CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Revision Notes
Chapter 2: Microorganisms-Friend And Foe Revision Notes
-
Microorganisms are too small to be seen by our eyes.
-
They cannot be seen without a microscope, except for fungus that grows on bread.
-
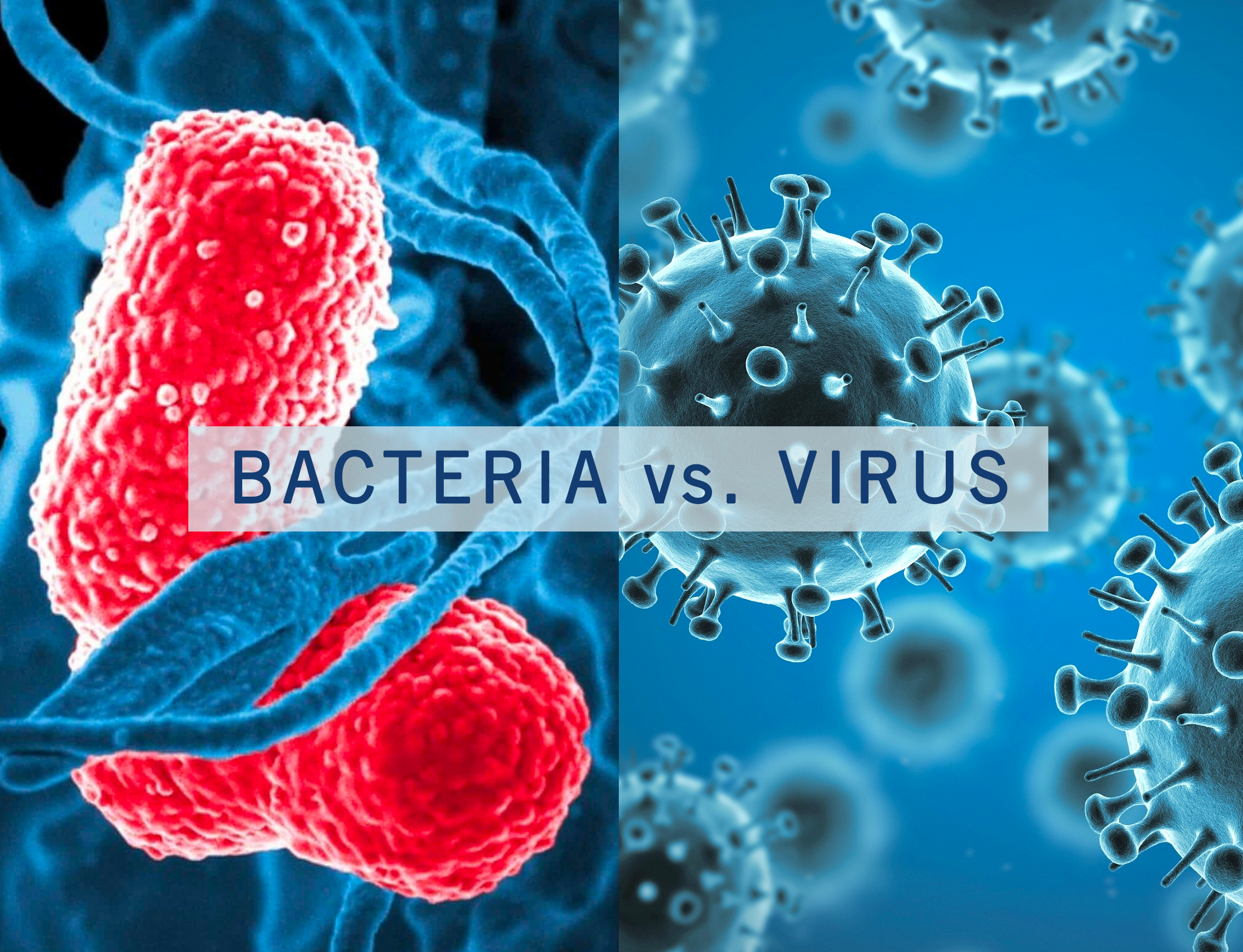
Microorganisms are divided into four categories: Bacteria, fungus, protozoa, and certain algae are among these groupings.
-
Viruses are tiny as well. They, on the other hand, only multiply within the cells of the host organism, which can be bacteria, a plant, or an animal.
| DISEASE | AGENT |
| cold, influenza (flu), polio, and chicken pox | Viruses |
| dysentery and malaria | protozoa(protozoans) |
| typhoid and tuberculosis (TB) | bacterial diseases |
Microorganisms can thrive in a variety of environments, including arctic temperatures, hot springs, deserts, and marshy regions.
Microorganisms are extremely crucial in our life: Both beneficial and harmful
BENEFICIAL USES OF MICROORGANISMS
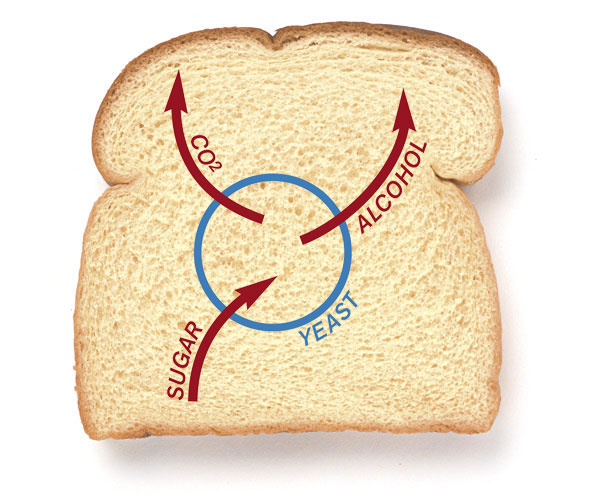
- Making curd (Lactobacillus), bread (yeast), and cake
- Decomposition of organic wastes into simple substances that can be used again.
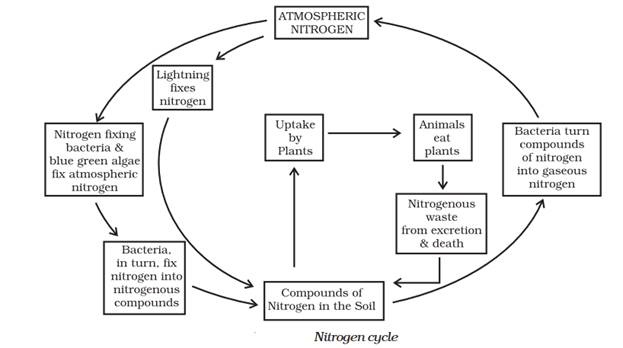
- Improve soil fertility by fixing nitrogen: biological nitrogen fixers such as certain bacteria and blue-green algae
- Production of alcohol, wine and acetic acid (vinegar)
- Fermentation is the term for the process of turning sugar into alcohol carried out by yeast.
- Production of antibiotics such as Streptomycin, tetracycline, and erythromycin made from fungi and bacteria.
- To produce vaccines against polio, cholera, tuberculosis, smallpox, and hepatitis by helping the body produce antibodies.
HARMFUL MICROORGANISMS
- Humans, plants, and animals are all harmed by some of the microbes. Pathogens are microbes that cause disease.
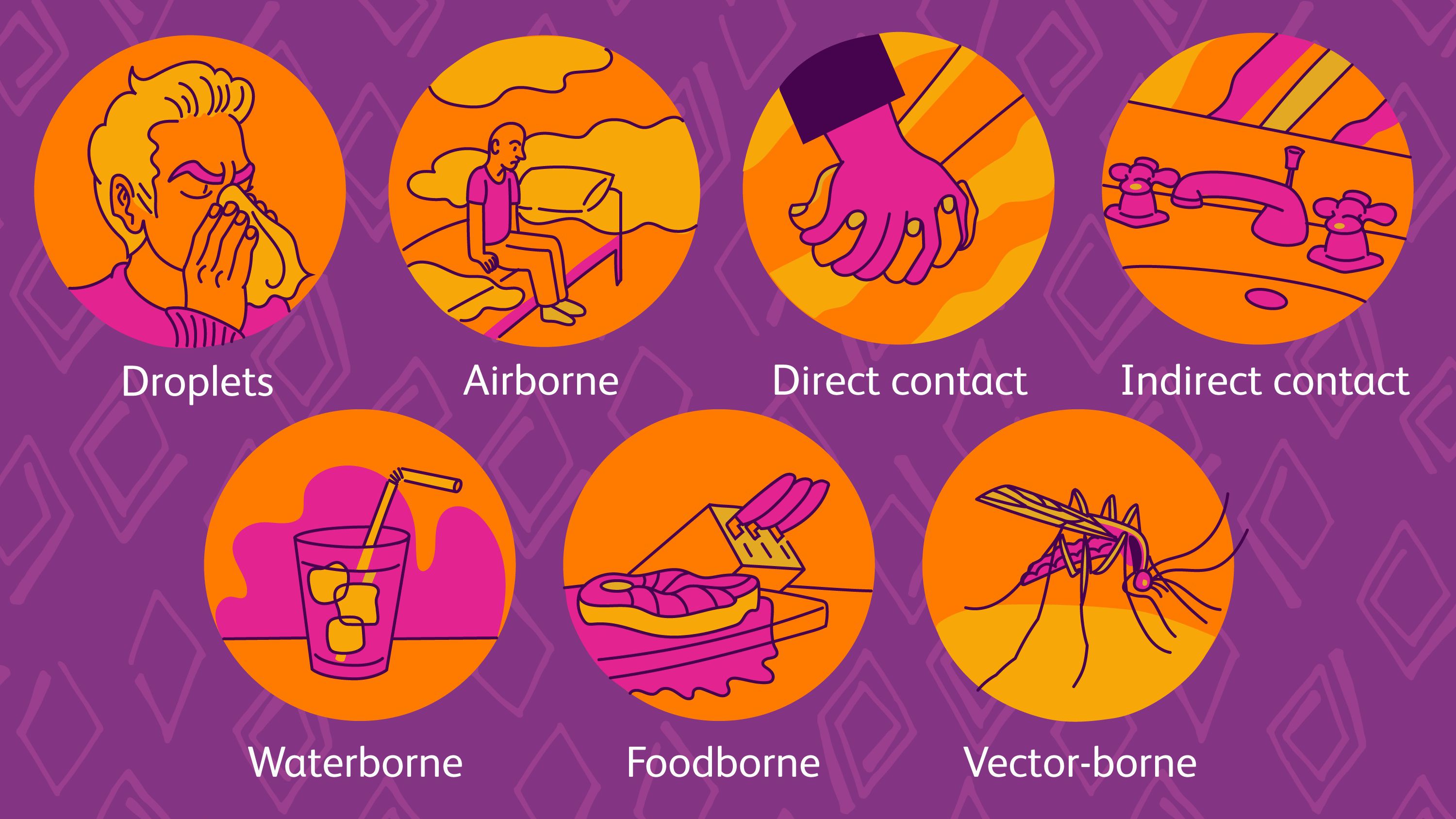
- Communicable illnesses are microbial infections that can transmit from an infected person to a healthy person by the air, water, food, or personal contact.
- Insects and animals that help carry disease-causing microbes are called carriers (Anopheles mosquito for malaria).
- Anthrax (bacteria) and foot and mouth (virus) are disease-causing microorganisms in animals.
- Citrus canker (bacteria), and rust of wheat (fungi) are common plant diseases caused by microorganisms
- Food poisoning could be caused by eating food that has been spoiled by bacteria due to the release of toxic chemicals.
FOOD PRESERVATION
-
Chemical method: Preservatives such as salts, edible oils, sodium benzoate and sodium metabisulphite are used in the jams and squashes.
-
Common salt: salting to preserve meat, fish, amla, and raw mangoes.
-
Sugar: Lowers moisture content in jams, jellies, and squashes.
-
Oil and vinegar: Vegetables, fruits, fish, pickles, and meat.
-
Pasteurisation: heat and cold treatments are seen in pasteurised milk (70 degrees C for 15 to 30 seconds and then suddenly chilled and stored).
-
Storage and packing: dry fruits and vegetables are sealed in airtight packages to prevent microbial contamination.
NITROGEN FIXATION
Rhizobium is a symbiotic bacteria that resides in the root nodules of leguminous plants like beans and peas and helps fix nitrogen.
Source: Chapter-2.pmd (ncert.nic.in)
]]>