Bird – Structure, and Function Study Guide
Introduction
Birds are vertebrates, having a vertebral column and a skull. These warm-blooded animals have feathers, and their forelimbs are modified to form wings. Birds were the last vertebrates to evolve, but they increased and diversified in no time. Today they are the most numerous vertebrates on the earth (number & species). We have birds as tiny as 5 cm and as large as 9 feet surviving strongly.
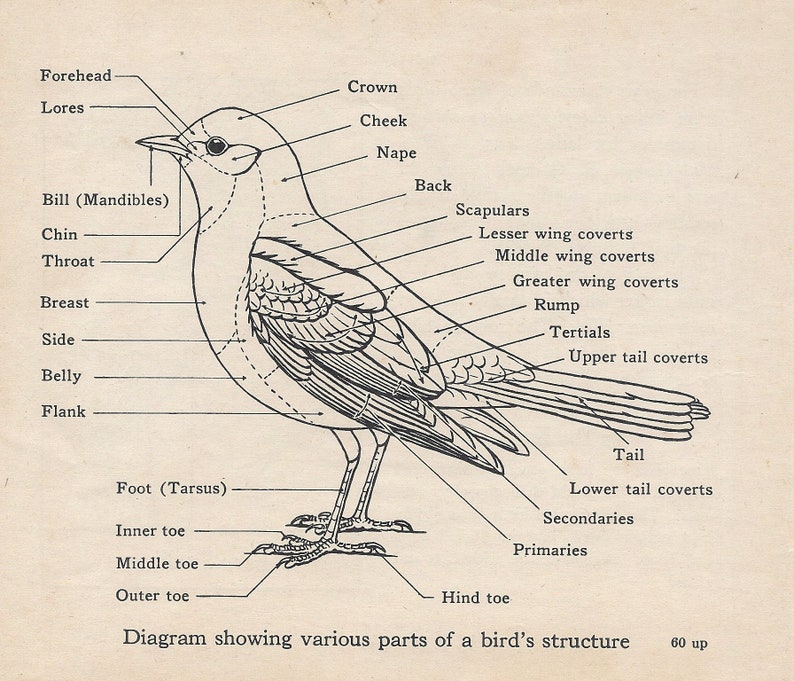
Bird Structure
Birds have different anatomy. Somebody parts of birds are different than that of other animals. This is a result of several structural adaptations, making them more sustainable.
Wings
-
The most distinctive feature of the birds is their wings. Wings are their modified front legs. To move these wings, birds have very strong and large muscles in their chest. These muscles contribute to about 35% of the bird’s weight.
-
The main function of the bird’s wings is to provide them with the ability to fly. All birds have two wings, but that does not imply flying. The terrestrial birds which can’t fly have very small wings, and some birds like penguins use them as flippers.
Feathers
-
Feathers are a chief distinguishing feature of birds. Bird’s feathers are made up of keratin and have many functions. The most important being helping them to fly and to insulate their body.
-
There are two types of feathers for each function- Flight feathers and Down feathers. Flight feathers are stiff, long, and waterproof. Without adding weight, they help in flight, whereas the down feathers are short and fluffy and help insulate the body by trapping the air next to the bird’s skin.
Beak
-
Like other vertebrates, birds don’t have dense and heavy jaws and teeth. Instead, they have lightweight keratin beaks. It is an example of structural adaptation for flight in birds, and the flight would not have been possible if birds had heavy jaws.
-
The shapes and sizes of beaks vary with different birds, but they all have a similar underlying structure. The main function of the beak is to eat, preen, feed their young ones, collect things, attack their prey and defend themselves.
Feet
Feet of the bird are generally covered with scales.There are predominantly two major types of feet present in the birds.
-
Three toes are directed towards the front and one at the back. They are very powerful, with sharp, curved talons used to catch, hold and kill prey. Owls, Hawks, Eagles have such feet.
-
The other common feet structure have a web between three front toes, providing an expanded surface for swimming and walking on soft surfaces. These kinds of feet are generally seen in seagulls, ducks, etc.
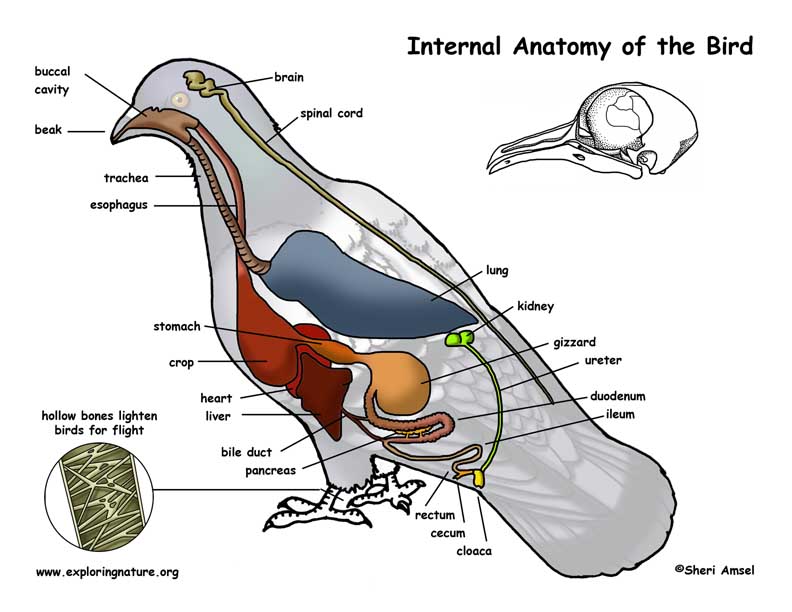
Organs of the bird
The body of a bird has to be very light to stay aloft. Thus, nature has provided them with such an organ system that serves the purpose, and all the bird’s body parts contribute towards that.
Bones
- The bones of a bird are generally very lightweight and filled with air. A bird’s skeleton is very lightweight because of the thin and hollow bones and thus does not add to the bird’s overall weight, hence helping in their flight.
Air Sacs
- The flying muscles of birds need a constant oxygen supply. To ensure this, nature has provided them with air sacs that store inhaled air and push it to the lungs, hence, keeping the lungs always filled with oxygenated air.
Heart
- Birds have a large four-chambered heart. The size of their heart is 0.2%- 2.4 % of their body weight, which is quite high compared to other mammals. Birds also have relatively high heart rates, which help them to keep a constant flow of oxygenated blood to muscles and other tissues.
Digestive tract
- The two important parts of a bird’s digestive tract are- Crop & Gizzard. The crop is a sac-like part used to keep and moisten food before digestion, whereas Gizzard is used to store the swallowed stones, which help digest the food more quickly.
Brain
- Generally, birds have a big brain compared to their body size, which accounts for their intelligent and complex behavior. Ravens & Crows are said to have more intelligence than many mammals.
Kidneys
- The bird’s kidneys lie on the underside of the pelvis.
Urinary Bladder
- Birds do not have a bladder, and urine is secreted with the feces.
Sight
- Birds have excellent sight, making up for their low sense of smell.
Conclusion
-
Birds have evolved, and with the help of many structural adaptations, today they are the most occurring (in numbers & species) and sustainable vertebrates on the earth.
-
The organ system of the birds is highly adaptive to their flight. The skeletal system, circulatory system, respiratory system are such that they aid the bird’s flight.
-
Birds have a relatively larger heart and a large brain, and their intelligence is found more than many mammals.
FAQs
1. What structures help the birds get and eat their enemies?
Ans. The bird’s beak and feet are the two structures that help them get and eat their enemies. Every bird has a distinctive, adaptive beak and feet structure according to its habits and habitats.
2. What is the structure of a bird’s bones?
Ans. Bird’s bones are hollow and thin, filled with air.
3. What are the structural adaptations in birds?
Ans. The major structural adaptations in birds areBeaks instead of heavy jaws and teeth.Feathers instead of heavy fur. Feathers are lightweight, streamlined, and adjustable for flight control.Pneumatized (hollow) bones keep the body of birds lightweight.
4. What is a bird structure?
Ans. Birds have a light skeletal system and light yet strong muscles. They have a circulatory and respiratory system that gives them a high metabolic rates and abundant oxygen supply to help them with their flight.
5. What are 5 examples of structural adaptations?
Ans. The 5 examples of structural adaptations in birds are-
- Webbed feet
- Beaks
- Hollow bones
- Sharp eyesight
- Feathers
6. What is the function of a bird’s wing structure?
Ans. The function of a bird’s wing structure is similar to that of human arms. Wings in birds adapt to flight, and they are the modified front legs. With the help of strong chest muscles, birds use their wings to fly.
7. What is the function of a bird’s beak?
Ans. The main function of a bird’s beak is to eat and preen along with gathering & catching prey, feeding their young ones, picking materials for the construction of their nests, and sometimes to defend themselves.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Birds- Structure, and Function! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! We promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
Sources
-
Bird Structure and Function https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/12.19/primary/lesson/bird-structure-and-function-bio/ accessed on 6 Dec 2021
-
Bird anatomy https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bird_anatomy accessed on 6 Dec 2021
-
Bird Classification https://www.britannica.com/animal/bird-animal/Classification accessed on 6 Dec 2021