CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Revision Notes
Chapter 14: Natural Resouces Revision Notes
- The only planet on which life exists is Earth. Land, water, and air are the earth’s resources. Fossil fuels, sunshine, wind, minerals, and other resources are examples of other resources. Living entities in the ecosystem are referred to as biotic factors.
- The non-living or abiotic components of the biosphere are air, water, and soil.
AIR QUALITY AND POLLUTION
- A planet’s atmosphere is a gaseous layer that surrounds it.
- By volume, atmospheric air contains 78 percent nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% additional gases.
Role of Atmosphere
- The earth’s average temperature is maintained by the atmosphere.
- It avoids a dramatic spike in temperature during the day by slowing the departure of heat into outer space at night.
Air Pollution
- Pollutants, organic molecules, and other hazardous compounds are introduced into the Earth’s atmosphere, resulting in air pollution.
- Combustion of fuel, smoke from industry, burning crackers, and other man-made sources are among the causes.
- Forest fires, volcanoes, and other natural disasters are examples of natural sources.
- Respiratory disorders, global warming, acid rain, and other effects
Ozone Layer
- The ozone layer is a thin layer of the Earth’s atmosphere that acts as a barrier above the stratosphere and absorbs the most ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun.
- In comparison to other portions of the atmosphere, the ozone layer has high quantities of ozone (O3).
Depletion of the ozone layer
- Depletion of the ozone layer occurs when the quantity of ozone in the stratosphere decreases, allowing more UV radiation to reach the earth’s surface.
CFCs
- CFC stands for chlorofluorocarbon, which is an organic molecule made up of carbon, chlorine, and fluorine.
Greenhouse effect
- The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon that happens when the Earth’s atmosphere contains greenhouse gases that trap the solar energy.
- Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), ozone (O3), chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor (H2O).
WATER: A NATURAL SOURCE
- Water is responsible for two-thirds of our body weight and maintains a constant body temperature.
- It’s also employed for agricultural, domestic, and industrial uses, among other things.
- Water distribution on Earth: Only 3% of the water on the surface is fresh, with the rest 97% residing in the ocean.
Water Pollution
- Water pollution is the pollution of fresh and clean water bodies because of contaminants being let out directly or indirectly into them without being properly treated.
- Water contamination is mostly caused by urbanisation.
- Industries\sAgriculture
- Social and Religious Practices
- Water withdrawal and drying of water bodies
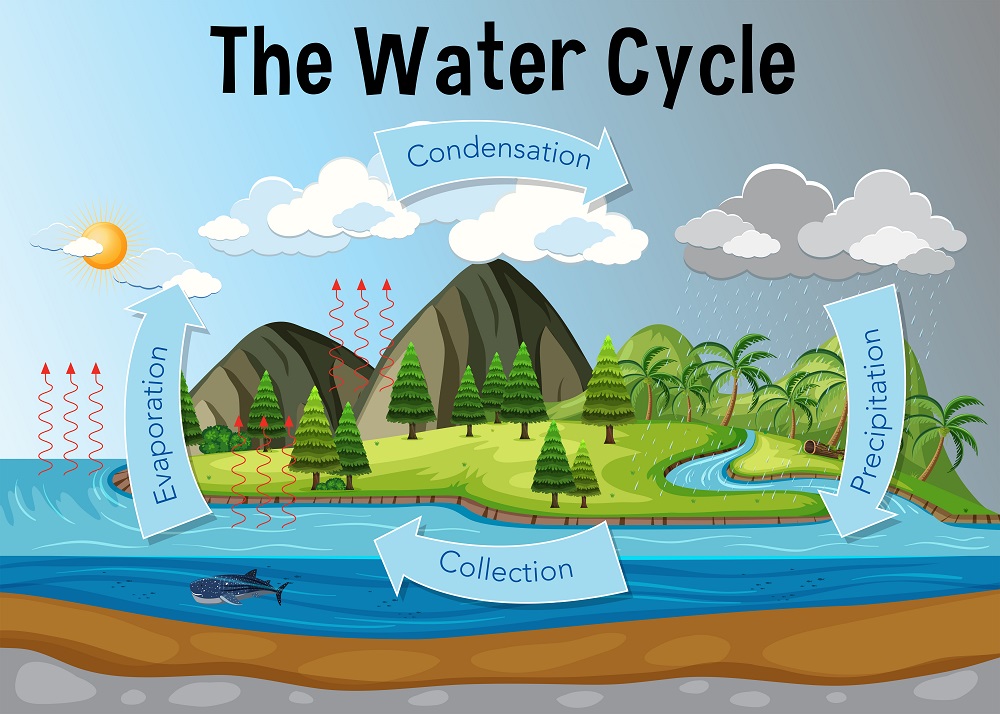
Water cycle
- The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle, is the continual transfer of water from the ground to the atmosphere and back.
Evaporation and Transpiration
- Transpiration is the biological process through which water is lost from the aerial sections of plants called stomata in the form of water vapour.
- Evaporation is the transformation of a liquid or solid into a vapour.
SOIL
Soil and its formation
- Soil is the top layer of the Earth’s crust, generated through ongoing mountain weathering. Parent material, time, climate, and organisms are all factors that contribute to soil formation.
Composition of the soil
- Soil is made up of a variety of organic materials.
- Minerals, inorganic matter, water, and air are the four fundamental components of soil.
- Clay, loam, silt, sand, and more soil types exist.
Humus
- The top organic layer, known as humus, is formed by the decomposition of organic elements such as dry leaves, twigs, and plant and animal remnants.
- It performs a vital function in enhancing the soil’s fertility.
Soil pollution
- Soil pollution is defined as the adding of hazardous or poisonous compounds to the soil that renders it unproductive.
- Fertilizers, pesticides, industrial wastes, oil spills, acid rain, and other pollutants are the main sources of soil contamination.
Soil erosion
- One type of soil deterioration is soil erosion.
- Soil erosion is mostly caused by flowing water, precipitation, and the wind.
- This results in the loss of topsoil, as well as a reduction in agricultural production capacity.
BIO-GEO-CHEMICAL CYCLE
- The natural cycle or paths via which necessary stuff is circulated across an ecosystem’s biotic and abiotic components.
- Biological Chemical + Geological Process = Biogeochemical
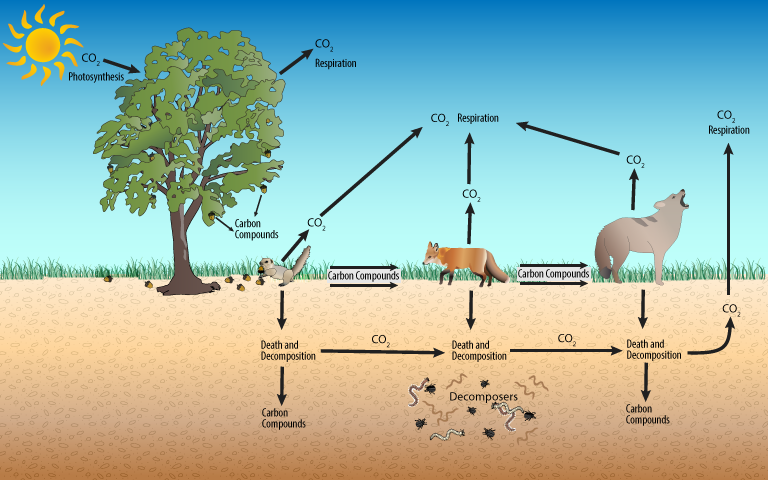
Carbon cycle
- The Carbon Cycle is the movement and change of carbon between living organisms and the environment.
Nitrogen Cycle
- The nitrogen cycle is the process of recycling and repurposing nitrogen in various forms in order to fulfil the needs of diverse environmental activities.
Oxygen Cycle
- It is a biological activity that aids in the preservation of oxygen levels.
- Photosynthesis is a biological process in which plants use sunlight and energy to manufacture their nourishment.