Symbiosis Study Guide
Introduction:
Some organisms in both the plant and animal kingdom evolved relationships that benefited one or both. Whether it is a defense against other predators or an adaptation that helps thrive by offering what the other lacks, the organisms live in a symbiotic relationship.
What is symbiosis?
A symbiotic relationship is between two dissimilar organisms in which the interaction benefits one or both the organisms. These benefits would not exist if the organisms lived alone or without the symbiotic association. The symbiotic relationship could be positive, negative, or neutral.
Types of Symbiotic Relationships
The symbiotic definition had undergone changes from when it only included mutualism, and now it also includes parasitism and predation. Here are some of the well-known symbiosis types:
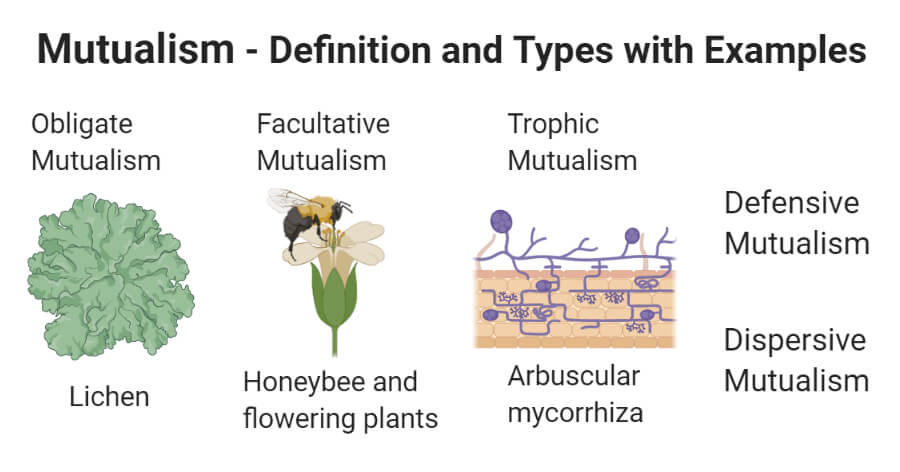
Mutualism
Mutualism has been the symbiosis definition of biology for the most part until recently. It is the symbiotic relationship where two different species coexist to benefit both organisms. There are plenty of examples of mutualism, with the goby fish and shrimp being one of the well-known ones.
The two organisms spend most of their time together, and the shrimp has a very poor vision that makes it an easy target for predators. However, the shrimp has a burrow-digging skill which enables both the fish and shrimp to take shelter. Whenever a predator approaches, the fish warns the shrimp by touch.
Commensalism
Commensalism in symbiosis meaning is when one of the organisms benefits from the symbiotic relationship while the other remains unaffected.
A well-known example is sharks and remoras. The remoras are fish that attach themselves to the shark’s bodies through a suction disk. The shark has no benefit, but the remoras get protection from predators, food, and increased potential to mate. Other examples include hermit crabs that take shelter in the shells of dead snails.
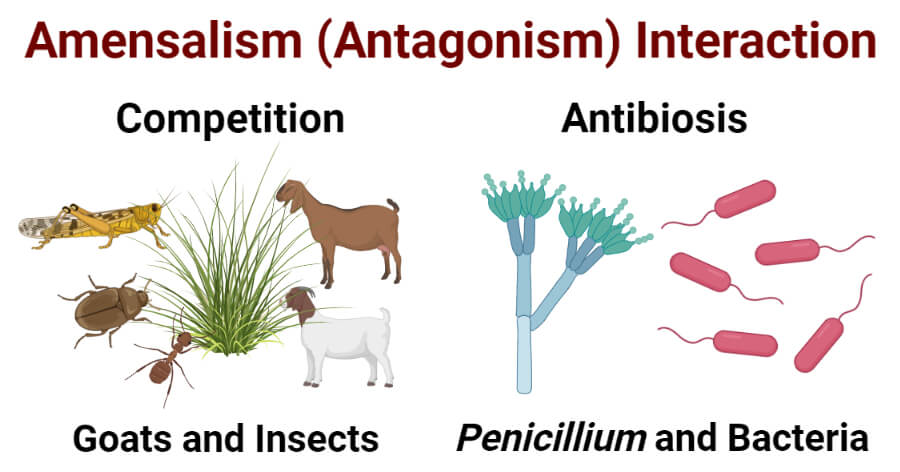
Amensalism
In this type of symbiotic relationship, one of the organisms negatively affects the other while the second one has a negligible effect on the first. A good example is mussels and infaunal species that live in them. Since both are filter feeders, the infaunal species gain while mussels lose nutrition.
One more example can be found in plants that grow in close proximity, and the shorter plant growing in the shade of the taller one loses the sunlight needed for photosynthesis.
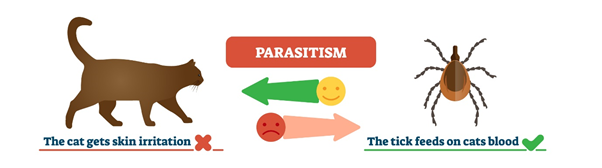
Parasitism
A parasitic relationship is where one organism benefits while the other is affected negatively. It is thought that about two-thirds of the species on Earth are parasites. Parasitic organisms come in many different sizes, and some are only parasites during the early stages of their life. Generally, parasites live on the host’s skin or inside its body.
Examples include tapeworms, roundworms, fleas, ticks, and mosquitoes. Most organisms have parasitic species that feed on them. Although parasites negatively affect their host, they rarely kill them.
Predation
The symbiotic relationship between predator and host is where the predator kills the host instead of causing harm for a long time. One example is the relationship between hermit crabs and sea anemones. Sea anemones ride on the shells of the hermit crabs. During periods of starvation, the hermit crab feeds on the sea anemones.
What are some symbiosis examples?
Here are some examples of symbiosis:
Clownfish and anemones: One of the most studied symbiotic relationships in the animal kingdom. The sea anemones give nutrients and protection to the clownfish, while the clownfish provide nitrogen, carbon, and ventilation to the host.
Oxpeckers and host mammals: Oxpeckers are birds that feed on parasitic organisms that live on larger mammals. The mammals benefit by getting the parasites removed.
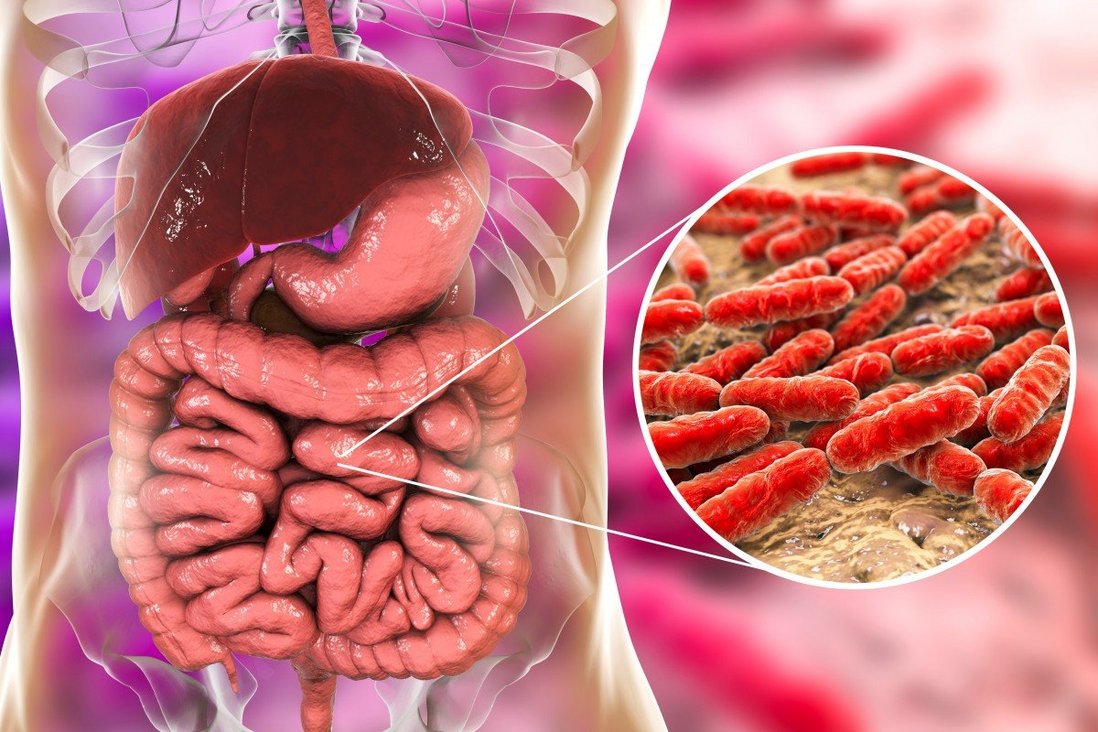
Human gut bacteria: The gut bacteria in humans help break down different types of food while they get a suitable environment to thrive.
Rhizobium-legume symbiosis: This is a symbiotic relationship between nitrogen fixation bacteria and legume plants. The bacteria give nitrogen while the plants offer resources.
Conclusion:
- A close relationship between two different organisms from which at least one of the organisms benefits is called symbiosis.
- Symbiosis can be broadly classified into mutualism, commensalism, amensalism, parasitism, and predation.
FAQs:
1. What is a symbiosis in biology?
To define symbiosis, it can be said that it is the relationship between two dissimilar organisms in which one or both benefit from the relationship.
2. What is an example of symbiosis in biology?
Many types of mammals in the wild such as buffalos, zebras, and elephants, allow the oxpecker birds to cling or sit on them. The birds eat the parasitic ticks, and the animal benefits by having the ticks removed.
3. What are 5 examples of symbiosis?
The 5 examples of symbiosis are Mutualism, Commensalism, Amensalism, Parasitism, and Predation.
4. What is symbiosis and give 2 examples?
Symbiosis meaning is that two different organisms have a relationship where both are benefited; one is benefited while the other is neutral, or one is benefited while the other is harmed.
Examples:
- Goby fish safeguards the nearly blind pistol shrimp from predators. The pistol shrimp build tunnels for both to live inside.
- Remoras attach themselves to sharks to get protection from predators and also food. The sharks have no benefit from these fishes.
5. What are the 3 types of symbiosis?
The 3 most commonly known symbiosis are Mutualism, Commensalism, and Amensalism.
6. What do you understand by symbiosis?
It can be learned from symbiotic organisms that two different types of organisms can coexist in such as way as to benefit one another. However, symbiosis can also become parasitic with two-thirds of organisms on the planet, where one benefits and the other loses.
7. What is the difference between symbiosis and mutualism?
Mutualism is a symbiosis where two organisms mutually benefit from the relationship. Although the term symbiosis was mostly associated with mutualism, it is now a broader concept that incorporates parasitism and predation.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Symbiosis! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App and check out our awesome VR room for this guide – we promise it makes studying much more fun 😎
Sources:
- Symbiosis. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/6.15/primary/lesson/symbiosis-bio/ Accessed on 6 Dec 2021
- Symbiotic Relationships. https://www.ck12.org/book/cbse_biology_book_class_xii/section/17.2/ Accessed on 6 Dec 2021
- Symbiosis. https://www.biologyonline.com/dictionary/symbiosis Accessed on 6 Dec 2021
- Symbiosis Definition. https://byjus.com/biology/symbiosis-definition/ Accessed on 6 Dec 2021
- Parasitic Symbiosis Definition. https://byjus.com/biology/parasites-symbiosis/ Accessed on 6 Dec 2021
- Symbiosis. https://courses.lumenlearning.com/wm-biology2/chapter/symbiosis/ Accessed on 6 Dec 2021