The Atom Study Guide
INTRODUCTION
Whenever you are cooking, you have to chop the vegetables in order to make the recipe. We can’t use the whole vegetable in cooking. Imagine drinking soup, and a whole cauliflower is floating in it. That’s not very desirable. Chopping is basically dividing a given substance into its finer constituents. How about we take any random element, and we start diving in? How far can we go? Is there a point after which the element will not be divisible further? The answer is yes. That point will be reached when we reach the atom. An atom is the smallest unit into which matter can be split.
WHAT IS AN ATOM?
- An element’s fundamental unit is the atom.
- An atom is a unit of matter that cannot be subdivided further by chemical processes.
- Protons, neutrons, and electrons make up a typical atom.
- An atom is the smallest particle of an element into which matter may be split while retaining an element’s characteristic qualities.
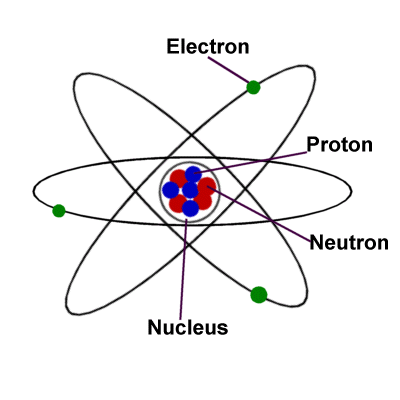
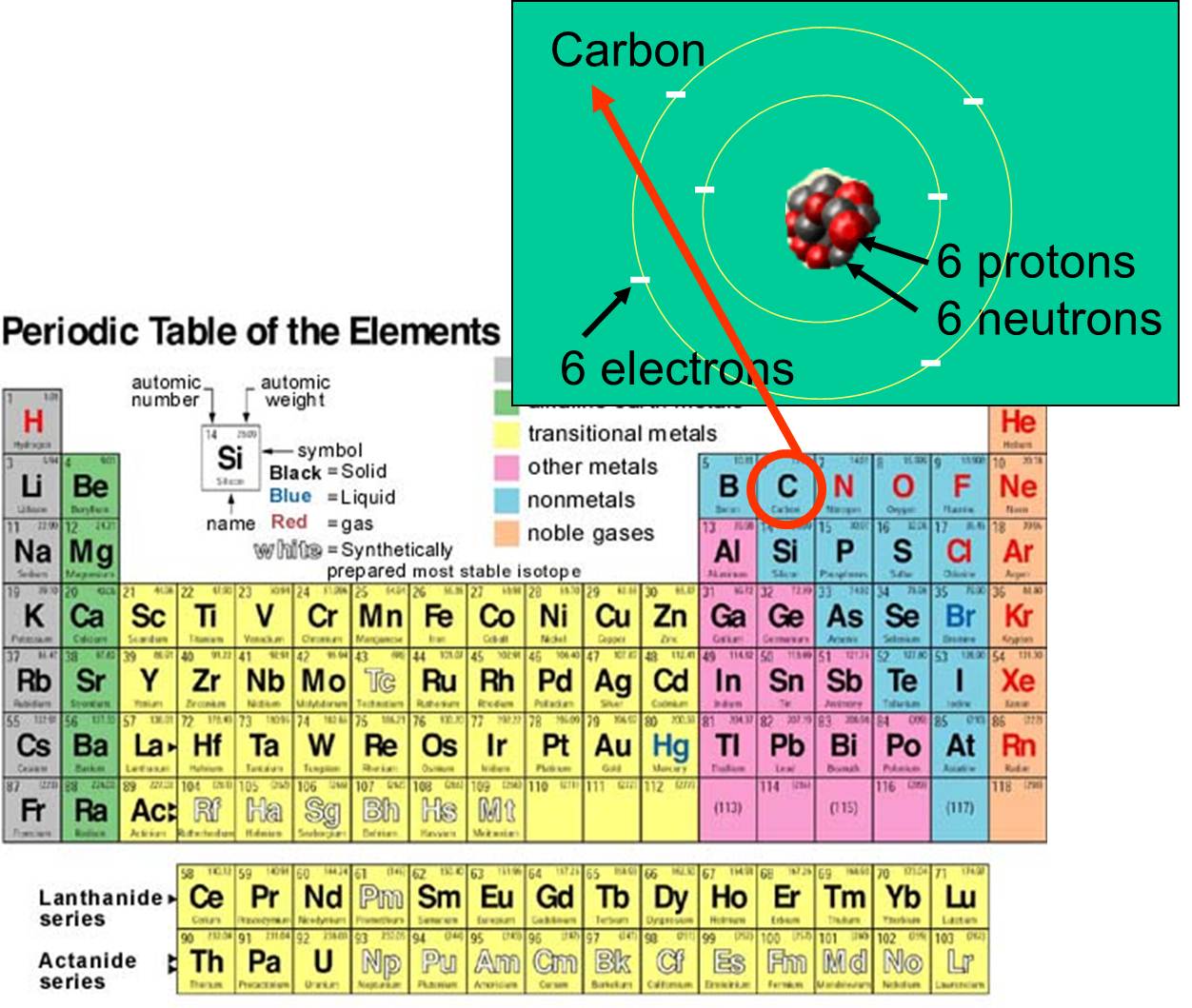
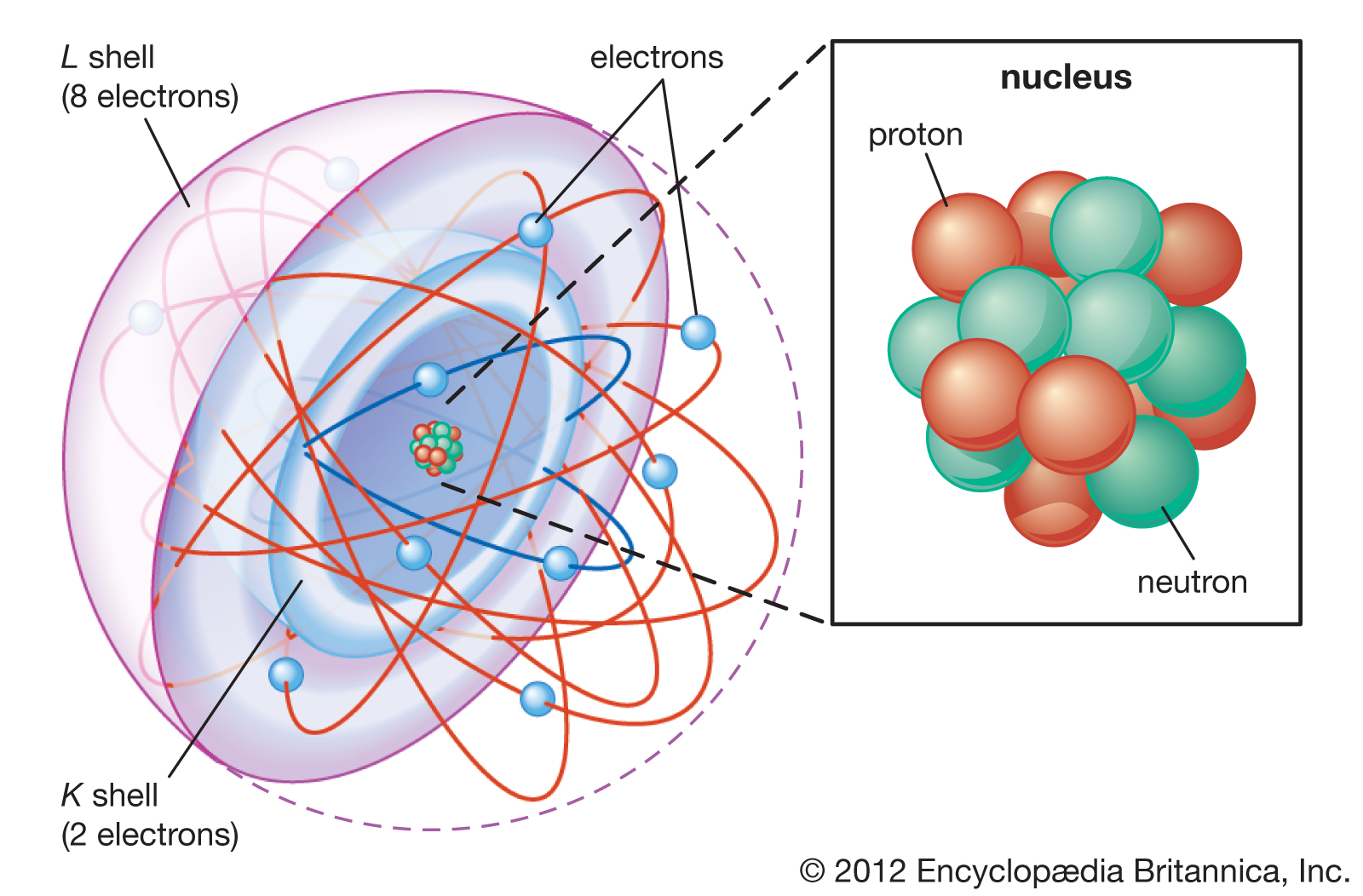
STRUCTURE OF ATOM
- The majority of the atom is made up of empty space.
- The rest is made up of a cloud of negatively charged electrons surrounding a positively charged nucleus of protons and neutrons.
- The nucleus is small and dense compared to electrons, which are the tiniest charged particles in existence.
- Electrostatic forces attract electrons to every positive charge.
- Electrostatic forces bind electrons to the nucleus in an atom.
THE ATOMIC THEORY OF DEMOCRITUS
But if we cannot see atoms, then how did we get to know about them?
- Democritus, a Greek philosopher, named the atoms ‘atomos,’ which literally means indivisible.
- He believed that atoms were uniform, strong, hard, indivisible, and indestructible.
- Different shapes and sizes of atoms give rise to different elements.
- Atoms move through empty space until they are stopped.
- The amazing part about this theory is that the idea of the existence of atoms was given when it could not be proved as it was just a theoretical concept back then.
- After 4200 years only, it could be proved.
SUBATOMIC PARTICLES
- A subatomic particle, also known as an elementary particle, is one of many self-contained components of matter or energy that make up all matter.
- Subatomic particles encompass electrons, which are negatively charged, nearly massless particles, as well as the heavier structural components of the atom’s small but compact nucleus, positively charged protons, and electrically neutral neutrons.
DISCOVERY OF SUBATOMIC PARTICLES
The electron was discovered in 1897, and the atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911, proving that the atom is made up of a cloud of electrons encircling a tiny yet hefty core. It was discovered in the early 1930s that the nucleus is made up of even smaller particles termed protons and neutrons.
CONCLUSION:
- An element’s fundamental unit is the atom.
- An atom is a unit of matter that cannot be subdivided further by chemical processes.
- The majority of the atom is made up of empty space.
- The rest is made up of a cloud of negatively charged electrons surrounding a positively charged nucleus of protons and neutrons.
FAQs:
1. What are the atoms in an element?
The number of protons and electrons in an atom is always the same, and the combination of protons and neutrons is typically the same as well. A proton added to an atom creates a new element, but a neutron added to the same atom creates an isotope or heavier form of that atom.
2. How many types of atoms are in one element?
A material composed completely of one sort of atom is known as an element. The element hydrogen, for example, is made up of atoms with only one proton and one electron.
3. Who said atoms of one element are the same?
According to Dalton, every atom of an element, like gold, is just like every other atom of that element. He also pointed out that the atoms of one element are not the same as those of all other elements.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Atoms! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun VR classrooms – we promise it makes studying much more fun! 😎
SOURCES
- Subatomic Particles: https://www.britannica.com/science/subatomic-particle/Elementary-particles accessed 26 Feb 2022
- Atomic mass and Isotopes: https://www.britannica.com/science/atom/Atomic-mass-and-isotopes accessed 26 Feb 2022
- What is an Atom? https://www.thoughtco.com/what-is-an-atom-603816 accessed 26 Feb 2022
-
- Atom: https://www.ck12.org/c/chemistry/atom/lesson/Atoms-MS-PS/ accessed 26 Feb 2022