Leaves Study Guide
Introduction to Leaves
Any flattened and green outgrowths from the stems of vascular plants are called leaves. They are the first and primary sites of photosynthesis, the process by which plants manufacture food and energy to help nourish and sustain themselves.
What is a Leaf?
Leaves are the lateral appendages of the vascular plant systems. Collectively, they’re called foliages. Leaves are usually found above the ground and they serve as a key part of photosynthesis.
In most leaves, the important photosynthetic tissue is located on the upper side, or lamina, of the leaves. They are generally green in color due to chlorophyll, which absorbs light from the sun and helps in photosynthesis. A leaf that is light in color is called a variegated leaf.

Leaf Structure
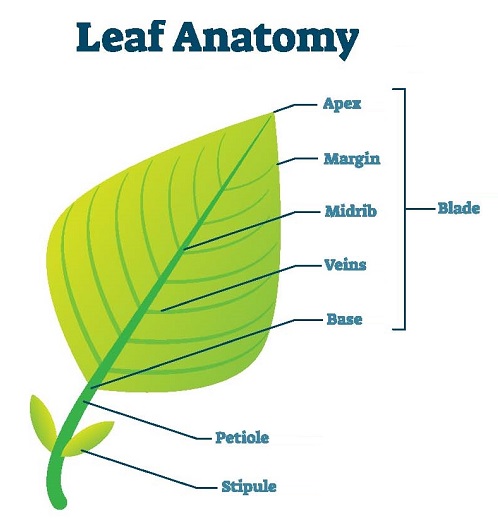
Leaves have many different shapes and sizes. Most of them are flat, broad, and green in color. Some shapes are like needles, as in the case of conifers. Shapes of leaves are adapted to suit a plant’s habitat and maximize the process of photosynthesis. Some of the basic structures of leaves are the leaf blade, margin, veins, midrib, base, petioles, and stipules.
-
Leaf blade: The broad portions of leaves, also called the lamina.
-
Margin: The edge of the leaf. They can be smooth, parted, lobed, or rough.
-
Veins: Tissue bundles that help support leaves and transport mineral nutrients.
-
Midrib: The main central vein that arises from secondary veins.
-
Base: The area of a leaf that connects the leaf blades to the petioles.
-
Petioles: Thin stalks that attach the leaf to the stems of plants.
-
Stipules: Leaf-like structures found at the base of a leaf.
Characteristic Features of Leaves
-
Leaves are always born at the nodes of stems.
-
The growth of leaves is generally limited.
-
Leaves do not possess any apical buds.
-
They are not related to the lateral part of stems.
-
Leaves are exogenous in origin.
-
They develop from the primordium of growing apex of swollen leaves.
-
Leaves do not have any regular growing points.
Types of Leaves
Leaves are classified into various types depending on various criteria, including position on stem, division of blades, and shape. Let’s go over them below.
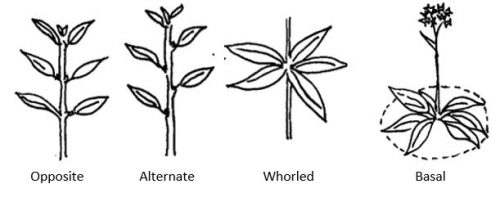
Position on Stem
-
Whorled Leaves: Leaves that form a ring around the edge of the stem and generally develop in groups.
-
Opposite Leaves: Leaves that are paired together at one node on the stem that grow in opposing directions.
-
Alternate Leaves: Leaves that each grow from a single node that alternate direction along the stem.
-
Basal Leaves: Leaves that grow near the base of plants that sometimes make contact with the ground.
Division of Blades
-
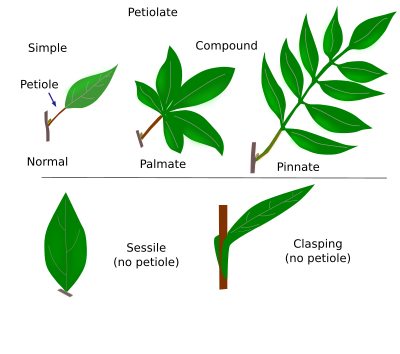
Simple leaves: They have a blade that does not possess a split. In some plants, the divisions do not reach the main veins.
-
Compound leaves: They are also called divided leaves. They possess a blade that completely divides the main vein and is joined by a single petiole.
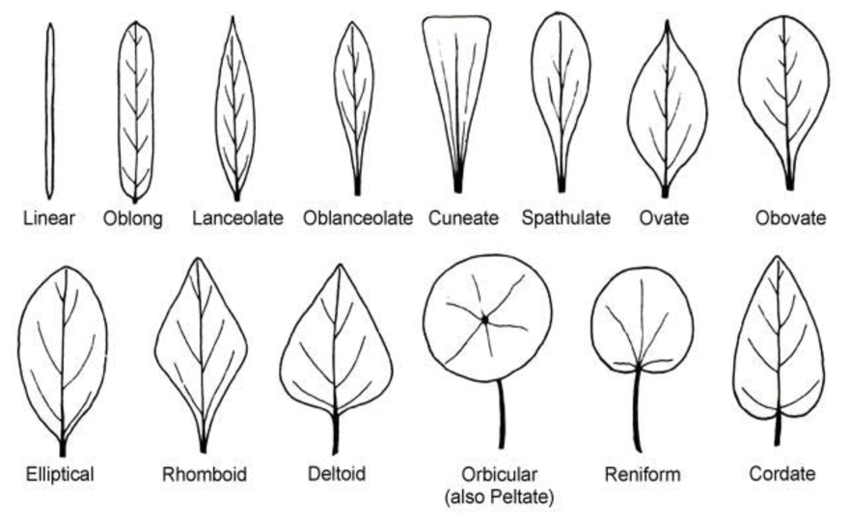
Leaf Shape
-
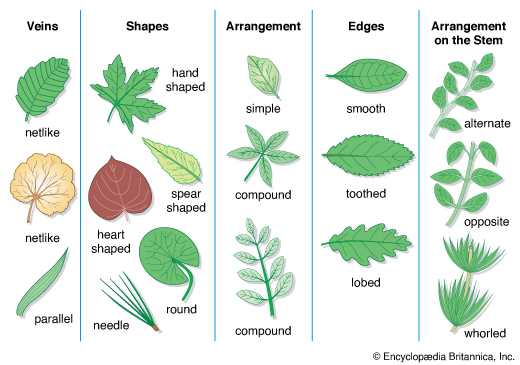
Elliptical Sheet: A simple leaf with a shape that resembles an elongated ellipsis (example: spicebush).
-
Lanceolate Leaves: Leafs with blades that show characteristic shapes of a spearhead or an arrowhead. They have wider bases and sharp, narrow points (example: tall ragwort).
-
Acicular Leaves: Slender, narrow, and needle-like leaves (example: conifers).
-
Oval Blades: Leaves that are similar to elliptical leaves but are wider at bases and have a sharp point (example: elm tree).
-
Sagittate Blade: Leaves with a central point and two other openings to the sides (example: longbarb arrowhead).
-
Linear Leaves: Long, straight, and narrow leaves that look like ribbons and have regular edges (example: grass).
Other Leaf Types
-
Cordiform: Heart-shaped and the base is the widest.
-
Ensiform: Shape very similar to a sword
-
Spatulate: Spoon or spatula-shaped.
-
Hastada: Shaped like halberds.
-
Falcada: Flattened and curved.
-
Lancolada: Spear shaped.
Leaf Functions
Leaves perform the following functions:
-
Transpiration: Transpiration releases the excess water from plants into the atmosphere through the stomatal opening in the leaves.
-
Storage: Leaves like those found on succulents store water and nutrients.
-
Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis is the primary function of leaves. During this process, they convert water, sunlight, and CO2 into glucose with the presence of chlorophyll.
-
Guttation: Guttation helps remove excess water from the xylem at the leaf edges when the stomata are closed.
-
Defense: Some leaves are modified into spines that help them protect the plant from being damaged or eaten by animals.
Conclusion
-
Any flattened and green outgrowths from stems of vascular plants are called leaves.
-
Basic structures in a leaf are leaf blade, margin, veins, midrib, base, petioles, and stipules.
-
Leaves are classified into various types depending on their location on the stem, the division of blades, and leaf shapes.
-
Leaves perform transpiration, storage, photosynthesis, guttation, and defense.
FAQs
1. Which spelling is correct, leafs or leaves?
- “Leaves” is the appropriate spelling.
2. What are the 2 types of leaves based on division of blades?
- Two types of leaves are simple and compound leaves.
3. What are the main functions of leaves?
- The main functions of leaves are Transpiration, Guttation, Photosynthesis, Defense, and Storage.
4. What is the plural of foliage?
- “Foliages” is the plural of foliage.
5. Is maple a leaf?
- A maple leaf is the characteristic leaf of maple trees.
6. What is the plural of a leaf?
- “Leaves” is the plural of leaf.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Leaves! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
]]>