Biotechnology Study Guide
Introduction:
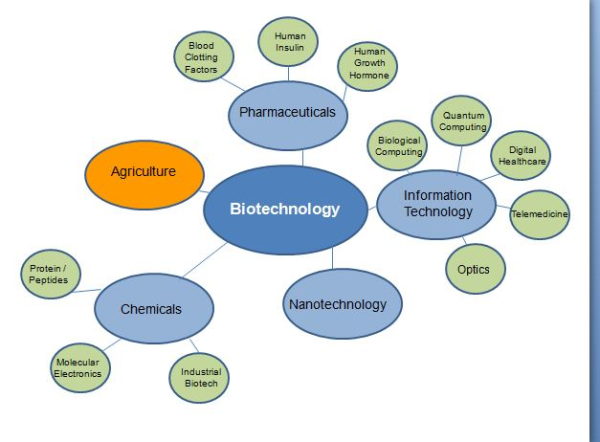
Biotechnology is a large field of biology that involves the development, modification, and production of useful goods for human welfare using both the technology and the application of live organisms and their components.
Principles of biotechnology:
Biotechnology’s primary concepts, as per modern biotechnology, are:
- Genetic engineering is a technique for altering the DNA of a target organism to change its phenotype.
- Bioprocess engineering is the process of maintaining a sterile environment to promote the growth of large quantities of preferred microbes and other eukaryotic cells for the production of new or altered biotechnological products such as antibiotics, enzymes, vaccines, and other biotechnological products.
The most common genetic engineering approaches are:
- The donor organism’s DNA is extracted as a fragment.
- The vector DNA is introduced into it.
- It is then transferred to a suitable host.
- In the host organism, the recombinant DNA is cloned.
Genetic Engineering is another name for recombinant DNA technology. It is the process of connecting two DNA molecules from different species together. This is referred to as recombinant DNA.
The following are the steps involved in recombinant DNA technology:
- DNA isolation
- DNA fragmentation utilizing restriction endonucleases
- The required DNA segment is ligated into the vector
- Incorporation of recombinant DNA into the host
- The transformed cells are cultured in nutritional media
- The desired product is extracted
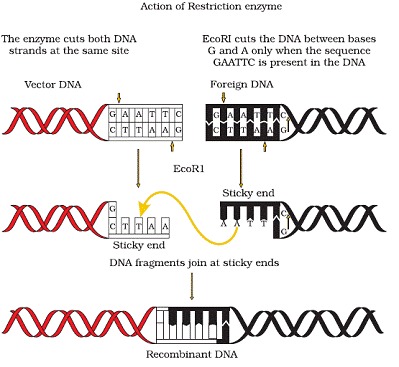
Restriction Enzymes (Molecular Scissors):
- Restriction enzymes are part of the Nucleases family of enzymes, and exonucleases and endonucleases are the two types. Endonucleases create cuts at specified positions inside the DNA, whereas exonucleases remove nucleotides off the ends.
- Each restriction endonuclease recognizes a unique palindromic nucleotide sequence in the DNA. Palindromes are a set of letters that, when reading both forward and backward, produce the same word.
- Restriction enzymes cut the DNA strand between the identical two bases on opposing strands with the sticky strands. Because the strands are sticky, the enzyme DNA ligase can work more efficiently.
- In genetic engineering, restriction endonucleases are employed to create recombinant DNA molecules made up of DNA from various sources or genomes.
- When DNA fragments are cut with the same restriction enzyme, they have the same sticky-ends and may be linked with DNA ligases.
DNA fragment separation and isolation:
- Gel electrophoresis is a method for separating DNA fragments generated by cutting DNA using restriction enzymes. Negatively charged DNA fragments can be segregated by causing them to migrate towards the anode through a medium while being subjected to an electric field. The sieving action of an agarose gel separates DNA fragments as per their size.
- Upon staining the DNA with ethidium bromide and exposing it to UV light, the separated DNA fragment may be seen. Elution separates distinct bands of DNA from an agarose gel and extracts them from the gel. This purified DNA fragment is then utilized for recombination.
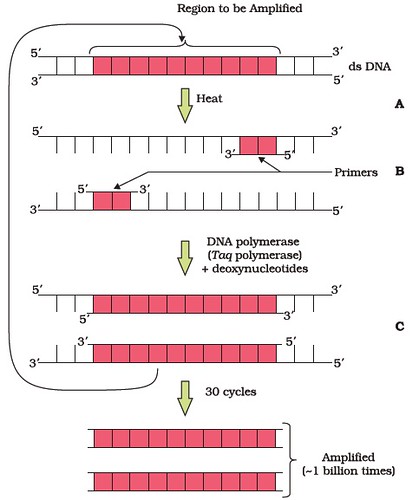
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction): Amplify a gene of interest to obtain numerous copies of the DNA of interest in vitro using a set of primers and the enzyme DNA polymerase.
Each cycle of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) consists of three steps:
- Primer denaturation
- Primer annealing
- Primer Extension
Bioprocess Engineering:
The proliferation of cells in bioreactors is known as bioprocess engineering. The technique yields a huge culture volume, resulting in a greater yield of the needed protein. The obtained goods are put through a variety of procedures. Before further testing, the goods are filtered by downstream processing and put through a quality check. Antibiotics, vaccines Influenza), and other therapeutic medications (Insulin) are made using this method.
DNA sequencing of our genome, detailed studies on the genetic basis of heritable diseases, and the invention of technology to manipulate DNA provides methods to treat diseases. Gene therapy involves altering the genes inside your body’s cells in an effort to treat or stop a disease. Biotechnology in agriculture can enhance resistance to disease (transgenic plants), pests (the organic insecticide Bacillus thuringiensis), and environmental stress, and improve both crop yield and quality (Flavr Savr Tomato).
Conclusion:
- Biotechnology is a large field of biology that involves the development, modification, and production of useful goods for human welfare using both the technology and the application of live organisms and their components.
- Genetic engineering is a technique for altering the DNA of a target organism to change its phenotype.
- Gel electrophoresis is a method for separating DNA fragments generated by cutting DNA using a restriction enzyme.
- Restriction enzymes are part of the Nucleases family of enzymes. Exonucleases and Endonucleases are the two types. Endonucleases create cuts at specified positions inside the DNA, whereas exonucleases remove nucleotides off the ends.
FAQs:
1. What is gene expression in biotechnology?
The process through which the instructions in our DNA are transformed into a functioning result, such as a protein, is known as gene expression. Transcription and translation are the two most important processes in producing a protein.
2. What is meant by regulation of gene expression?
The process of turning genes on and off is known as gene regulation. Cells begin to take on distinct tasks throughout early development. Gene regulation ensures the right genes are expressed at the right times. Gene control can also aid an organism’s response to its surroundings.
3. Why is gene expression important to biotechnology?
Biotechnology is technology that utilizes biological systems, living organisms to develop or create different products. The cells manipulated using this technology contain genes that encode proteins of interest (the product). Gene expression is the process by which the instructions in these genes are converted into the desired protein. Thus gene expression is important to biotechnology.
4. What are restriction enzymes? What is their function?
Restriction enzymes cut DNA at or near restriction sites, with particular recognition nucleotide sequences. Isolated restriction enzymes are key tools for recombinant DNA technology and modify DNA for many scientific applications.
5. What are bioreactors?
A bioreactor is a cylindrical cylinder in which large-scale biological activities are carried out. By supplying appropriate growth conditions such as temperature, pH, substrate, salts, vitamins, and oxygen, a bioreactor helps to get the desired result.
6. What is a cloning Vector?
Cloning vectors transfer foreign DNA into another cell and replicate it numerous times. The foreign DNA is copied and expressed using the host cell’s machinery. It multiplies a single copy of DNA into several copies.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Biotechnology! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! We promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
Sources:
- Biotechnology. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/3.13/primary/lesson/biotechnology-bio/. Accessed 20 Dec, 2021.
- What is Biotechnology?. https://www.ntnu.edu/ibt/about-us/what-is-biotechnology. Accessed 20 Dec, 2021.
- What is Biotechnology?. https://www.bio.org/what-biotechnology. Accessed 20 Dec, 2021.
- Biotechnology. https://www.nature.com/subjects/biotechnology. Accessed 20 Dec, 2021.