CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Revision Notes
Chapter 11: Work and Energy Revision Notes
Work Done
- The product of the amount of the force applied on the body and the displacement in the direction of the force is defined as work done on an item. F.s = W
- The work done is 0 if a force acting on a body causes no displacement. For instance, pushing against a wall.
ENERGY
- The ability to work is defined as energy. It has the same unit of measurement as work.
- Joule (Nm) or Kgm2s2 is the SI unit of energy or work.
- Light, heat, chemical, electrical, and mechanical energy are all examples of energy.
Forms of energy
(i) Kinetic energy (K.E)
(ii) Potential energy (P.E)
Kinetic energy
- The energy of motion is referred to as kinetic energy.
- The energy possessed by a body as a result of its motion, which can occur at any level from the atomic to that of a whole organism.
- This is not an exhaustive list of kinetic energy examples.
- Atomic motion is referred to as electrical motion.
- The movement of waves (electromagnetic or radiant)
- The movement of molecules (thermal or heat)
- Object movement is referred to as motion.
- Sound is the movement of waves through space.
- Thermal/heat energy is commonly referred to as “internal energy” by engineers, while “kinetic energy” is only used in the context of motion.
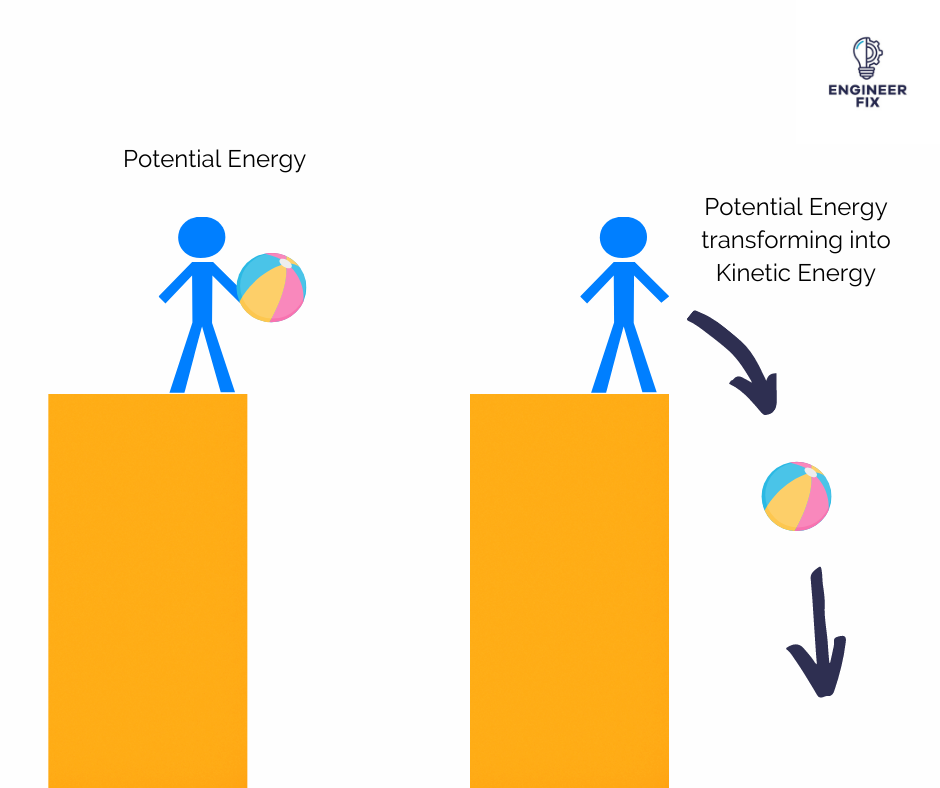
Potential Energy (Stored energy or gravitational energy)
-
The ability to perform labour as a result of one’s position or arrangement.
-
As a result of its location or elastic source, an item can store energy.
-
At the highest HEIGHT, potential energy is at its highest.
-
The conversion of one kind of energy into another is known as energy transformation.
The following are some examples of energy transformation:
-
Food is ingested and turned into motion in order to participate in sports or take an exam.
-
Radiant – Plants absorb sunlight and transform it into energy for growth.
-
Electrical – When energy is supplied to an oven, it is transformed to thermal energy, which is used to heat our meals.
Types of Energy
- There are two types of energy sources: renewable and nonrenewable.
- A renewable energy source is one that is renewed continuously and quickly by natural processes.
The following are some examples of renewable energy sources:
• Biomass — The utilisation of a living or formerly alive creature as a source of energy.
• Hydropower is the energy generated by the flow of water.
• Geothermal – Using heat from deep under the Earth or from the atmosphere near seas to heat homes and other structures.
• Wind turbines — wind turbines are used to generate power.
Solar– The use of the sun as a heat source, such as to heat a room within a house, and so on.
Conversion of Energy
- Fossil fuels are a type of energy that comes from the decomposition Chemical, heat, mechanical, and electrical energy are all sources of energy.
- Solar cells are made up of solar cells that absorb sunlight and convert it into electricity.
- Turbines powered by wind Mechanical Electrical
- When an item is lifted to a greater height, its energy rises.
- The ground level or zero level determines the potential energy of an item at a height.
POWER
- Work is completed or energy is consumed at a certain rate.
- The fundamental unit of Power is **Watt (P=w/t). **
- One joule of labour per second equals one watt.
Types of Power
- Electrical power is a type of energy that is used to perform tasks.
- Mechanical power is a type of energy that is used to perform tasks (linear, rotary)
- Fluid power is based on the transmission of energy between liquids (hydraulic) and gases (gaseous) (pneumatic)
- The rate at which we consume energy is referred to as power.
- Work or Energy / Time = Power