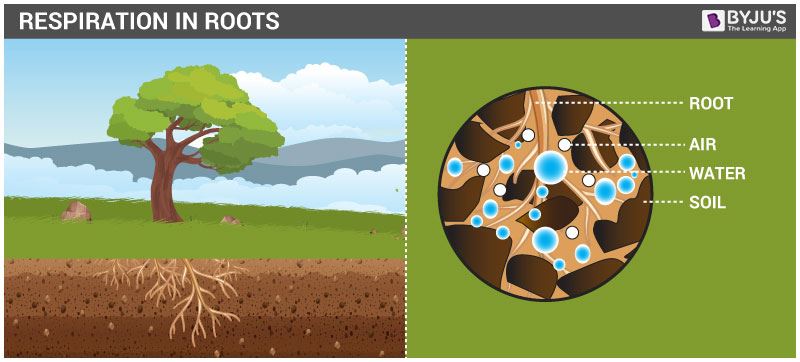
Plants’ root stays under the ground, but roots also need oxygen to carry out their respiration process in plants and release energy. Roots of plants inhale air from the gaps between the soil molecules, and oxygen from the air in soil molecules diffuse into root hair and reach all the parts of the root, where it is used for respiration. Carbon dioxide produced in the cells of the root during respiration goes out through the same hair of the root during diffusion.
Plant Adaptation and Responses in Different Environments
1. Adaptation in Water
Plants living in water have different types of advantages. The very first advantage is that there is plenty of water present. So, most aquatic plants do not need adaptation for absorbing or conserving water. They can store their energy by not growing extensive root systems. Support of water is present to manage its stem inside the water.
Aquatic plants have adapted to keep their flowers above water, allowing them to collect the maximum amount of sunlight that does not penetrate very deeply. Plants that live underwater have leaves with large air pockets inside them. These large leaves allow the plant to soak up oxygen from the water. These leaves of aquatic plants are also very soft to allow the plant to move with the waves.
2. Adaptation in dryness and desert
Plants living in extreme dryness have different problems, and they want to adapt how to get maximum water. These types of plants help themselves to increase their water intake, decrease their loss of water and store more water when it is available. Few of the plants don’t have leaves, so long roots help them collect water from the soil, which assists them in their development. They have a waxy gel-like coating that aids them in preventing loss of their moisture in the environment. This is how the adaptation of plants takes place.
✅ Conclusion
-
Plants live everywhere on earth; they have hormones that allow changes as per the environment’s need and help them survive.
-
Like all organisms, plants also respond to stimuli and to the changes required for their development. Plants also respond to daily and seasonal cycles.
-
The exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen through photosynthesis or cellular respiration worldwide helps to keep atmospheric oxygen and CO2 at stable levels.
FAQs
1. What are 5 plant adaptations?
The main five adaptations of plants are their root structure, leaves, waxy or oily texture, the environment in which they are growing, and their inborn behavior.
2. How are plants adapted to photosynthesis?
-
Leaf increases its surface area to absorb more sunlight.
-
The presence of a cuticle prevents the loss of water.
-
The thin structure of leaves allows carbon dioxide to reach easily.
-
The presence of chlorophyll contains a large amount of chloroplast for photosynthesis.
-
Veins support leaves and transport water, minerals, and sugar.
-
Stomata allow carbon dioxide to diffuse into the leaf and oxygen to diffuse out.
3. What are some plant adaptations in the grasslands?
Grassland plants have a deep root system that allows them to strengthen themselves and get moisture during dry days.
4. What are the responses of plants?
Plants respond through their stimuli in the environment. So their response is generally controlled by their hormones, which are chemical messenger molecules.
5. What are two types of adaptation that plants can show?
The two main types of adaptation that plants can show are physical adaptation, which helps the plant survive in a different environment. The other is its behavior adaptation in which plants take action to survive.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Plant Adaptation and Responses! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
]]>