Introduction to Natural Selection Study Guide
Introduction:
Natural selection is a process in which an organism adapts to its surroundings by preferentially reproducing changes in its genotype or genetic composition. It is a key idea in evolutionary theory. It is frequently referred to as the survival of the fittest, and Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace proposed it. Darwin chose the name as a metaphor for artificial selection (selective breeding).
Causes of Natural Selection
- Natural selection occurs when organisms with desirable characteristics are more likely to reproduce. They pass on these characteristics to the next generation in this way. This mechanism helps organisms to adapt to their surroundings throughout time. This is because the population’s frequency of genes for desirable qualities rises.
- Because of variances in inheritance, members of a species are not all alike (genetics). This is true even when the children are siblings.
- Some of these distinctions may make one creature better suited to living and reproducing in a given environment than others. When this creature reproduces, the genes that provide it an advantage are passed down to its offspring.
- Some adaptations have a long lifespan and are beneficial in various environments. A good example is the development of bird wings. Others are present as long as the environment remains unchanged. Another creature could perform better if the environment changes enough.
Process of natural selection impacting population:
Natural selection explains why living creatures evolve to have the architecture, functions, and behaviors over time. This is how it works:
- All living organisms have such high fertility that their population might continue to grow at an exponential rate indefinitely.
- In reality, population size does not expand to this amount. The figures are mostly consistent.
- There is a scarcity of food and other supplies. As a result, there is a battle for food and resources.
- There are no two people who are the same. As a result, they don’t have the same survival and reproduction chances.
- A large portion of this variance is inherited. Through their DNA, parents pass on their characteristics to their offspring.
- Those that live and reproduce generate the next generation. The comparative fit between the people and the environment in which they dwell causes the elimination. The population has more beneficial genetic variations and fewer negative ones over many generations. Natural selection is essentially an elimination process.
- In other words, Evolutionary fitness is measured by reproductive success.
Examples of natural selection:
1. Antibiotic Resistance:
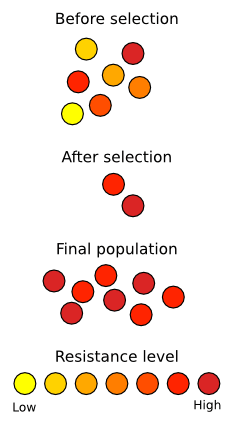
The evolution of antibiotic resistance in bacteria is a well-known example of natural selection at the action. Antibiotics have been used to treat bacterial infections since Alexander Fleming discovered penicillin in 1928. As a result of mutations, natural populations of bacteria include significant variation in their genetic makeup among their large numbers of individual individuals. Most bacteria die fast when exposed to antibiotics, but others contain changes that make them somewhat less vulnerable. These microbes will survive medication if only exposed to antibiotics for a brief time. Natural selection may be seen in removing individuals who have no resistance. A colony of antibiotic-resistant microbes will evolve given sufficient time and frequent exposure to the antibiotic. This results in an evolutionary arms race, often known as co-evolution, wherein bacteria produce strains less vulnerable to antibiotics while medical researchers discover new drugs that can kill them. Different, stronger antibiotics are routinely used in response efforts; nevertheless, new strains of MRSA have recently arisen that are immune to even these medications. Pesticide resistance in plants and insects and malarial quinine resistance are related situations.
2. Mimicry:
Another instance: Certain innocuous insects can be mistaken for harmful or foul-tasting insects. Mimicry evolves as a result of the best mimics surviving longer. They live longer to have more progeny than the less talented mimics. In the species, the genes of the better mimics grow more frequently. Mimic organisms become closer to their models over time. This is the method of evolution through natural selection.
The monarch butterfly (left) and the viceroy butterfly (right) both have the same warning design (right). The Monarch butterfly has a horrible taste and is toxic. However, the Viceroy butterfly does not taste bad and is not hazardous. This is a case of Batesian mimicry in action. A bird that has tasted a Monarch will shun Viceroys.
Continue your learning journey
Learn about Mendelian Genetics
Learn about Non-Mendelian Genetics
Learn about Population Genetics
Conclusion:
- Natural selection is a key idea in evolutionary theory. It is frequently referred to as the survival of the fittest, and Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace proposed it.
- Natural selection explains why living creatures evolve to have the architecture, functions, and behaviors over time.
- The evolution of antibiotic resistance in bacteria is a well-known example of natural selection at the action.
FAQs:
1. How do you explain natural selection?
Natural selection is the adaptation and modification of populations of living organisms. Individuals in a population are inherently varied, which means they differ in certain respects. Because of this variety, some people have more suited to their surroundings than others.
2. What are the three types of natural selection?
The three types of natural selection: stabilizing, directional, and diversifying. Stabilizing, directional, and diversifying selection reduce, shift, or enhance a population’s genetic diversity.
3. What are the five main principles of natural selection?
Natural selection is a basic mechanism that affects the evolution of populations of living organisms through time. It’s so simple that it can be broken down into five simple processes, abbreviated as VISTA: Variation, Inheritance, Selection, Time, and Adaptation.
4. What are the 4 components of natural selection examples?
- Variation: Organism (within populations) inherited individual diversity in appearance, and behavior is inherited by organisms (within populations).
- Individual diversity in appearance and behavior is inherited by organisms (within populations). Some characteristics are continuously handed down from one generation to the next.
- High rate of Population growth
- Differential reproduction and survival
5. How do you explain natural selection?
Natural selection occurs when organisms best suited to their environment survive and pass on their genetic features to succeeding generations in increasing numbers. Simultaneously, less suited species fail to live or reproduce faster and are pushed out of the ecosystem.
6. What are some key facts about natural selection?
- Traits are frequently inherited. Many qualities are inherited or handed down from parent to child in living beings.
- More offspring are produced who can thrive. Organisms can produce more offspring than their surroundings can support.
- Heritable qualities in offspring vary.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Introduction to Natural Selection! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
Sources:
- Natural Selection. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/5.21/primary/lesson/natural-selection-bio/. Accessed 20 Dec, 2021.
- Understanding Natural Selection: Essential Concepts and Common Misconceptions. https://evolution-outreach.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1007/s12052-009-0128-1. Accessed 20 Dec, 2021.
- Natural Selection. https://www.nationalgeographic.org/encyclopedia/natural-selection/. Accessed 20 Dec, 2021.