Principles of Biology Study Guide
Introduction
The word biology is obtained from the Greek words “bios,” which means life, and “logos,” which means study. Aristotle, the father of biology, created the basic theory of biology, which describes five biological processes: metabolism, regulation of temperature, inheritance, processing of information, and embryogenesis.
What are the Principles of Biology?
Biology is a broad scope topic and comprises many disciplines like zoology, botany, anatomy, physiology, cell biology, microbiology, etc. There are five basic principles of biology: cell theory, gene theory, homeostasis, evolutionary theory, and the laws of thermodynamics.
1. Cell theory
Cell theory is one of the basic principles of biology which implies that all living things are composed of cells the basic unit of life. Living organisms are made up of one or more cells, and cells are derived from other pre-existing cells.
Theodore Schwann proposed the cell theory in 1839. It led to the modern cell theory, which has three parts and states that DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is distributed between the cells during cell division. It also says that within a particular species, the organisms possess similar cells both chemically and structurally. And that there is a flow of energy within the cells.
2. Gene theory
Gene theory states that all the characters of living organisms are controlled or directed by genes. Genes are smaller parts of DNA that are passed from parents to the offspring. DNA is a part of chromosomes present in every cell. They possess instructions to encode a protein which in turn directs every action of the cell.
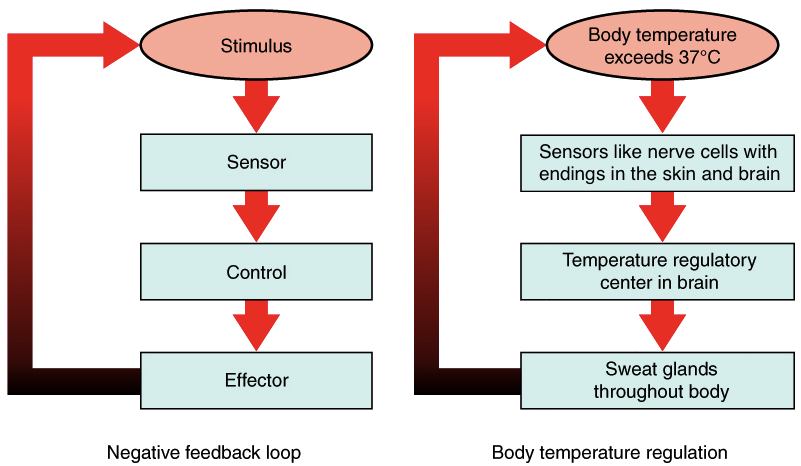
3. Homeostasis
- Homeostasis means maintaining stability within the environment, denoting the principles of biology. It refers to both living and nonliving parts of nature as a whole.
- Living organisms possess the ability to regulate different physiological processes occurring within themselves to survive.
- The chemical and physical conditions within them are maintained at an equilibrium irrespective of the external environment.
- Walter Cannon developed homeostasis in 1926 from the Greek words “Homoios” and “Histemi,” which mean similar and standing still.
4. Evolution theory
- Evolution is the process by which living organisms have matured from ancient single-celled life forms. A change in the characteristics of a living organism over some time is the basic theory of biology.
- This occurs parallel to the theory of natural selection (by Charles Darwin), which states that some living organisms reproduce and generate more offspring than other living organisms and more genes or traits are passed to the next generation than others.
- This process aids adaptation in which the subsequent generations of offspring become better suited to the environment. Adaptation allows a living organism to learn how to survive and reproduce in any environment.
5. Laws of thermodynamics
-
Thermodynamics is the science between temperature, work, heat, and energy.
-
It explains the energy changes within a particular system and whether it can perform any beneficial work on its surroundings.
-
It deals with the transfer of energy from one form to another and from one place to another.
-
As the name suggests, thermal means “heat,” a form of energy obtained when a particular amount of mechanical work is performed. Sir Benjamin Thompson put forward this theory in 1798.
-
The three basic laws of thermodynamics were initiated by Rudolph Clausius, a mathematician, and physicist.
- First law of thermodynamics: Energy can neither be created nor destroyed but can only be transferred from one form to another. It is also called the law of conservation of energy.
- Second law of thermodynamics: Within any particular isolated system, the entropy always increases.
- Third law of thermodynamics: Entropy of a system tends to move to a constant amount while its internal temperature approaches absolute zero.
Conclusion
- The unifying principle of biological sciences is that living organisms are made up of smaller units called cells; they grow and develop based on the universal genetic code.
- They can adapt and maintain inner stability in any environmental condition through homeostasis, reproduce and evolve over time.
- They can also use a chemical reaction to obtain energy and are interdependent on other living organisms.
FAQs:
1. What are the major principles of biology?
Cell theory, gene theory, evolution, and homeostasis are the four unifying principles of biology.
2. What are the six biological principles?
Six biology principles: Organization and function, adaptation, response to the environment, growth and development, reproduction, and Homeostasis.
3. What are the four principles of biology?
The four principles of biology are cell theory, evolutionary theory, gene theory, and concept of homeostasis.
4. What do principles mean in biology?
Biological principles are based on the fundamental concept that all living organisms are similar in composition, growth, heredity, reproduction, metabolism, and homeostasis.
5. What are the three biological principles?
Variation, selection, and heredity.
6. What are the examples of principles?
Examples of biological sciences are reproduction, homeostasis, evolution, heredity, and metabolism.
*We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about the Principles of Biology! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun 😎*
Sources:
- Biology: The Study of Life. https://www.thoughtco.com/biology-meaning-373266. Accessed Nov 24, 2021.
- Principles of Biology. https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Introductory_and_General_Biology/Book%3A_Introductory_Biology_(CK-12)/01%3A_Introduction_to_Biology/1.05%3A_Principles_of_Biology. Accessed Nov 25, 2021.
- Basic Principles of Biology. https://humanbiology.pressbooks.tru.ca/chapter/2-3-basic-principles-of-biology/. Accessed Nov 25, 2021.
- Principles of Biology. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/1.5/primary/lesson/principles-of-biology-bio/. Accessed Nov 25, 2021.