CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 16 Revision Notes
Multiple Choice Questions
- The posterior opening of the alimentary canal is _________.
- If a tooth is embedded in a socket of jaw bone then it is known as _________.
- Which of the following is the largest gland in the body? ______
- Which of these is NOT a salivary gland? ________
- Glucagon is secreted by _________
- The tongue is attached to the floor of the oral cavity by the _________.
- Which of the following acts as a common passage for food and air? _______
- The opening of oesophagus into the stomach is regulated by which of the following? ___________
- Which part of the stomach opens into the first part of the small intestine? __________
- Which of the following is a highly coiled part of the small intestine? _______
- Assertion: Defecation is a voluntary process.Reason: External anal sphincter is under voluntary control. ______________
- Absorption is a process by which the end product of digestion passes through the intestinal mucosa into _______.
- Assertion: Saliva is antibacterial in nature.Reason: Saliva contains lysozyme. _______________
- Where are fecal matters temporarily stored till defecation?__________
- Assertion: Tongue contains receptors for taste.Reason: The upper surface of the tongue has small projections called papillae, all of which bear taste buds which act as receptors for taste. _______
Chapter 16: Digestion and Absorption Revision Notes
- Digestion is the chemical breakdown of the nutrients into tiny absorbable molecules in the small intestine.
- It is carried out by mechanical and biochemical methods in the digestive system.
- Absorption refers to the movement of nutrients from the small intestine into the cells and then into the blood.
Where does digestion occur?
- Digestive system consists of the alimentary canal and the associated glands.
- Digestion occurs in the small intestine through the action of enzymes.
- The intestine consists of three parts: duodenum (25cm), jejunum (around 2.5m) and ileum (around 3.5m).
- It is about 20 feet long but has a small diameter, so it is called the ‘small’ intestine.
- Its folds and the projections in its lining create an extremely large surface area of approximately 200 square meters, which is imperative for absorbing nutrients.
- To achieve this large surface area, the small intestine consists of circular folds, villi and microvilli.
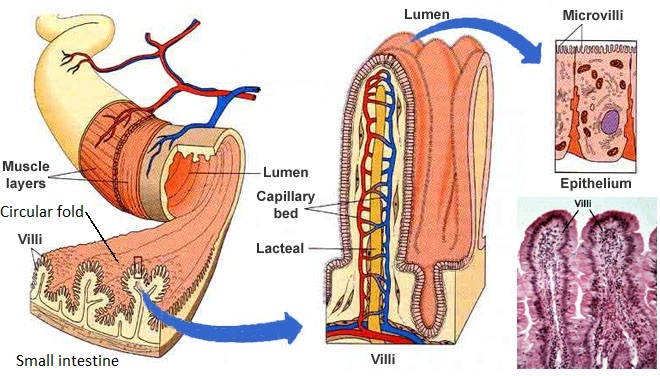
Source: Small intestine parts
How does digestion take place?
- The digestion process occurs through the gastrointestinal tract (GI Tract), which consists of the mouth, the oesophagus, the stomach and the small intestine.
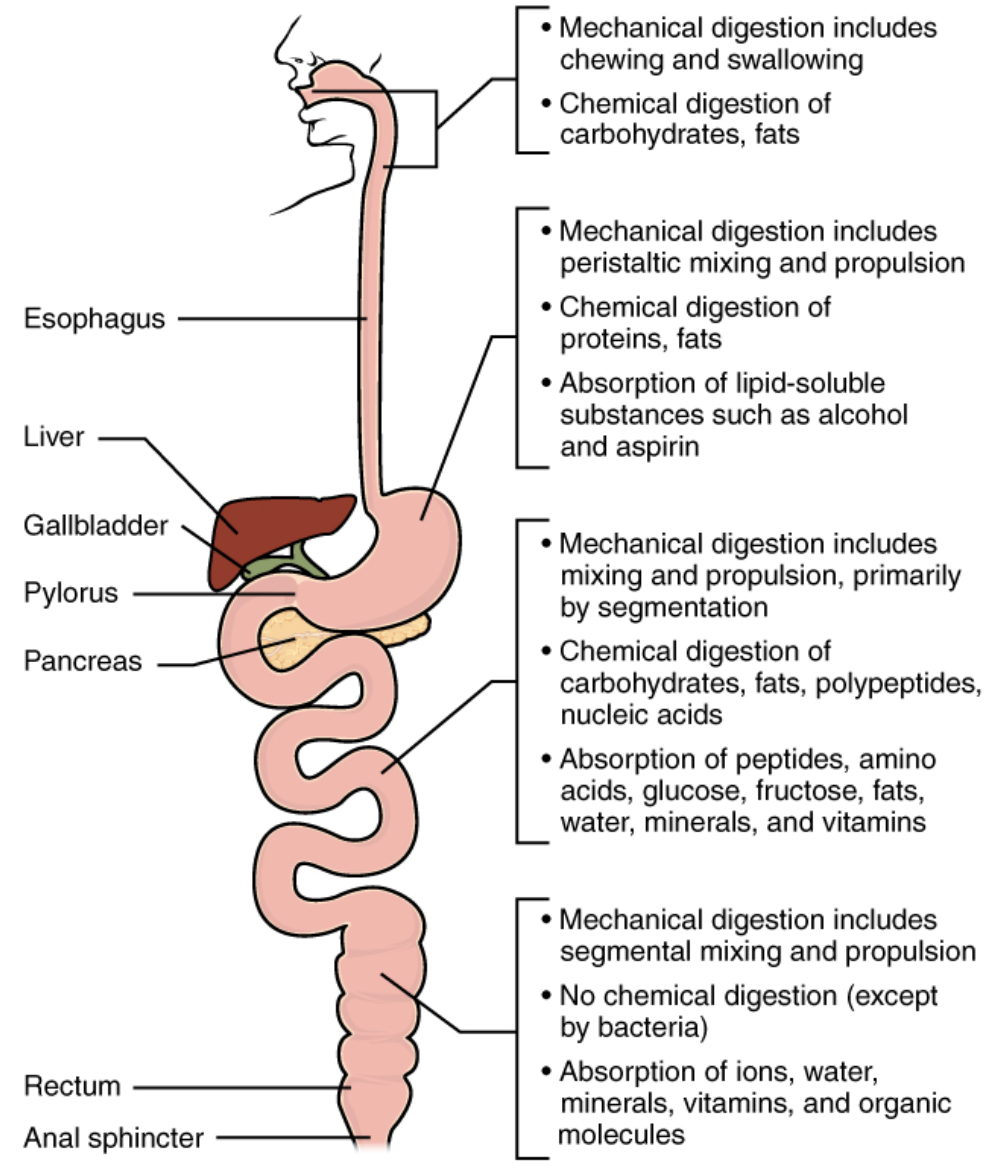
Source: Digestion process
Mouth
- Mechanical digestion takes place in your mouth.
- It involves physically breaking down food into smaller molecules to undergo chemical digestion.
- When a tooth is embedded in a socket of the jaw bone, the attachment is called thecodont.
- Temporary milk teeth are called deciduous teeth.
- When a set of temporary teeth are replaced by permanent teeth it is known as diphyodont.
- The hard surface of teeth is made up of enamel and helps in the mastication of food.
- The tongue is a muscular organ that freely moves and is attached to the floor of the oral cavity by the frenulum.
- The taste buds are on the tiny projections on the upper surface of the tongue called papillae.
- When you swallow, your tongue pushes the food into your throat, and the food moves on into your oesophagus.
Oesophagus
- Once the food is swallowed, the process becomes involuntary, and peristalsis begins.
- Food moves through your GI tract by peristalsis which is a series of muscle contractions occurring in the digestive tract.
- This long, hollow organ of the intestinal tract contains muscles that enable its walls to move.
- This movement shoves food and liquid through the tract.
- The oesophagus leads to a J shaped bag like structure called stomach.
- The gastro-oesophageal sphincter regulates the opening of the oesophagus into the stomach.
Stomach
- Stomach has 4 parts – cardiac, fundic, body and pyloric.
- After food enters your stomach, the muscles combine the food and liquid with enzymes and digestive juices.
- This churned mixture of nutrients is known as chyme.
- The stomach slowly empties this chyme into the small intestine.
Small intestine
- The muscles in the small intestine mix chyme with digestive juices and enzymes from the pancreas, liver, and intestine.
- The mixture is in the duodenum of the small intestine, where the majority of the chemical digestion takes place.
- In the duodenum, enzymes such as trypsin, elastase, and chymotrypsin act on the chyme to reduce them to smaller absorbable molecules.
- Other enzymes are produced in the pancreas, such as trypsin elastase, carboxypeptidase, and chymotrypsin, and released to act on the chyme present within the duodenum.
- Bile is also released into the duodenum, which neutralizes the acidic food from the stomach and breaks up large chunks of lipids.
Where and how does absorption take place?
- Most absorption of food occurs in the small intestine.
- It occurs in the middle section of the small intestine, known as the jejunum, and the last section known as the ileum.
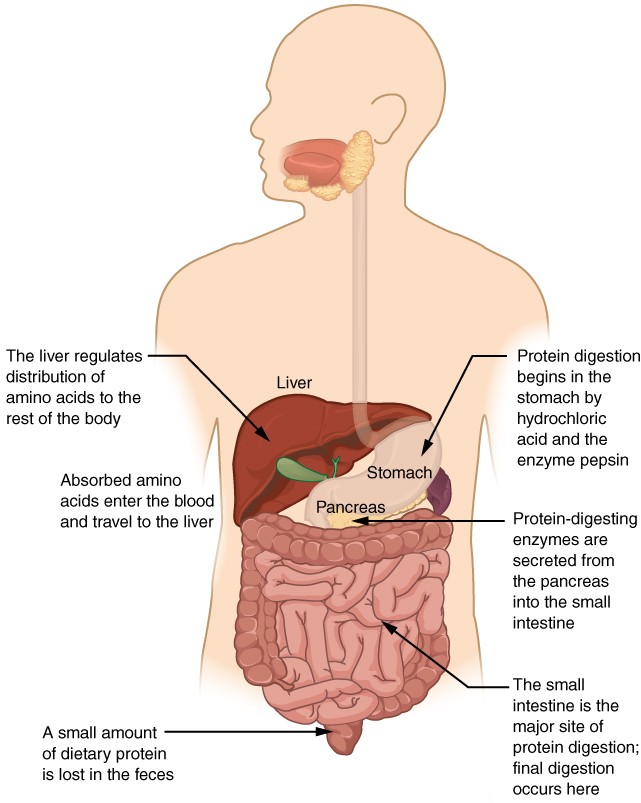
Source: Absorption process
- The jejunum is the middle part of the small intestine, where the substances move from the duodenum.
- It has a lining present that absorbs carbohydrates and proteins.
- The inner surface of the jejunum is covered with minuscule projections known as villi.
- The villi in the jejunum are of much greater length than the villi present in the duodenum or ileum.
- The ileum is the final section of the small intestine.
- The function of the ileum is mainly to absorb bile salts, vitamin B12, and all products of digestion that were not previously absorbed by the jejunum.
- The absorbed substances finally reach the tissues, passing through the cells of the jejunum and ileum, which utilize them for their activities. This process is called assimilation.
How can you assist the process of digestion and absorption?
The processes of digestion and absorption can be aided by:
- Consuming a balanced diet that includes fiber
- Staying hydrated
- Taking probiotics
- Undertaking physical activity
- Managing stress
- Managing dental hygiene
- Controlling and observing digestive conditions
