Hydrocarbons Study Guide
INTRODUCTION
“It’s hard to imagine a life without hydrocarbons”: this statement may sound a bit exaggerated, but believe it or not, it’s not. Petroleum and natural gas are mostly made up of hydrocarbons. They’re used as fuels, lubricants, and raw materials for polymers, fibres, solvents, explosives, and chemical products. Our lives are surrounded by hydrocarbons. But before we discuss the properties and uses of hydrocarbons in daily life, let’s try to understand what exactly a hydrocarbon is.
WHAT IS A HYDROCARBON?
Hydrocarbons are a group of organic chemicals made up only of the atoms carbon (C) and hydrogen (H). The carbon atoms bind together to create the compound’s structure, and the hydrogen atoms adhere to it in various ways.
Based on the amount of bonds between their carbon atoms, hydrocarbons are divided into two categories: saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
TYPES OF HYDROCARBONS:
SATURATED HYDROCARBONS:
Single bonds hold carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen atoms together in these molecules. These single-bonded hydrocarbons are the simplest. There are no double or triple bonds in these hydrocarbons.
UNSATURATED HYDROCARBON:
A double, or triple bond connecting carbon-carbon atoms make up these molecules. The unsaturated hydrocarbons are the alkenes with one double bond and the alkynes with one triple bond in its carbon chain.
PROPERTIES OF HYDROCARBONS:
- The size of hydrocarbons varies widely, affecting qualities like melting and boiling temperatures.
- Hydrocarbons can be gases, liquids, or solids at room temperature.
- They are nonpolar and therefore are not soluble in water in most cases.
USES OF HYDROCARBONS:
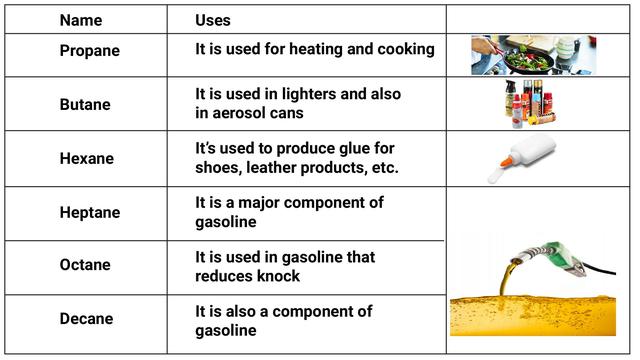
- Fuels made of hydrocarbons are commonly utilized. LPG (liquefied petroleum gas) and CNG (compressed natural gas) are examples.
- They’re employed in the production of polymers like polyethylene and polystyrene.
- As a precursor material, these organic compounds are used to produce pharmaceuticals and colors.
- They are used as lubricants and grease.
CONCLUSION:
- Hydrocarbons are a group of organic chemicals made up only of the atoms carbon and hydrogen.
- Based on the amount of bonds between their carbon atoms, hydrocarbons are divided into two categories: saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
- Hydrocarbons are used for several purposes, the most essential as fuel.
FAQs:
1. What property do all hydrocarbons have?
Hydrocarbons are nonpolar, meaning that their particles do not have oppositely charged ends. As a result, they are not soluble in water, even though water is a polar substance. Hydrocarbons, in general, tend to repel water.
2. What determines the chemical and physical properties of hydrocarbons?
The size of the particles influences the melting and boiling temperatures of hydrocarbon molecules. As a result, certain hydrocarbons are gases at room temperature, while some are liquids or solids.
3. What are the 4 types of hydrocarbons?
One or more core carbon atoms are surrounded by hydrogen atoms in a branching or chain-like configuration in hydrocarbon molecules. Hydrocarbons are divided into four categories: Alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, and aromatic hydrocarbons.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Hydrocarbons! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
SOURCES:
- Hydrocarbon. https://www.ck12.org/c/chemistry/hydrocarbon/lesson/Hydrocarbons-MS-PS/. Accessed 22 Feb 2022.
- Hydrocarbons. https://www.vedantu.com/iit-jee/hydrocarbons. Accessed 22 Feb 2022.
- Hydrocarbons. https://byjus.com/jee/hydrocarbons/. Accessed 22 Feb 2022.