Cell Structure Study Guide – Part 2
Lesson Objectives
- Understand the overall cell structure and the structure of each cell organelle that constitutes the cell.
- Learn about the functions of each organelle in a cell.
Cytoskeleton
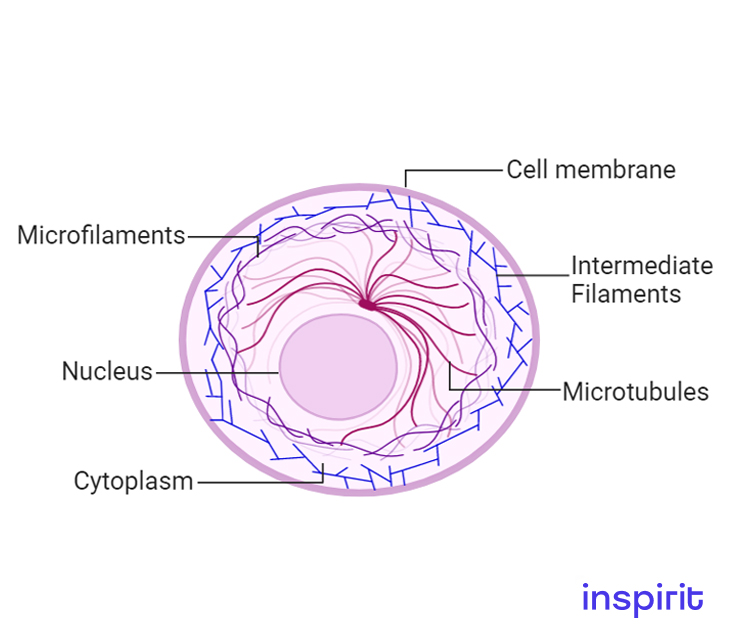
Structure
- Various proteins of long chain amino acids form a fibrous network called the cytoskeleton.
Function
- Its primary function is to create a network organizing the cell components and maintaining the cell shape.
Microtubules
Structure
- They are straight and hollow cylindrical filaments found only in eukaryotic cells and are formed from 13-15 sub-filament strands of tubulin ( a special protein).
- They are present all over in the cytoplasm of the animal cell.
Function
- They contribute to the rigid and organized part of the cell’s cytoskeleton, thereby giving a cell its particular shape.
- They also help in the formation of spindle fibers during mitotic cell division.
Centrioles
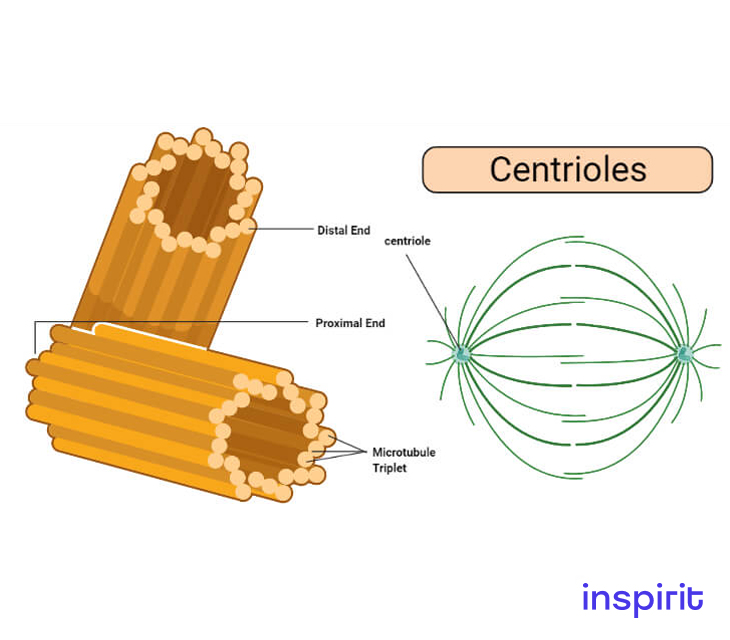
Structure
- It is a tiny structure made up of 9 sets of microtubules placed in groups of three. Hence, they are triplet microtubules.
- These triplet microtubules are held together by proteins, giving the centriole its shape.
Function
- The centriole microtubules are involved in the transportation of substances that are linked together with a glycoprotein to any cell location. The glycoprotein linkage acts as a signaling unit to move specific proteins.
Peroxisome
Structure
These are quite common micro-bodies in the cytoplasm of the cell. They are also spherically shaped and bound by a membrane.
Function
- They help in lipid metabolism.
- They are involved in moving hydrogen atoms from several oxygen molecules to produce hydrogen peroxide. Therefore, they neutralize body poisons like alcohol and help in chemical detoxification.
Cilia and Flagella
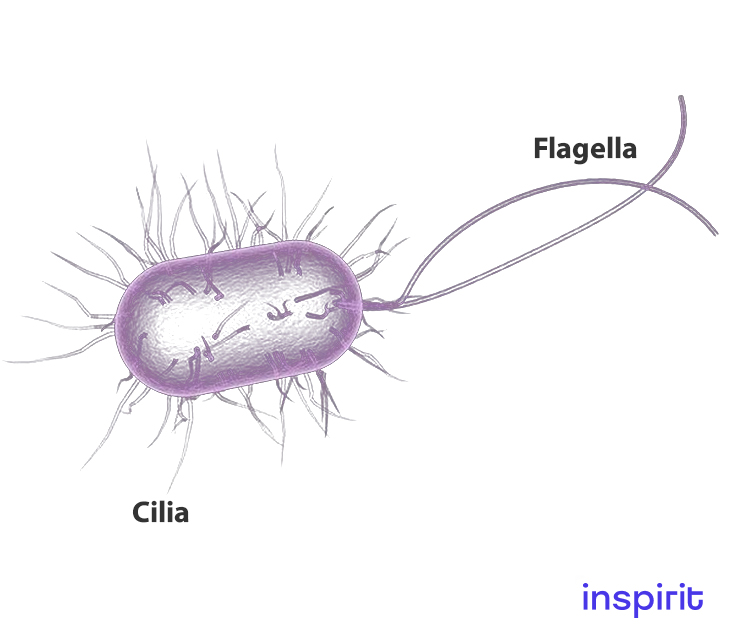
Structure
- They are made of strands of filaments that have partial and complete microtubules extending into projections. Partial microtubules do not extend to the tip of the cilium while the complete microtubules extend to the tip of the cilium.
Function
- Cilia helps move fluids away from immobile cells.
- Cilia are also involved in the movement of surface particles particularly on the epithelial lining of the nostrils, and in moving mucus over the surface of the cell.
Endosome
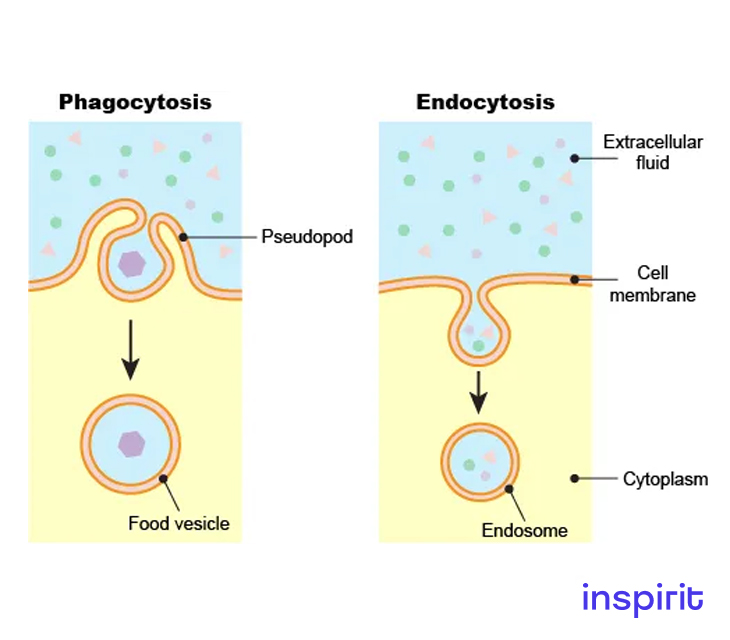
Structure
These organelles are bound to the cell membrane and are membranous.
Function
- It is involved in the folding of the plasma membrane. This folding helps in the diffusion of molecules through the extracellular fluids.
- It also helps remove waste materials from the cell by endocytic processes such as exocytosis and phagocytosis.
Vacuoles
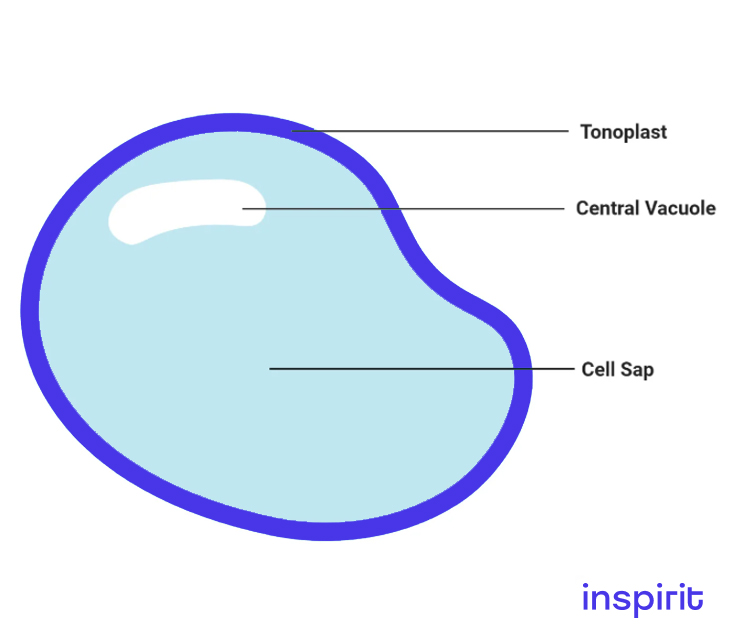
Structure
- These are membrane-bound structures present in the cytoplasm of the cell.
Function
- Food, water, and carbohydrates are stored in these vacuoles in the form of sugars and waste materials.
Microvilli
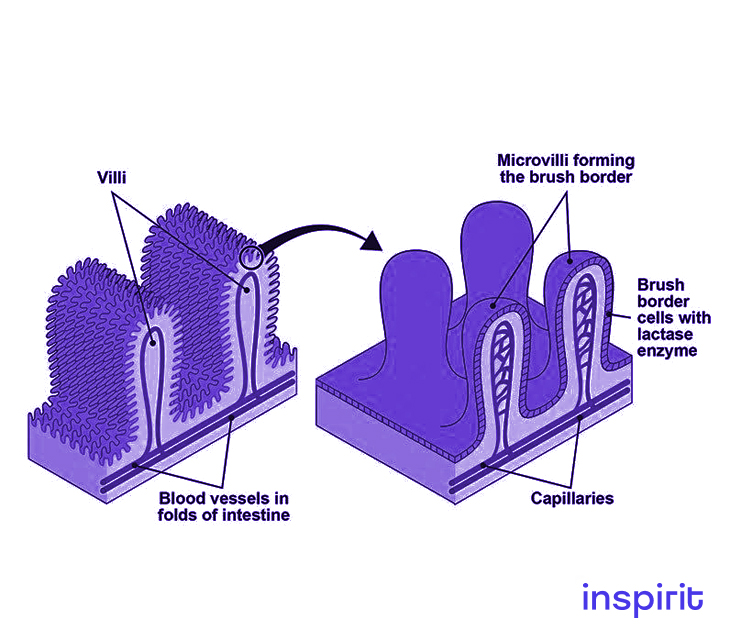
Structure
- Accessory proteins of the actin filaments form surface protrusions called microvilli. They are formed on the surface of the cell membrane.
Function
- They aid in increasing the surface area for the absorption of digested food and water in the small intestine.
Key Questions
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about the Cell Structure! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun 😎
]]>