Origin of Species Study Guide
Introduction:
The concept of variation is central to Darwin’s hypothesis, and it claims that the many features and adaptations that distinguish species also explain how species originated and diverged over time. Variations in organisms can be seen within domesticated species and across species in the wild world.
Origin of species
Darwin’s theory consisted of two main points;
1) Diverse groups of animals evolve from one or a few common ancestors.
2) The mechanism by which this evolution takes place is natural selection.
According to Darwin, heredity is the mechanism that keeps variations alive by passing qualities down from parents to children. What matters to Darwin about these variances is how they enable species to adapt and thrive in the natural environment.
He presents various instances of variations that demonstrate the amazing adaptations that allow animals to live in their native settings, such as the woodpecker’s beak for gathering insects, the bat’s wings for flying, the porpoise’s paddles for swimming, and so on.
Darwin theorizes that minute changes within a single species, such as differences in organism size, form, and color, are connected to more significant variances found between species. His theory of evolution describes how changes in the environment lead to the emergence of new species.
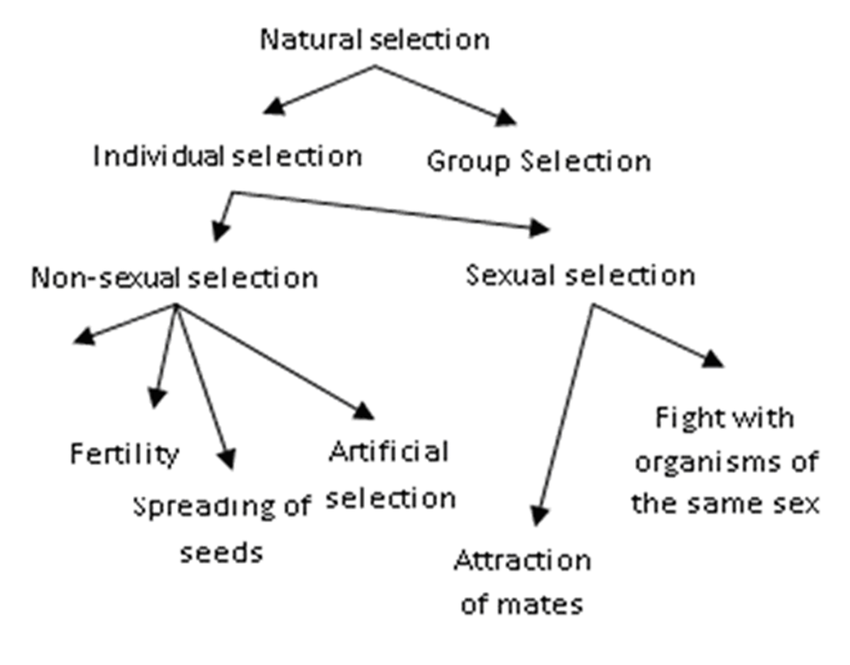
Importance of natural selection
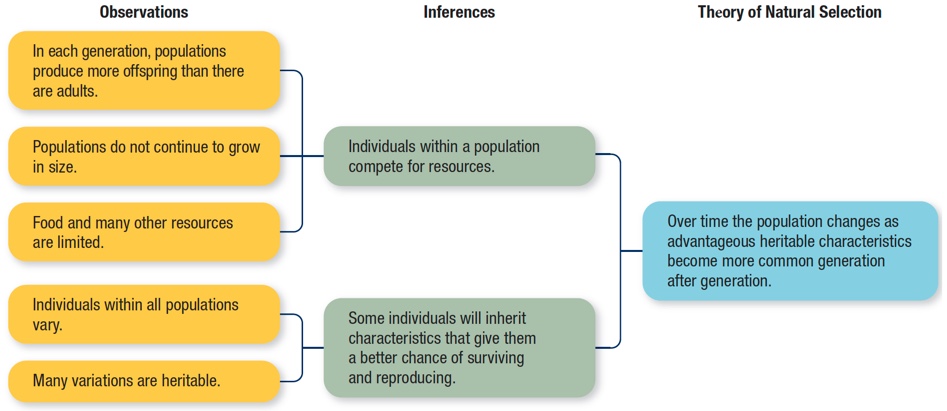
Natural selection is an important part of Darwin’s theory because it explains the link between variety and species progression. Darwin contends that the prospect of endless population expansion is prevented by the boundaries of geography and natural resources, which will not allow an infinite number of creatures to exist, based on Thomas Malthus’s premise of exponential population growth.
Due to scarcity of food, water, shelter, and other resources, species must participate in a “fight for life,” resulting in survival competition. So, what determines which species will survive and which will perish? This is when “natural selection” enters the picture.
Darwin claims that creatures with “advantageous variations”—variations that enable them to adapt to their environment more effectively than other species—are more likely to survive. These favorable mutations will be handed down to the progeny of the organisms through inheritance.
- Natural selection will eventually allow species most adapted to their habitats to live and thrive. At the same time, those that lack these favorable adaptations will lose the battle for survival and go extinct.
- Natural selection is the mechanism that leads to Darwin’s phrase for evolution, “descent with modification.” Organisms will continue to produce offspring with differences, some of which are beneficial and others are not.
- Beneficial variants are naturally selected and passed down across generations, resulting in creatures with these favorable variations diverging from the original species and eventually forming their species.
- As a result of continuous change and divergence, a branching evolutionary scheme emerges, in which new species continuously branch out from old ones. The “branches” aid biologists in determining the point at which various species are connected, allowing them to trace later species back to an initial parent species. According to Darwin, existing categorization systems devised by naturalists already reveal these links between species.
- As a result, Darwin’s theory of descent with modification explains why many species appear to be so similar: they either developed from one another or evolved from a common parent species.
- Darwin also tries to explain how species differences drive natural selection and the emergence of new species, and Darwin’s hypothesis relies heavily on geographical isolation.
- Because all species are thought to have evolved from one or a few original beings, Darwin theorizes that species require mechanisms of transportation to travel across geographical locations around the planet.
- Barriers like seas and mountain ranges limit creatures’ capacity to migrate. The few that do have a significant impact in determining the development of species on islands and in geographically isolated places.
- Geographic isolation explains why islands have so many distinct species and why species are distributed so widely across continents.
- After laying out the major ideas of his hypothesis in the first few chapters of Origin of the Species, Darwin spends the rest of the book defending his theory and giving comprehensive instances of how natural selection works.
Conclusion:
- Natural selection is evolution’s last force. This is the evolutionary process that Charles Darwin described the origin of species, and it is the image that most people think of when they think of evolution.
- The concept of variation is central to Darwin’s hypothesis, and it claims that the many features and adaptations that distinguish species also explain how species originated and diverged over time.
- According to Darwin, heredity is the mechanism that keeps variations alive by passing qualities down from parents to children.
- Natural selection is an important part of Darwin’s theory because it explains the link between variety and species progression.
FAQs:
1. What is Darwin’s theory of the origin of species?
Darwin’s theory claims that all creatures emerge and develop due to the natural selection of minute, hereditary differences that improve an individual’s capacity to compete, live and reproduce.
2. What were the main points of the origin of species?
Darwin’s thesis included two key points:
1) Various groups of creatures develop from one or a few common ancestors
2) Natural selection is the process by which this evolution occurs
3. What did the origin of species explain?
It claims that the many features and adaptations that distinguish species also explain how species originated and diverged over time. Variations in organisms can be seen within domesticated species and across species in the wild world.
4. Why was the origin of species banned?
The most frequently banned science book is Charles Darwin’s On the Origin of Species, initially published in 1859 and prohibited in 1895 for opposing Christian beliefs.
5. What was Owen’s belief about the origin of species?
Owen, an ardent opponent of Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection, accepted that evolution took place but felt it was more complicated than Darwin’s On the Origin of Species suggested.
6. Why was the origin of species so important?
Darwin’s book popularized the scientific concept of natural selection, which states that populations evolve over generations. The book offered evidence that life’s variety emerged from common descent through a branching evolutionary pattern.
7. What were Darwin’s 5 points?
Darwinism, or Darwin’s theory of evolution, is separated into five parts: “evolution as such,” “common descent,” “gradualism,” “population speciation,” and “natural selection.”
8. Is the origin of species easy to read?
The origin is quite easy to find. It is not technical; it was written for any educated person to read. While the style may not suit your taste, the book is not difficult to read. As a result, you may get a lot out of the origin without performing any preliminary research.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about the Origin of Species! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
Sources:
- Origin of Specieshttps://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/5.22/primary/lesson/origin-of-species-bio/ Accessed on 7 Dec 2021
- Origin of Specieshttps://www.britannica.com/biography/Charles-Darwin/On-the-Origin-of-Species Accessed on 7 Dec 2021
- On the Origin of Species https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/On_the_Origin_of_Species Accessed on 7 Dec 2021
- Darwin: From Origin of Species to Descent of Manhttps://plato.stanford.edu/entries/origin-descent/ Accessed on 7 Dec 2021