CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 4 Revision Notes
Chapter 4: Reproductive Health Revision Notes
Multiple Choice Questions
-
___________ is not a copper releasing IUD.
-
MTP stands for ___________
-
__________ is a widely accepted method of contraception in India.
-
Which part of the female reproductive system remains blocked after tubectomy? ____________
-
Amniocentesis is a process used to ____________
-
A couple suffering from infertility can still have a baby through ________ process.
- Reproductive health refers to the healthy and proper/normal functioning of all reproductive organs, which includes all elements of reproduction.
- India was one of the first countries to use family planning policies and programs to achieve overall reproductive health as a societal aim.
- It was established at the national level in 1951 to raise knowledge about all reproduction elements by providing facilities and assistance to create a reproductively healthy community.
Both governmental and non-governmental entities have taken numerous initiatives to raise citizen knowledge of reproduction-related issues to carry out these programs successfully, including:
- Family planning is becoming more popular.
- Sex education is being implemented in schools.
- To raise awareness, printed materials were distributed.
- Reproductive Health Powerpoint Slides with Audio and Video
- Complete information about reproductive organs, puberty, safe and sanitary sexual activities, sexually transmitted illnesses, birth control techniques, mother and newborn child care, and so on.
Amniocentesis
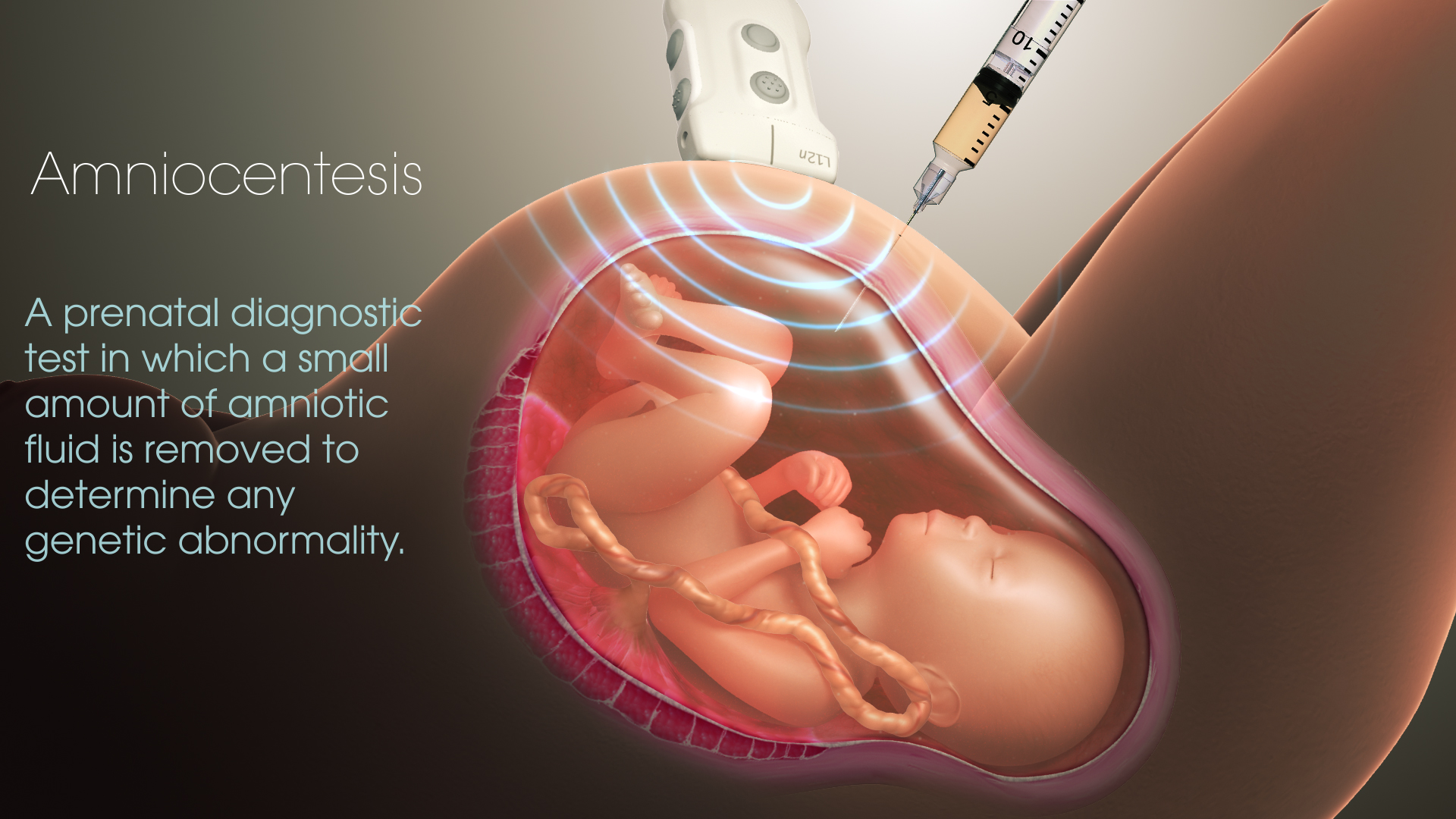
Source: Amniocentesis
- Amniocentesis is a method that uses amniotic fluid to detect chromosomal abnormalities such as down syndrome, sickle cell anemia, in a growing fetus.
- It’s also been utilized to confirm fetal sex based on the chromosomal pattern in the amniotic fluid around the growing embryo.
Population stabilization and birth control
- Causes such as a quick drop in the death rate, infant mortality rate, maternal mortality rate, and a significant rise in the reproductive age are contributing factors to an exponential rise in the population from the moment of independence until May 2011.
- As a consequence of the worrisome growth rate that has resulted in a scarcity of necessities, the government has been compelled to take drastic steps.
- The essential way to slow population increase is to encourage smaller families by using different contraceptives.
- Other initiatives included familiarizing slogans (Hum do Hamare do), mandatory increasing of both male and female marriageable ages, and incentives for couples with fewer kids, among others.
- Natural/traditional techniques (periodic abstinence), IUDs, barriers (diaphragms, condoms, cervical caps, vaults), oral contraceptives (pills), implants, surgical procedures (sterilization), injectables, and so on are all examples of contraceptive methods.
Methods of contraception
- Natural approaches function on the idea of preventing ovum and sperm from colliding.
- It entails periodic abstinence – couples avoid coitus from days 10 to 17 of the menstrual cycle since the chances of fertilization are highest during this time, known as the fertile period.
- Withdrawal or coitus interruptus — to avoid conception, the male partner withdraws his penis from the vaginal canal shortly before ejaculation.
- Lactational Amenorrhea – lack of menstruation after parturition, and owing to intensive milk feeding and no ovulation at this time, chances of fertilization are slim to none.
- Barrier techniques use a barrier to prevent ovum and sperm from physically meeting.
- Condoms are used by men, and women use a barrier made of rubber or latex sheet to cover their penis, vagina, and cervix. It also protects against STDs.
- Intrauterine Devices (IUDs) are medical devices put into the female uterus through the vaginal canal by a doctor or a trained nurse.
- Non-medicated IUDs (e.g., Lippes loop), copper-releasing IUDs (CuT, Cu7, Multiload 375), and hormone-releasing IUDs are all examples of IUCDs (Progestasert, LNG-20)
- Copper reduces sperm motility and reproductive capability, while IUCDs promote sperm phagocytosis in the uterus.
- IUDs that release hormones render the uterus unsuitable for implantation and the cervix unfriendly to sperm.
- It is good for women who desire to postpone pregnancy and space their children out.
- Females take oral pills containing progesterone or a progesterone-estrogen combo.
- They limit or delay sperm entrance by inhibiting ovulation and implantation and altering the quality of cervical mucus.
- The surgical approach is also known as sterilizing.
- It is used as a last-resort technique of contraception in both men and women to avoid conception.
Medical termination of pregnancy (MTP)
- In India, MTP, or induced abortion, was permitted in 1971 under tight restrictions to prevent abuse.
- It refers to the voluntary or purposeful termination of a pregnancy before the full term has been reached.
- It is regarded as safe until the first trimester, after which the odds of being in a dangerous situation grow.
Infertility
- Infertility is defined as the inability to create offspring despite sexual contact.
- It can be caused by various causes, including hereditary, physical, pharmacological, psychological, and immunological.
- There are specialist treatments to help such couples – ART (assisted reproductive technologies), which includes IVF (in-vitro fertilization) and ET (electronic fertilization) (Embryo transfer)
