Roots Study Guide
Introduction
The roots of the plants are vascular parts of plants that are found underground. They are the first parts of the plant to grow. Their important functions include water and nutrient absorption, that are critical for plant growth. However, while most plants have roots, they are absent in some plants like liverworts and mosses.
Let’s take a look at one of the most key components in a plant’s structure!
What are roots?
They are important parts of a vascular plant found underground. They are primarily responsible for anchoring the plants into the ground and storing food. However, some plants are above the ground, and are known as aerial roots.
Most of the vascular plants have one of the 2 types of roots, they are
- Primary roots: These roots grow downwards.
- Secondary roots: They branch on the sides.
Thus, all the roots of a plant make up the root system of a particular plant.
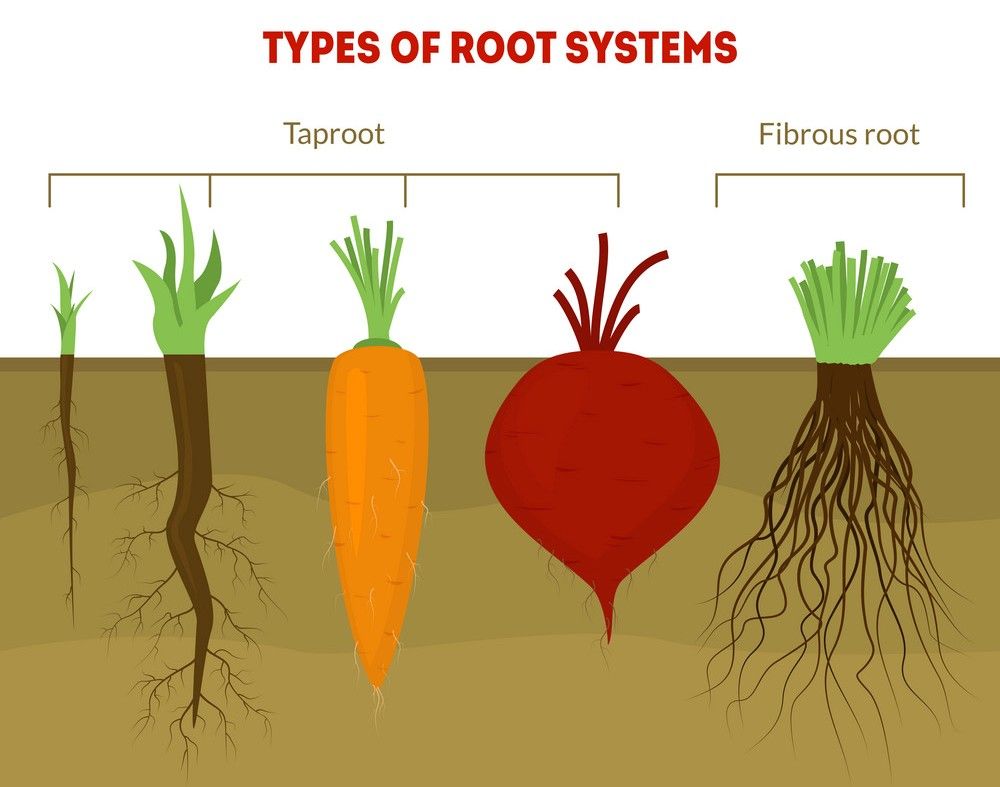
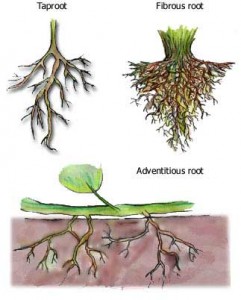
Types of root systems
Most of the roots have similar functions, but their structures vary from one another. Hence, they are classified into 3 root systems, they are:
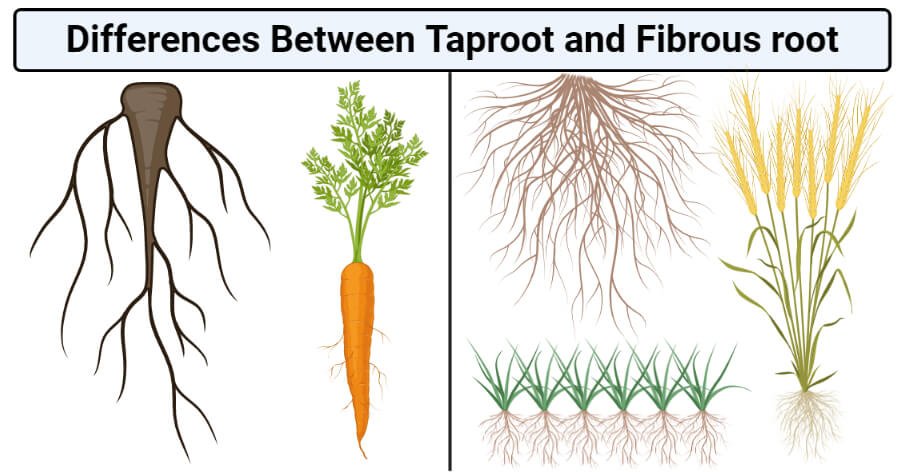
Tap Root Systems
-
They contain a single and a thick primary root known as a taproot.
-
Smaller, secondary roots grow from the sides of the main root.
-
Taproots can penetrate downward as low as 200 ft below the ground surfaces.
-
They penetrate even deep water resources and store a lot of food and energy, which help the plants to survive through droughts and other such extreme conditions.
-
They also help in securely anchoring plants to the ground. Examples include mustard, china rose, carrots, and all dicotyledons.
Fibrous Root Systems
-
They contain numerous small roots that branch out.
-
In this system, large primary roots are absent.
-
The vast number of thread-like roots increases surface areas for absorbing water and mineral salts.
-
Fibrous roots also can secure the plant systems, but not as efficiently as the taproot systems. Examples include rice, banana, and all monocotyledons.
Adventitious Root systems
-
These root systems arise after injury in the roots and main stems.
-
They include the roots formed on the leaf cuttings and stems produced by the layering of air.
-
They are the roots of plants that form from the non-root tissues and are produced during normal developments.
Other Types of Roots
Tuberous roots: They are very thick roots, and they help to store important amounts of food to help feed the whole plant system. They are fleshy, modified, and enlarged storage organs in their plants. They are generally modified from stems.
Water roots: It occurs in regions where plants can grow in the waters. They are more brittle and finer than the usual ones. They can allow the atmospheric oxygen to diffuse, which is later used by roots for their growth and metabolism. They are different from the usual soil roots morphologically.
Creeping roots: These are the roots that do not penetrate the deep soils. They are quite shallow, and they spread horizontally too long distances from the base area of plants. Many of the trees have these roots.
Parasite roots attach themselves to the other plants and suck the other plant’s nutrients. In this process, they do not benefit the host plants. They might cause serious damage to the other roots.
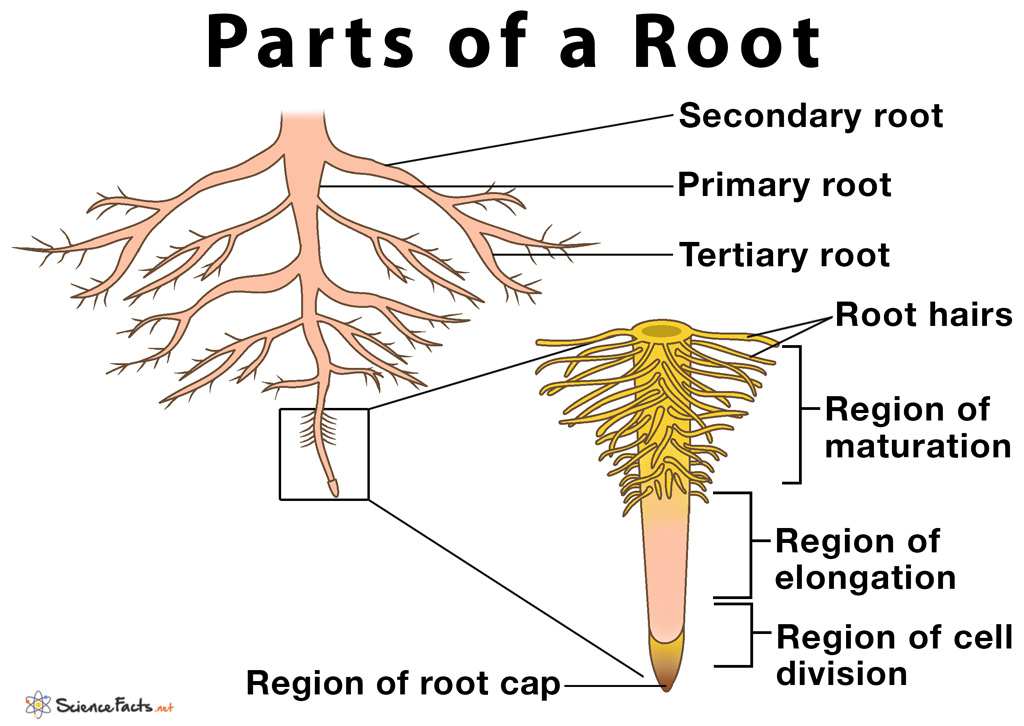
What are the parts of a typical root system?
There are 4 distinct regions and zones:
-
Region of a root cap: This is the tip of the roots. It is a multi-cellular structure always in a divisive state. They constantly renew and grow in number as roots penetrate the soil.
-
Region of cell divisions: Also called the meristematic region. It is situated a few inches above the root cap. They are small, thin-walled, and have dense cytoplasms.
-
Region of elongation: Located close to the meristematic regions. They are not capable of cell divisions.
-
Piliferous region: The region of maturation or differentiation is called a piliferous region. They develop after the cells of the elongation zones mature and differentiate into specialized tissues like the cortex, epidermis, and root hairs.
What are the functions of roots?
Some of the important functions of the root systems are:
-
Anchorage – Helps in the plant fixation and supports the aerial shoot systems.
-
Absorption of water from the soil.
-
Absorption of minerals and other nutrients from the soil.
-
Hold the particles of the soil firmly and prevent soil erosion.
-
Transport water, mineral soils, nutrients upward to the shoot systems.
-
Fleshy roots store food. For example, radish, carrots.
-
Help provide mechanical support to the plants.
-
Help some of the weak stem plants to climb up and cling to support.
-
Nodulated roots help in nitrogen fixation. For example, roots of a pea, gram, etc.
-
Some roots function as floats by storing air. For example Jussiaea
-
Reproduction: In some plants, roots are a means of reproduction, and the type of reproduction is called vegetative propagation.
Uses of roots to man
-
Most roots are used as a means of food by humans. For example, carrots, yams, radish, potatoes, etc.
-
They are also an important source for some important medicines, potentially saving lives. For example, ashwagandha, ginseng, etc.
-
They also contain lots of fiber and hence can be used to make brooms, brushes, baskets, etc.
-
They help in soil conservation by preventing erosion of the same.
-
They also play a primary role in preventing soil erosion.
Conclusion
-
The roots of the plants are found underground, and their important functions are water and nutrient absorption.
-
Root systems are classified into 3 they are: Tap Root systems, Fibrous Root systems, and Adventitious Root systems.
-
Parts of a typical root system are the Region of a root cap, Region of cell divisions. Region of elongation and The Region of maturation or differentiation.
-
To human beings, roots serve as food, medicines, utensils and also prevent soil erosion.
FAQs
1. Which part of the plant body serves as an anchorage to the plants?
The root systems.
2. What are the 3 types of root systems?
The 3 types of root systems are taproots, fibrous roots, and adventitious roots.
3. What are the main functions of roots?
The main functions are:a) They anchor the plant b) Absorb water and minerals from the soilc) Help store food
4. What are the various parts of a root?
The various parts of a root are:a) Lateral root b) Primary root c) Root hair d) Root tip e) Root cap
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Roots! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
Sources
-
Roots. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/9.14/primary/lesson/roots-bio/ Accessed 9 Dec, 2021.
-
Plant Tissues and Organs Study Guide. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/studyguides/biology/plant-tissue-and-organs-study-guide.html?encodedID=SCI.BIO.631&courseContextID=5292077 Accessed 9 Dec, 2021.