CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Revision Notes Part 2
Chapter 6: Molecular Basis of Inheritance Revision Notes Part 1
The study of genetics or molecular basis of inheritance helps understand genes, heredity, and genetic variation. DNA is a molecule carrying genetic information in nearly all living organisms, and is used in reproduction, functioning, growth, and development.
DNA Structure and Packaging
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a complex, organic, molecular structure found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells as well as several viruses. It is a hereditary material mainly involved in carrying genetic information, and it is found in the cell’s nucleus.
As per the double-helix model of DNA proposed by Watson and Crick based on Rosalind Franklin’s discovery of DNA’s structure, DNA is a double-stranded macromolecule with two polynucleotide strands running anti-parallel to each other.
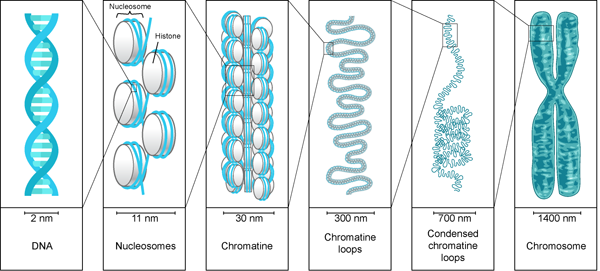
The double helix is negatively charged because of a phosphate group in its backbone. Cells makes histone proteins that bind the DNA to counterbalance the negative charge. These histone proteins are involved in DNA Packaging, which is the process of folding the DNA molecule to fit into the nucleus of a cell.
DNA packaging is required because DNA is around 3 meters in length, and it needs to be packed into the nucleus which is only a few micrometers in diameter. To fit the DNA molecules into the nucleus, it needs to be packed into an extremely compressed and compact structure called Chromatin.
Specifics of DNA’s structure include:
-
DNA strands are helically coiled, with every single strand making a right-handed coil.
-
The pitch of each helix is 3.32 nm, and about 10 nucleotides make up one turn.
-
A distance of 0.34 nm separates two succeeding base pairs.
-
The total length of a DNA is the distance between two succeeding base pairs and the product of a total number of base pairs.
-
A typical strand of DNA is 2.2 meters long.
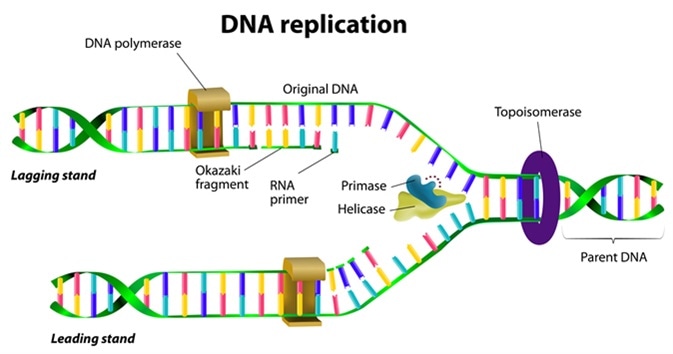
DNA Replication
In DNA Replication, the DNA makes multiple copies of itself. Replication is a biological polymerization that takes place in three stages: initiation, elongation, and termination. It is an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, and DNA Polymerase is the main enzyme involved in the replication process.
Genetic Code
Genetic Code is a framework of rules that determines the information encoded within the DNA or mRNA sequence being translated into proteins by the living cells. Ribosomes accomplish the process of translation by linking the amino acids in a messenger RNA (mRNA) specified order using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time.
Properties of genetic code include:
-
Triplet code
-
Non-ambiguous and Universal
-
Degenerate code
-
Non-overlapping code
-
Commaless
-
Start and Stop Codons
-
Polarity
Genetic Mutation
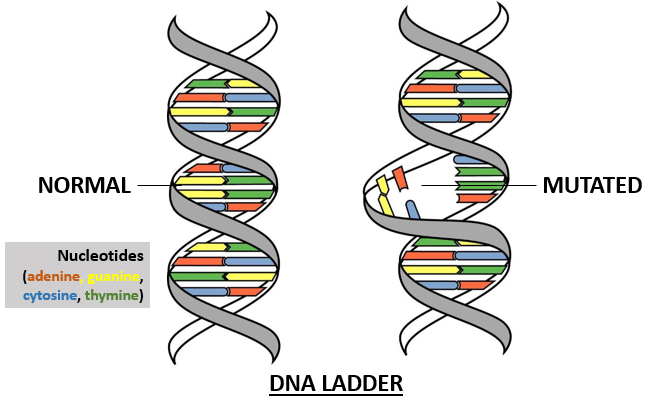
Genetic Mutation is the change in the DNA base pair sequence caused by environmental factors such as UV light or mistakes during DNA replication. There are 3 types of mutation: silent, nonsense, and missense.
Mutations that occur in somatic cells are called Somatic Mutations, and they cannot be passed on to progeny. Germline Mutations can be passed on to successive generations and occur in the reproductive cells.
Mutations can have many effects on a living being. Very rarely, a mutation may result in new versions of proteins or traits that help organisms adapt to changes in their environment, ultimately leading to evolution. Mutations in many bacteria can make them antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria, and mutation in genes can cause cancer.
Sources
Molecular Basis of Inheritance. https://ncert.nic.in/textbook/pdf/lebo106.pdf. Accessed 14 Dec, 2021.
]]>