Structural and Geometric Isomers Study Guide
INTRODUCTION
Chemical compound C₄H₁₀ has boiling points of 260 K and 272 K. But how can a compound have 2 different boiling points?It is because C₄H₁₀ exists in different isomeric forms. Let’s find out what are structural isomers and what are stereoisomers!
WHAT ARE ISOMERS?
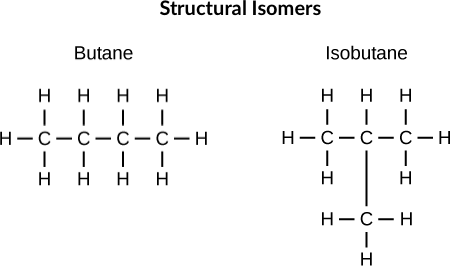
The compounds with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms are called isomers, like in the case of C₄H₁₀. Let’s understand what we mean by different arrangements! C₄H₁₀, when arranged linearly, forms n-butane, which has a boiling point of 272 K, while when arranged with the branch, the form is called iso-butane, which has a boiling point of 260 K. This means that even though the molecular formula of isomers is the same, their physical properties such as melting point, boiling point, solubility etc. and chemical properties can differ.
TYPES OF ISOMERS:
Let’s explore the types of isomers mentioned above.
STRUCTURAL ISOMERS:
Compounds with the same molecular formula, but the atoms bonded differently, are called structural isomers. The above-explained compounds n-butane and iso-butane are examples of structural isomers.
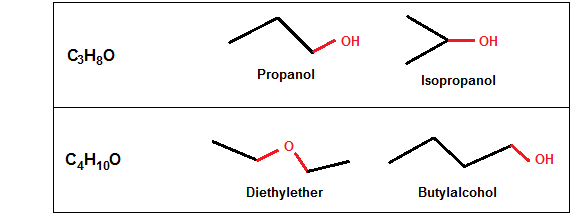
In this example, just the position of OH has generated two different structural isomers.
In this example, the number of atoms is the same, but the arrangement is different, which is responsible for making isomers with two different functional groups.
GEOMETRIC ISOMERS:
Isomers with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms in space are geometric isomers. Geometrical isomers have different physical and chemical properties.
The interesting fact about geometric isomers is that their groups cannot interchange their positions independently. Let’s understand with the help of an example:
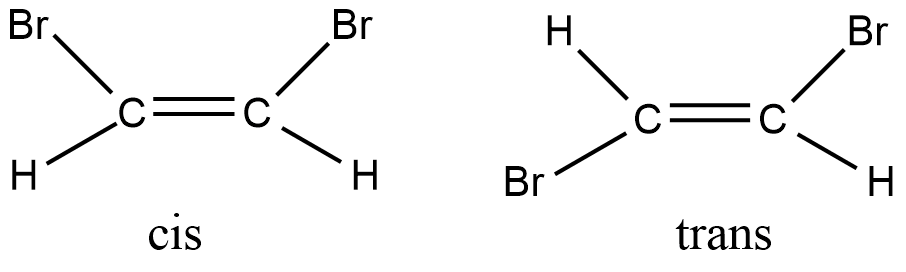
In cis-dibromoethene, the Br groups are on the same side, while in trans-dibromoethene, the Br groups are on opposite sides. But the cis and trans dibromoethene cannot interchange into one another on their own, which is why they are geometrical isomers.
For isomers to be geometrical, the rotation around the double bond has to be restricted along with different arrangements of groups in space. Since geometrical isomers are arranged differently in space, they are also called stereoisomers.
CONCLUSION:
- Isomers: Compounds with the same molecular formula but different arrangements.
- Structural Isomers: Compounds with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms in bonding.
- Geometric Isomers: Compounds with the same molecular formula but different arrangement of atoms in space and restricted rotation.
FAQs:
1. Which isomer is trans, and which one is cis?
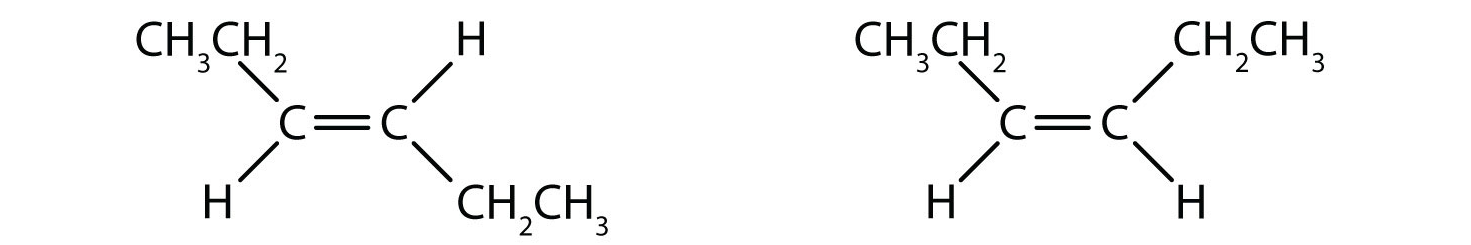
The one with -CH₂CH₃ groups on the different side is a trans isomer.The other one with -CH₂CH₃ groups on the same side is a cis isomer.
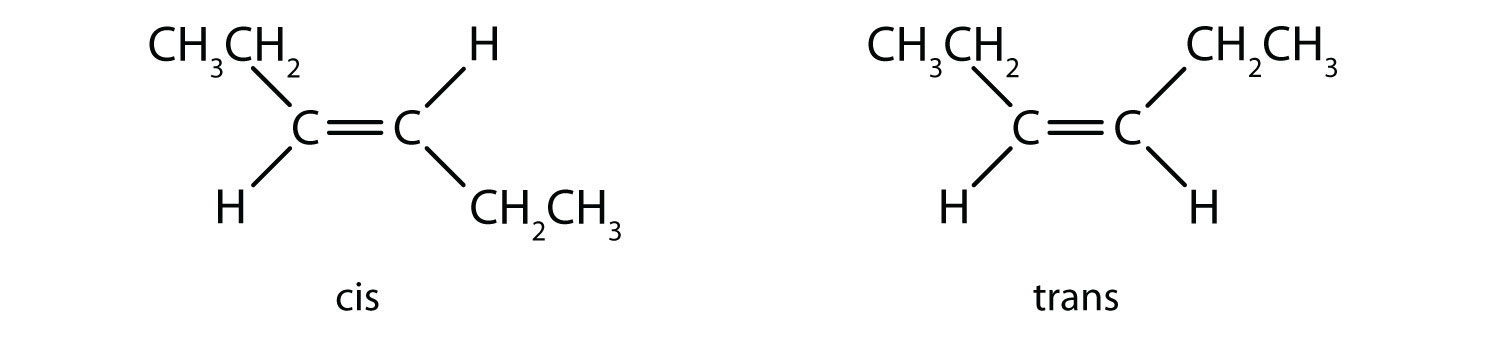
2. Can geometric isomers show rotation around double bonds?
No, geometric isomers have restricted rotation around the double bond.
3. The following compounds are structural or geometric isomers?
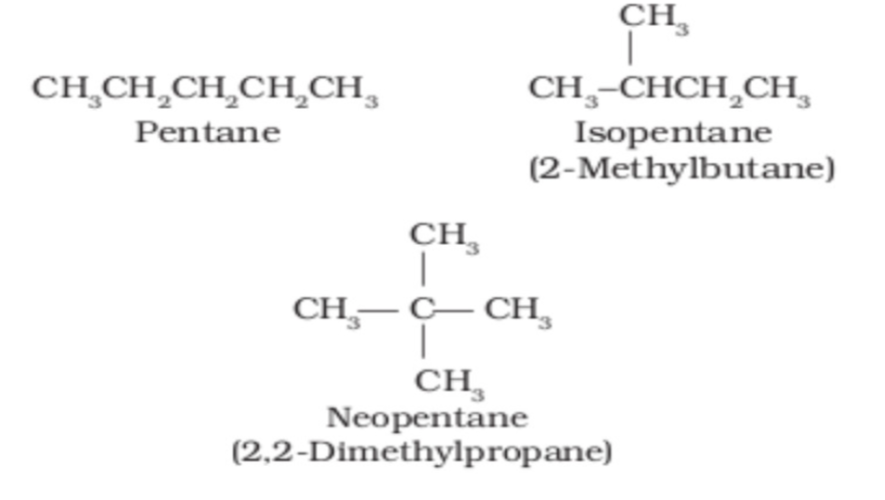
The compounds given are structural isomers as they have different arrangements of atoms in bonding.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about the Structural and geometrical isomers! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our app to experience our fun VR classrooms – we promise it makes studying much more fun! 😎
SOURCES:
- Structural Isomers and Stereoisoemrs: https://www.ck12.org/c/chemistry/structural-isomers-and-stereoisomers/lesson/Isomers-CHEM/. Accessed 24 Feb 2022.
- Hydrocarbon Structures and Isomers. Khan Academy, 2018, www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/properties-of-carbon/hydrocarbon-structures-and-functional-groups/a/hydrocarbon-structures-and-isomers.