CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 10 Revision Notes
Chapter 10: Reaching The Age of Adolescence Revision Notes
Adolescence is the phase of life when the body experiences changes that lead to reproductive maturity.
Puberty is the period during adolescence during which the sex organs begin to play their role.
It brings about changes in the body and growth in the reproductive organs.
Puberty begins much earlier, between the ages of 8 and 13 in girls, whereas between 10 and 14 in boys.
After puberty, humans become capable of reproducing.
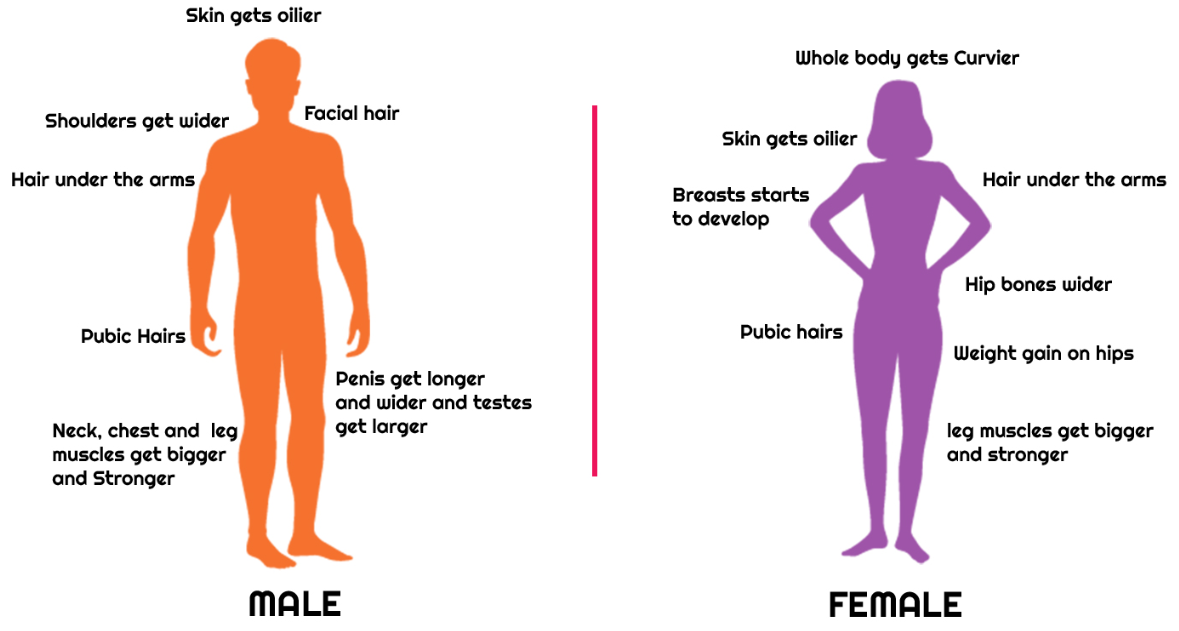
CHANGES AT PUBERTY
During puberty, several changes occur.
(i) Height Gain: The long bones in the legs and arms lengthen, making the person tall. Height depends on inherited genes.
(ii) Body Shape Changes: Boys’ bodies become more muscular, and their shoulders wider. The body of a female below the waist becomes wider.
(iii) Voice Change: Due to the additional growth of the larynx or voice box in boys (Adam’s apple), their voices become deep. The voice of a female becomes high-pitched.
(iv) Sweat and sebaceous glands: They become more active and secrete more sweat and oil due to the increased activity. Sebaceous or oil glands’ enhanced activity leads to pimples or acne.
(v) Development of Sex Organs: The sex organs mature and begin to operate. Male gametes known as sperms are produced in the testes. The ovaries mature and give out one mature ovum in a 28-day cycle.
(vi) Mental and intellectual growth (thinking and learning) have peaked.
-
Hormones (chemical substances) regulate the beginning of puberty and reproductive organ maturation.
-
They are secretions of the endocrine glands that enter the bloodstream directly.
-
Growth hormones and hormones that cause other glands to secrete hormones, such as the testes, ovaries, thyroids, and adrenals, are secreted by the pituitary gland.
-
The pancreas produces insulin,
-
The thyroid produces thyroxin, and
-
The adrenal glands produce adrenalin.
-
The male hormone is testosterone, and the female hormone is estrogen.
MENSTRUATION
In females, the uterine wall prepares to receive the developing fertilised egg. If pregnancy does not occur, the uterine wall’s lining breaks down and is expelled along with the blood. Menstruation is the term for this.
- The merging of the sperm and ovum forms a zygote.
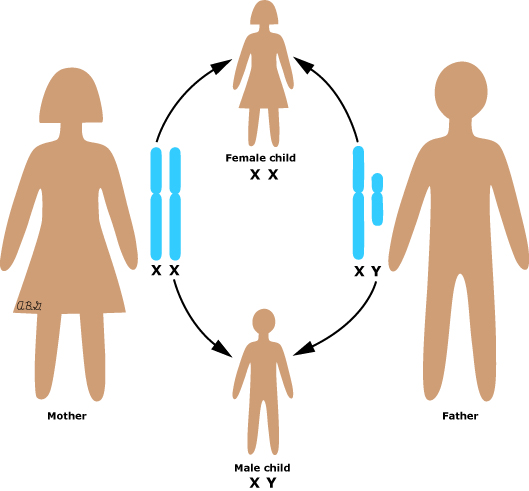
GENDER OF A BABY
-
The gender of a baby is determined by the sperm’s sex chromosomes.
-
Each cell in the human body contains 23 pairs of chromosomes.
-
The sex chromosomes are made up of a pair of chromosomes.
-
Males have XY chromosomes, while females have XX chromosomes.
-
If an X-chromosome-carrying sperm fertilises an X-chromosome ovum, it is a female baby.
-
If a Y chromosome sperm fertilises an X chromosome ovum, it is a male baby.
-
As a result, males determine the gender of a newborn.
SEXUAL AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH
-
Eating a well-balanced diet: proteins, carbohydrates, fats, and vitamins in necessary proportions is essential during adolescence.
-
Keeping your private regions clean to prevent bacterial infections is essential.
-
Bathing is required regularly as the activity of sweat glands increases, releasing foul odours from the body.
-
Physical activity aids in keeping the body fit and healthy by releasing a lot of sweat.
-
Drugs are addictive and harm the body (can help spread AIDS).
Source: Chapter-10.pmd (ncert.nic.in)
]]>